©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2013; 19(5): 682-691
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.682
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.682
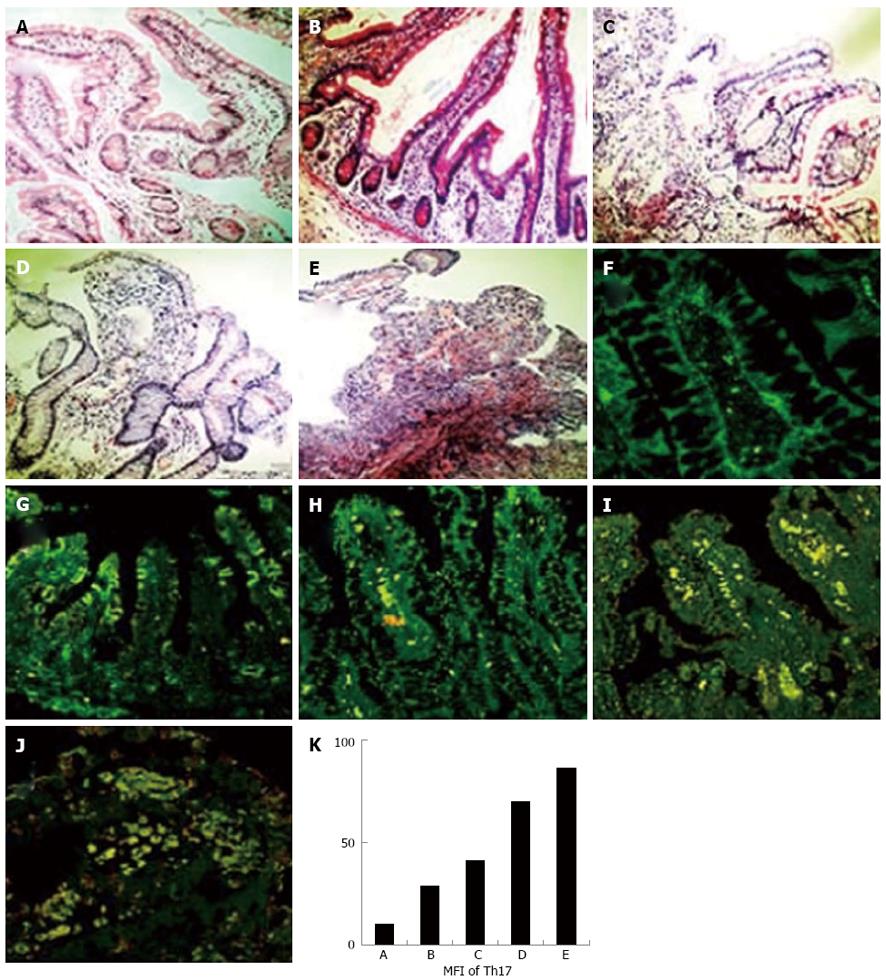
Figure 1 Expression levels of helper T cell 17 cells in intestine grafts paralleled with the degree of rejection in human recipients.
The paraffin-embedded human intestine tissues after small bowel transplantation were sectioned and stained with hematoxylin eosin (HE), anti-rat-interleukin-17, and anti-rat-CD4 fluorescence antibodies (× 400). A-E: HE staining of intestine graft; F-J: Helper T cell 17 (Th17) immunofluorescence staining of intestine graft; A, F: No acute rejection; B, G: Suspicious acute rejection; C, H: Mild acute rejection; D, I: Moderate acute rejection; E, J: Severe acute rejection; K: Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Th17 expression of intestine graft.
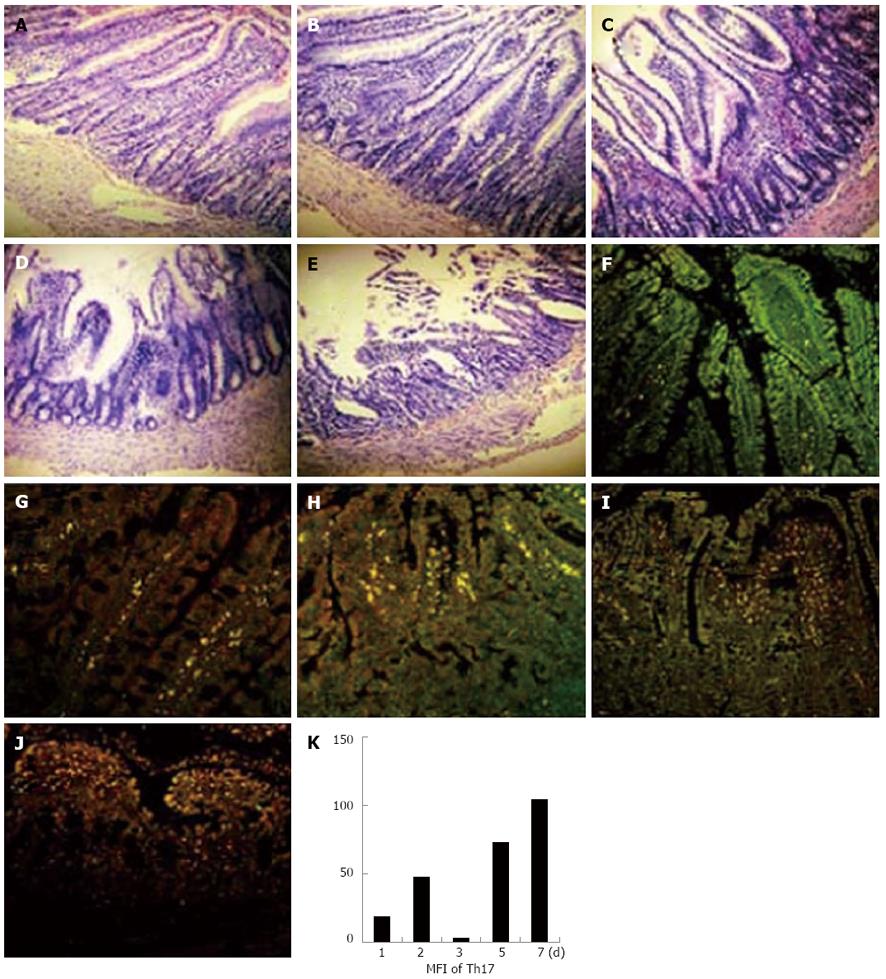
Figure 2 Expression levels of helper T cell 17 cells in intestine grafts paralleled with the degree of rejection in rat recipients.
