©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2015; 21(14): 4178-4183
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4178
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4178
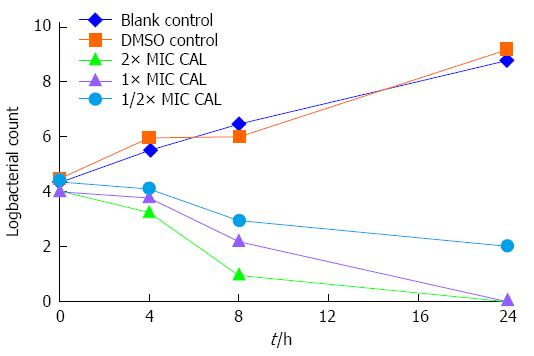
Figure 1 Time-kill curves of Chenopodium ambrosioides L.
at different concentrations. MIC: Minimal inhibitory concentration; CAL: Chenopodium ambrosioides L.
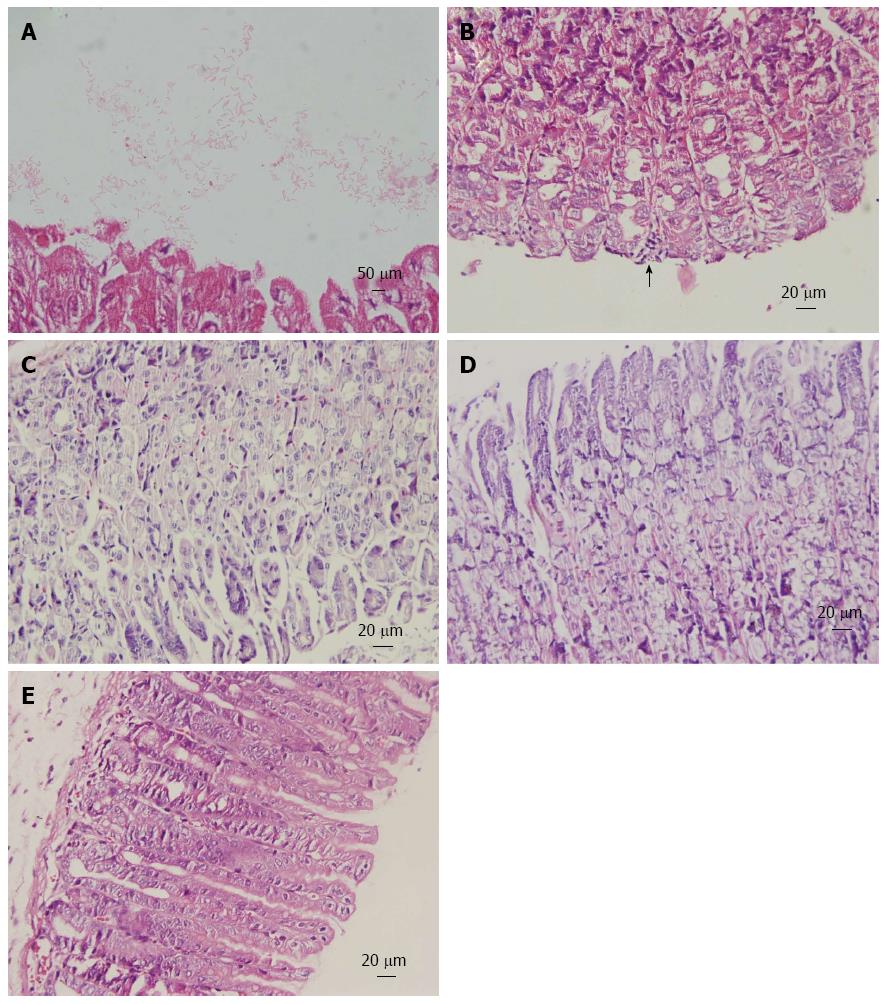
Figure 2 Histopathology of gastric mucosa.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining of gastric mucosa from mice inoculated with Helicobacter pylori. A: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) colonization on the surface of gastric mucosa (magnification × 100); B: Mononuclear cell infiltrates (arrow; magnification × 40); C: Uninfected mice exhibit a normal gastric mucosa (magnification × 40); D: Treatment with Chenopodium ambrosioides L. for 4 wk revealed no obvious inflammation (magnification × 40); E: Treatment with lansoprazole, metronidazole and clarithromycin for 1 wk showed no pathologic changes (magnification × 40).
-
Citation: Ye H, Liu Y, Li N, Yu J, Cheng H, Li J, Zhang XZ. Anti-
Helicobacter pylori activities ofChenopodium ambrosioides L.in vitro andin vivo . World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(14): 4178-4183 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i14/4178.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4178