©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 10050-10061
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10050
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10050
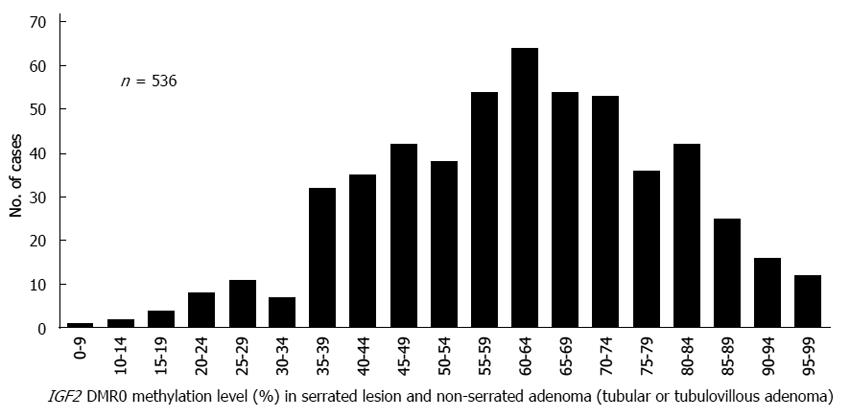
Figure 1 Distribution of IGF2 differentially methylated region 0 methylation levels in 351 serrated lesions.
Hyperplastic polyp, sessile serrated adenoma (SSA), SSA with cytological dysplasia, traditional serrated adenoma (TSA) and TSA with high-grade dysplasia (HGD) and 185 non-serrated adenomas (tubular adenoma, tubular adenoma with HGD, tubulovillous adenoma and tubulovillous adenoma with HGD). DMR: Differentially methylated region; IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor 2.
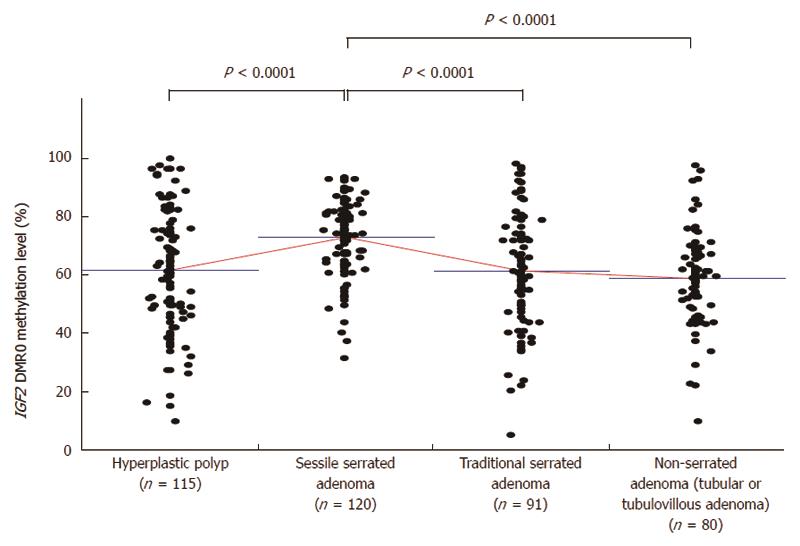
Figure 2 IGF2 differentially methylated region 0 methylation level according to histological type.
Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) differentially methylated region (DMR)0 methylation levels of sessile serrated adenoma (mean ± SD; 73.1 ± 12.3) were significantly higher compared with those of hyperplastic polyp (61.9 ± 20.5, P < 0.0001), traditional serrated adenoma (61.6 ± 19.6, P < 0.0001), and non-serrated adenoma (59.0 ± 15.8, P < 0.0001). P-values were calculated by analysis of variance.
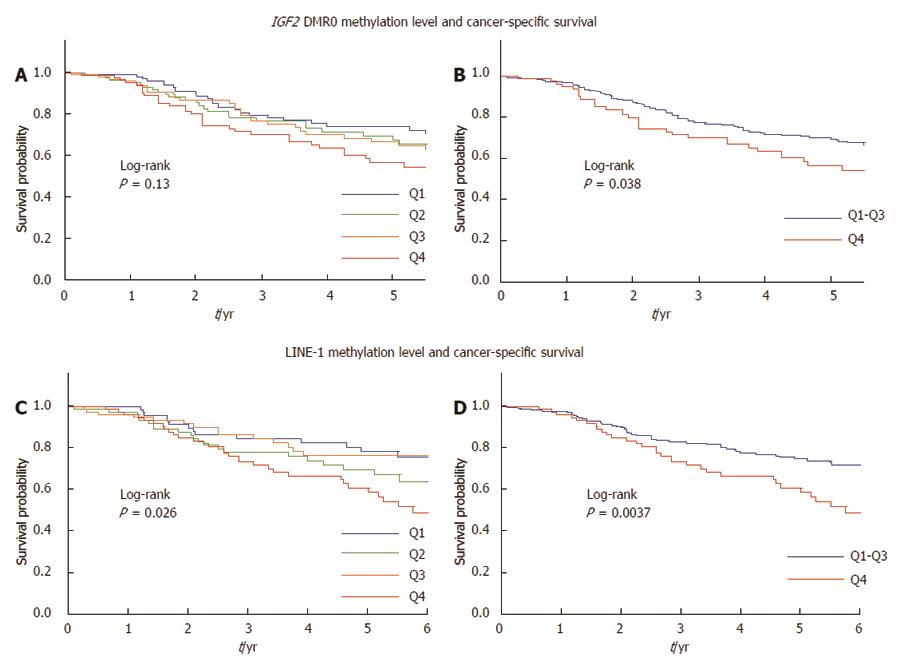
Figure 3 Kaplan-Meier survival curves for colorectal cancer according to the IGF2 differentially methylated region 0 and long interspersed nucleotide element-1 methylation levels in metastatic colorectal cancers.
A: Patients with Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) differentially methylated region (DMR)0 hypomethylation had a slightly higher mortality rate than those with IGF2 DMR0 hypermethylation, but this difference was not significant (log-rank test: P = 0.13); B: IGF2 DMR0 hypomethylation (Q4 cases) was significantly associated with unfavorable cancer-specific survival (log-rank test: P = 0.038); C: Significantly higher mortality was observed in patients with long interspersed nucleotide element-1 (LINE-1) hypomethylation compared with those with LINE-1 hypermethylation (log-rank test: P = 0.026); D: LINE-1 hypomethylation (Q4 cases) was significantly associated with unfavorable cancer-specific survival (log-rank test: P = 0.0037).
-
Citation: Naito T, Nosho K, Ito M, Igarashi H, Mitsuhashi K, Yoshii S, Aoki H, Nomura M, Sukawa Y, Yamamoto E, Adachi Y, Takahashi H, Hosokawa M, Fujita M, Takenouchi T, Maruyama R, Suzuki H, Baba Y, Imai K, Yamamoto H, Ogino S, Shinomura Y.
IGF2 differentially methylated region hypomethylation in relation to pathological and molecular features of serrated lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 10050-10061 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/10050.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10050