©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2013; 19(34): 5693-5699
Published online Sep 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5693
Published online Sep 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5693
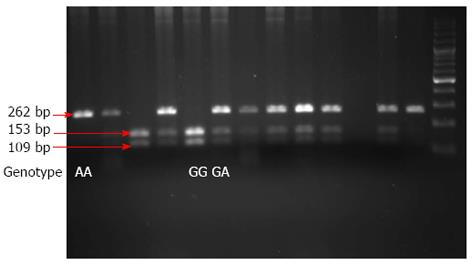
Figure 1 Interleukin-17 genotyping.
A representative image of the results of an interleukin-17 (IL-17) genotyping assay is shown. The IL-17 promoters were amplified by polymerase chain reaction and the resulting products were digested with XagI. Products were then separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The IL-17 GG genotype was evident as 153 and 109 bp fragments, GA as 262, 153 and 109 bp fragments, and AA as a single 262 bp fragment.
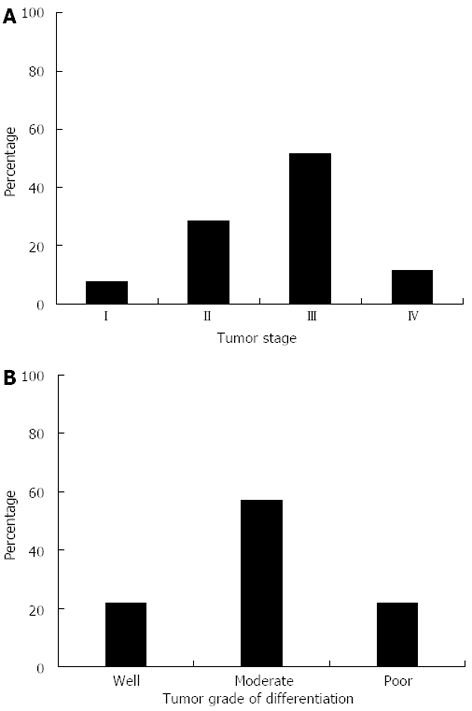
Figure 2 Tumor, node, metastasis staging, and cellular differentiation in the gastric cancer population.
A: Breakdown of tumor staging among a subset of the gastric cancer population. Staging was categorized as described in the Materials and Methods section. For simplicity, individuals that were categorized as Stage IA or IB were grouped into Stage I. Similarly, patients with Stage IIIA or IIIB tumors were grouped into Stage III; B: The degree of cellular differentiation seen in patient tumors was graded as well, moderate, or poor as described in the Materials and Methods.
- Citation: Rafiei A, Hosseini V, Janbabai G, Ghorbani A, Ajami A, Farzmandfar T, Azizi MD, Gilbreath JJ, Merrell DS. Polymorphism in the interleukin-17A promoter contributes to gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(34): 5693-5699
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i34/5693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5693