©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2014; 20(19): 5881-5888
Published online May 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5881
Published online May 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5881
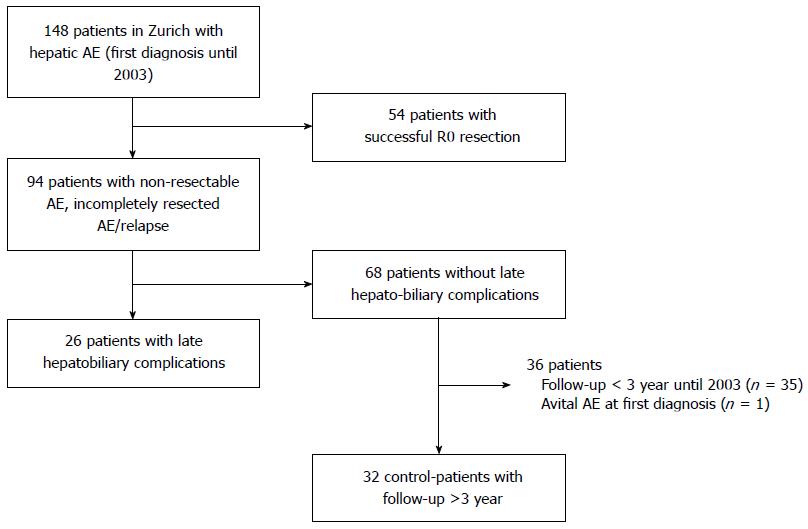
Figure 1 Patient selection process of patients with and a matched control group without biliary complications.
Of all patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis (AE), patients with successful surgery were excluded. The remaining patients either developed biliary complications or not. From the latter group of patients, individuals with insufficient follow up time or avital AE were excluded; the remaining patients were defined as the control group.
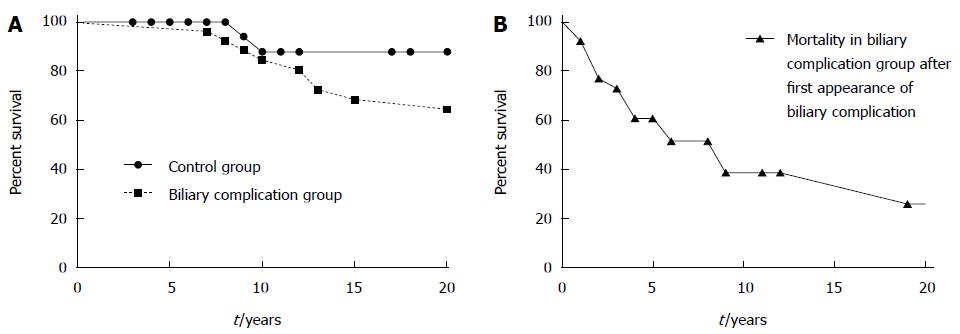
Figure 2 Survival of patients with alveolar echinococcosis with and without late biliary complications.
Survival of patients with and without late biliary complications is shown over the course of 2 decades. Survival of the biliary complication group is shown either as time after diagnosis of alveolar echinococcosis (AE) (solid line) or time after diagnosis of the late biliary complication (dotted line). Survival after diagnosis of AE does not differ. In contrast, survival after diagnosis of the late biliary complication is significantly shorter compared to overall survival in the control group (P < 0.0001) and in patients with AE after initial diagnosis (P = 0.0002), Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.
- Citation: Frei P, Misselwitz B, Prakash MK, Schoepfer AM, Prinz Vavricka BM, Müllhaupt B, Fried M, Lehmann K, Ammann RW, Vavricka SR. Late biliary complications in human alveolar echinococcosis are associated with high mortality. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(19): 5881-5888
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i19/5881.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5881