©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 4106-4109
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4106
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4106
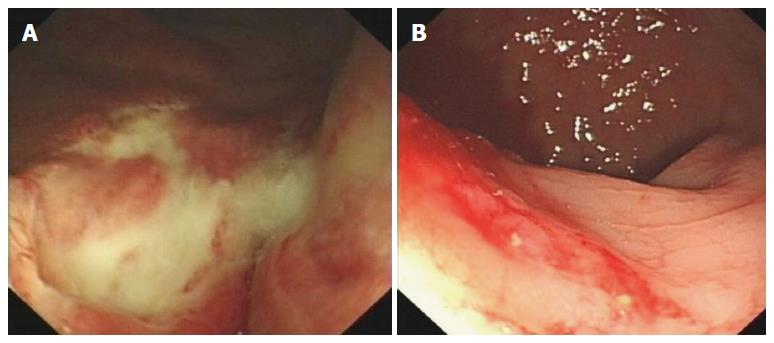
Figure 1 Colonoscopy showing an squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum.
The tumors are located about 2 cm (A) and 7 cm (B) from the anal verge, respectively.
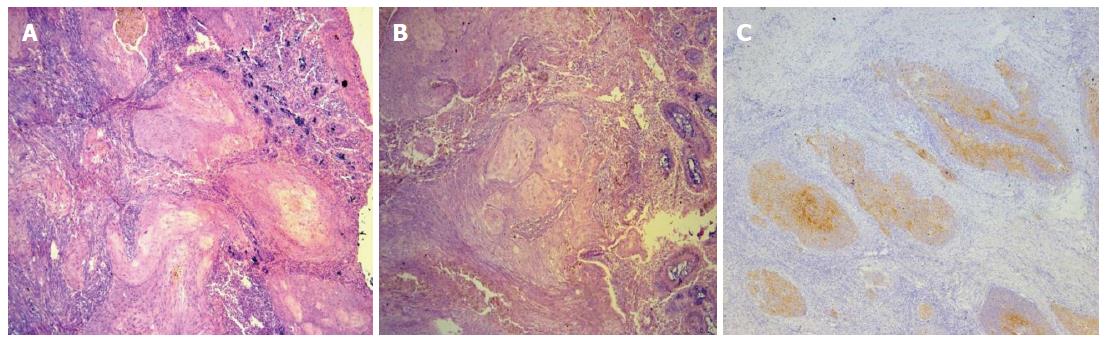
Figure 2 Pathologic examination found a moderately-poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum.
A, B: A high power view of the squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum, showing keratin formation (HE stain, × 100); C: Immunohistochemical analysis of the biopsy of the squamous cell carcinoma of the rectum showing positive CK stain.
- Citation: Wang JF, Wang ZX, Xu XX, Wang C, Liu JZ. Primary rectal squamous cell carcinoma treated with surgery and radiotherapy. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 4106-4109
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/4106.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4106