Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2013; 19(7): 1104-1110
Published online Feb 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i7.1104
Published online Feb 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i7.1104
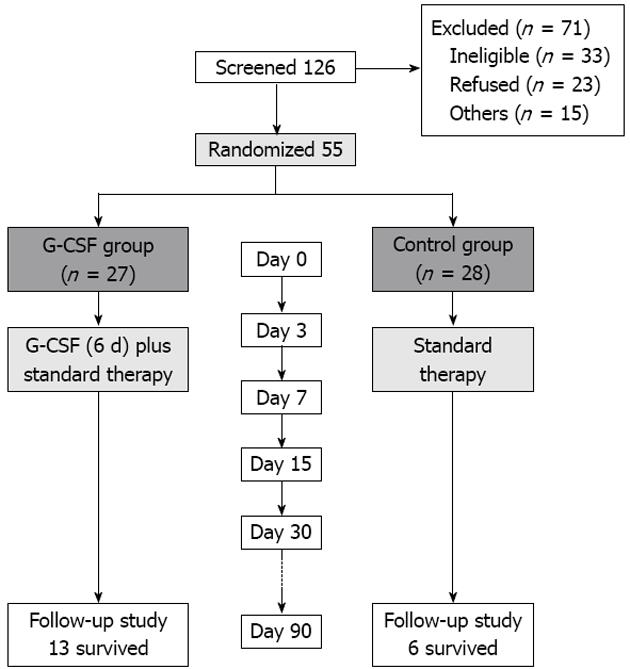
Figure 1 Study design and flow algorithm of patient selection.
G-CSF: Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.
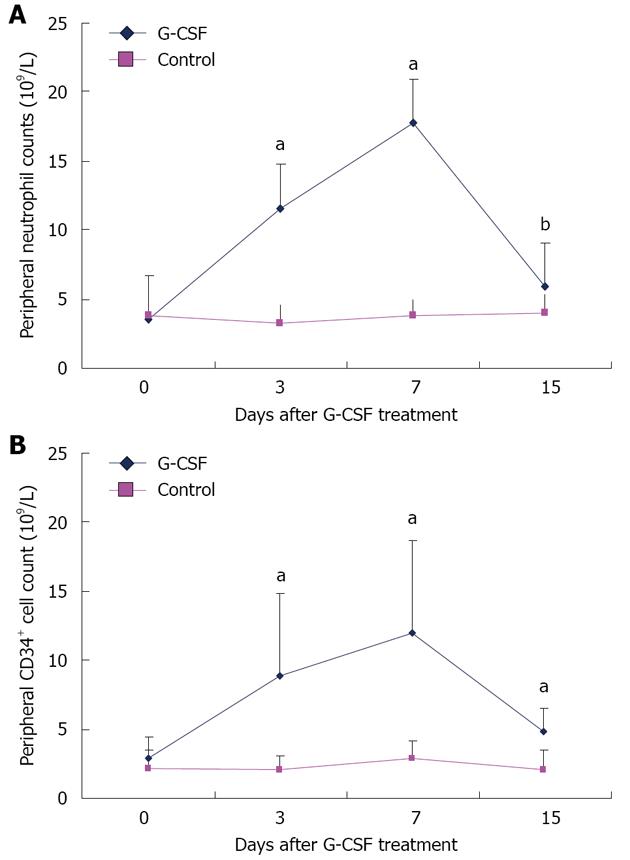
Figure 2 Kinetics of peripheral neutrophil count (A) and CD34+ cell count (B) in patients treated with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor and controls.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs controls. G-CSF: Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.
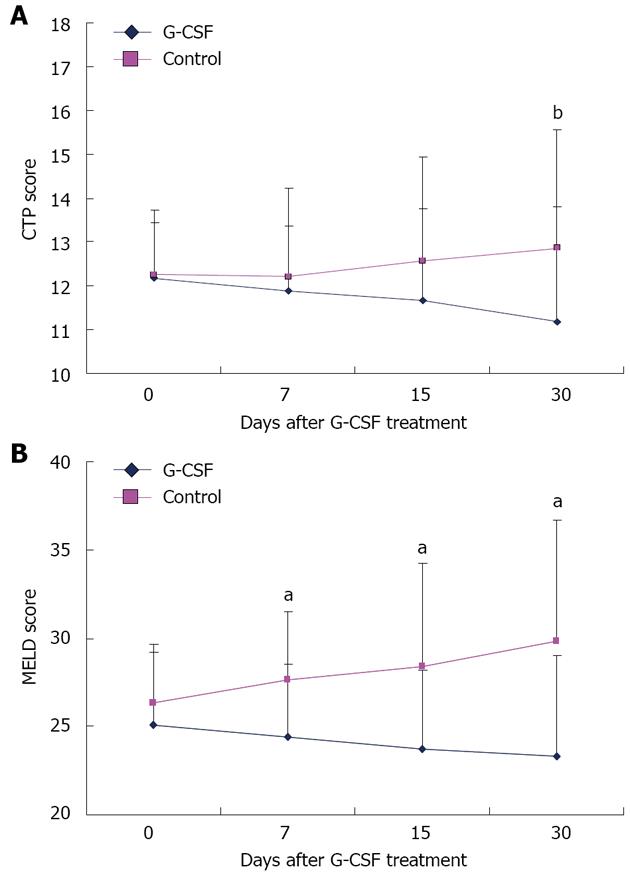
Figure 3 Changes in Child-Turcotte-Pugh score (A) and Model for End stage of Liver Disease score (B) in patients treated with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor and control groups.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs controls. G-CSF: Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor; CTP: Child-Turcotte-Pugh; MELD; Model for End Stage of Liver Disease.
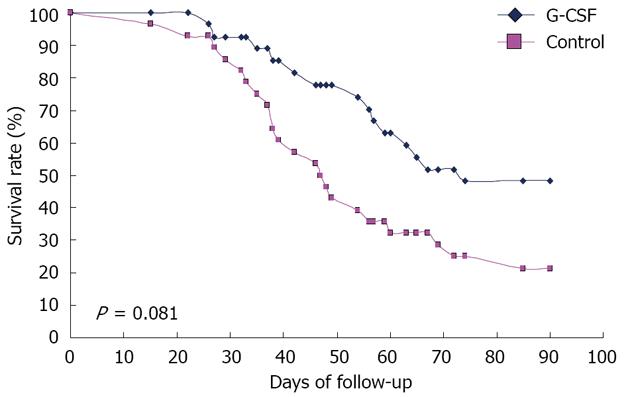
Figure 4 Survival rate of patients treated with granulocyte-colony stimulating factor and in controls.
G-CSF: Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.
- Citation: Duan XZ, Liu FF, Tong JJ, Yang HZ, Chen J, Liu XY, Mao YL, Xin SJ, Hu JH. Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor therapy improves survival in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(7): 1104-1110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i7/1104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i7.1104