©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2015; 21(23): 7320-7325
Published online Jun 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7320
Published online Jun 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7320
Figure 1 X-ray examination of the small intestine.
X-ray examination of the small intestine revealing thickened folds as well as a dilated lumen of the jejunum and ileum.
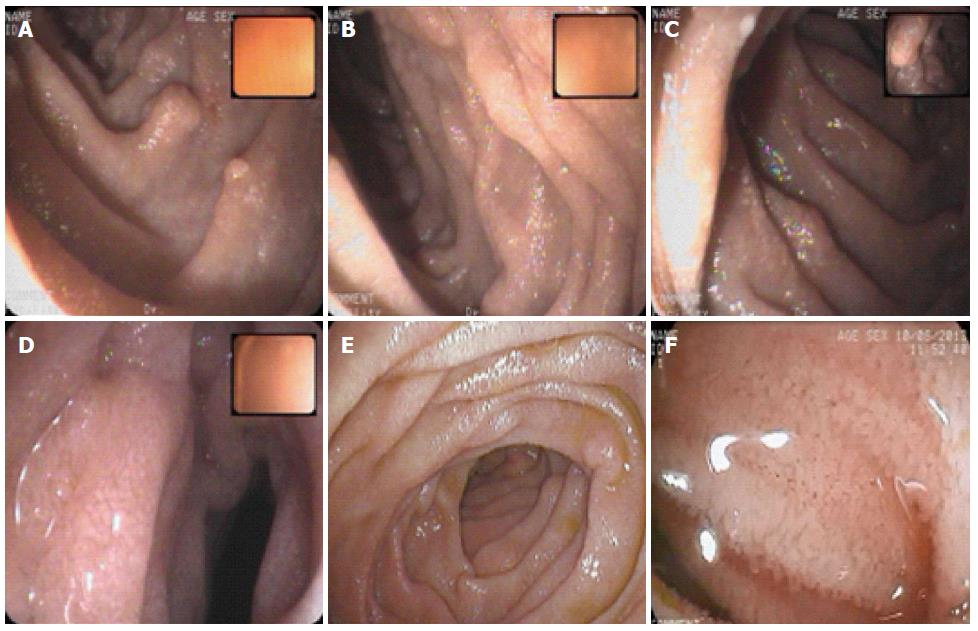
Figure 2 Double balloon enteroscopy.
Double balloon enteroscopy demonstrating edematous distal duodenum and jejunal mucosa scattered with white spots. A-C: duodenum; D-F: Jejunum.
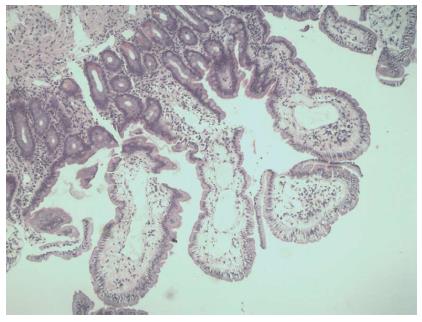
Figure 3 Histopathological findings.
Histopathological findings: dilated lymphatic vessels in the tips of whitish jejunal villi (hematoxylin-eosin stain, magnification × 40).
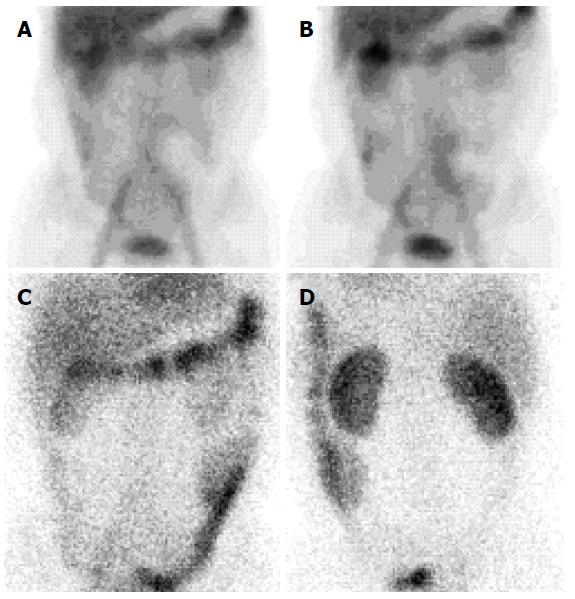
Figure 4 Technetium 99m human serum albumin scintigraphy.
Scintigraphy showing Technetium 99m labeled human serum albumin extravasation throughout small intestine after 6 h of injection (A and B) and presence in the large intestine after 24 h of injection (C and D).
- Citation: Troskot R, Jurčić D, Bilić A, Gomerčić Palčić M, Težak S, Brajković I. How to treat an extensive form of primary intestinal lymphangiectasia? World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(23): 7320-7325
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i23/7320.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7320