The intestines from inbred F344 were transplanted to LEW rats. The recipient rats were sacrificed on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, and 7th d after transplantation. The grafts were removed, fixed, and embedded. The sections were stained with hematoxylin eosin (HE), anti-rat-interleukin-17, and anti-rat-CD4 fluorescence antibodies (× 400). A-E: HE staining of intestine graft; F-J: Helper T cell 17 (Th17) immunofluorescence staining of intestine graft; A, F: 1 d after transplantation; B, G: 2 d after transplantation; C, H: 3 d after transplantation; D, I: 5 d after transplantation; E, J: 7 d after transplantation; K: Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Th17 expression of intestine graft.
Figure 3 Administration of anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody prolonged the survival of rats after small bowel transplantation.
The intestines from inbred F344 were transplanted to LEW rats. The recipient rats were randomly divided into control and anti-interleukin (IL)-17 monoclonal antibody (mAb) treated groups. The survival of recipient rats was analyzed.
Figure 4 Administration of anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody decreased the expression levels of helper T cell 17 cells in intestine grafts in rat recipients.
The intestines from inbred F344 were transplanted to LEW rats. The recipient rats were randomly divided into control and anti-interleukin (IL)-17 monoclonal antibody (mAb) treated groups. The rats were sacrificed on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, and 7th d after transplantation. The grafts were removed, fixed, and embedded. The sections were stained with hematoxylin eosin (HE), anti-rat-IL-17, and anti-rat-CD4 fluorescence antibodies (× 400). A-E: HE staining of intestine graft; F-J: Helper T cell (Th) 17 immunofluorescence staining of intestine graft; A, F: 1 d after transplantation; B, G: 2 d after transplantation; C, H: 3 d after transplantation; D, I: 5 d after transplantation; E, J: 7 d after transplantation; K: Mean fluorescence intensity of Th17 expression of intestine graft. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
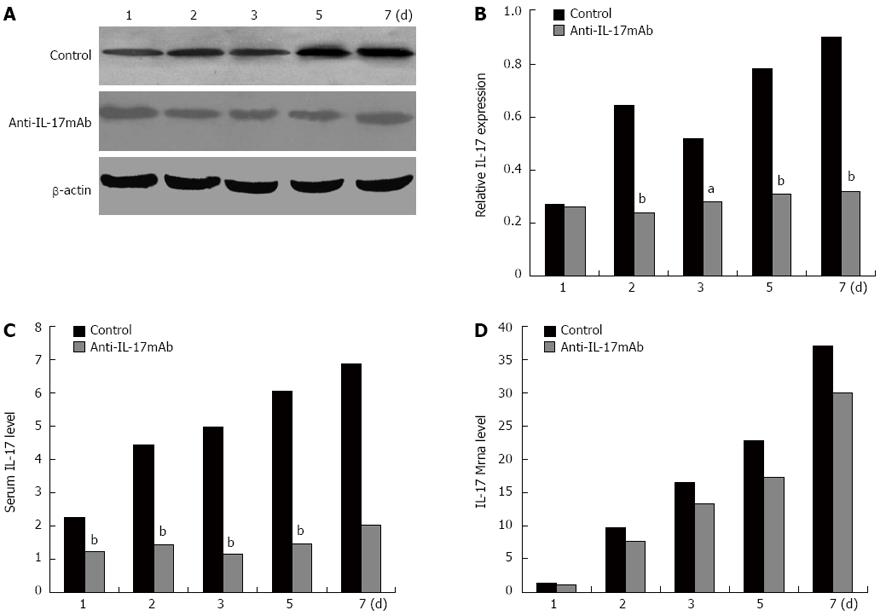
Figure 5 Expression of interleukin-17 in rat intestine and serum after transplantation.
The intestines from inbred F344 were transplanted to LEW rats. The recipient rats were randomly divided into control and anti-interleukin (IL)-17 monoclonal antibody (mAb) treated groups. The rats were sacrificed on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, and 7th d after transplantation. A: Western blot analysis of graft proteins of different groups. β-actin were considered as an internal control; B: The bands were scanned and the protein expressions were analyzed with Band Scan software; C: Blood from the heart was extracted and the serum IL-17 levels was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; D: The mRNA of IL-17 was detected by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. β-actin was considered as an internal control. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
Figure 6 mRNA level of interleukin-1β (A), tumor necrosis factor-α (B), interleukin-6 (C), and interleukin-8 (D) were analyzed by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction.
The intestines from inbred F344 were transplanted to LEW rats. The recipient rats were randomly divided into control and anti-interleukin (IL)-17 mAb treated groups. The rats were sacrificed on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, and 7th d after transplantation. The mRNA was extracted and quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction was performed. β-actin was considered as an internal control. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
- Citation: Yang JJ, Feng F, Hong L, Sun L, Li MB, Zhuang R, Pan F, Wang YM, Wang WZ, Wu GS, Zhang HW. Interleukin-17 plays a critical role in the acute rejection of intestinal transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(5): 682-691
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i5/682.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.682