©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2012; 18(43): 6250-6254
Published online Nov 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6250
Published online Nov 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6250
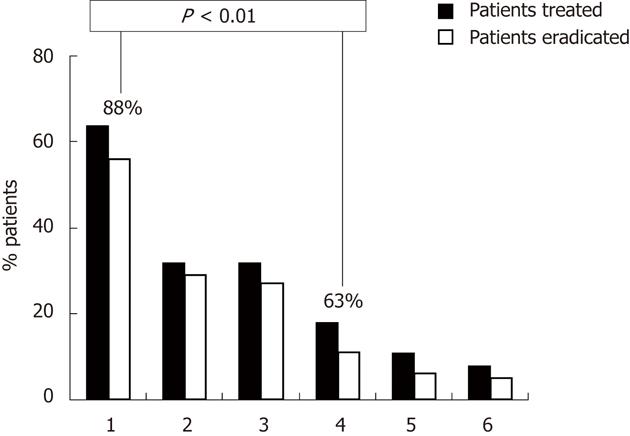
Figure 1 Helicobacter pylori eradication rate in the following groups of patients.
1: 10-d sequential therapy plus Lactobacillus reuteri (L. reuteri) post therapy; 2: 10-d sequential therapy plus L. reuteri during therapy; 3: 10-d sequential therapy; 4: 7-d standard triple therapy plus L. reuteri post therapy; 5: 7-d standard triple therapy plus L. reuteri during therapy; 6: 7-d standard triple therapy. The eradication rate was significantly higher in the sequential group compared with the 7-d triple therapy group (88% vs 63%, P = 0.01). No difference was found between patients submitted to L. reuteri supplementation during or after antibiotic treatment.
-
Citation: Efrati C, Nicolini G, Cannaviello C, O’Sed NP, Valabrega S.
Helicobacter pylori eradication: Sequential therapy andLactobacillus reuteri supplementation. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(43): 6250-6254 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i43/6250.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6250