©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2012; 18(39): 5601-5607
Published online Oct 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5601
Published online Oct 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5601
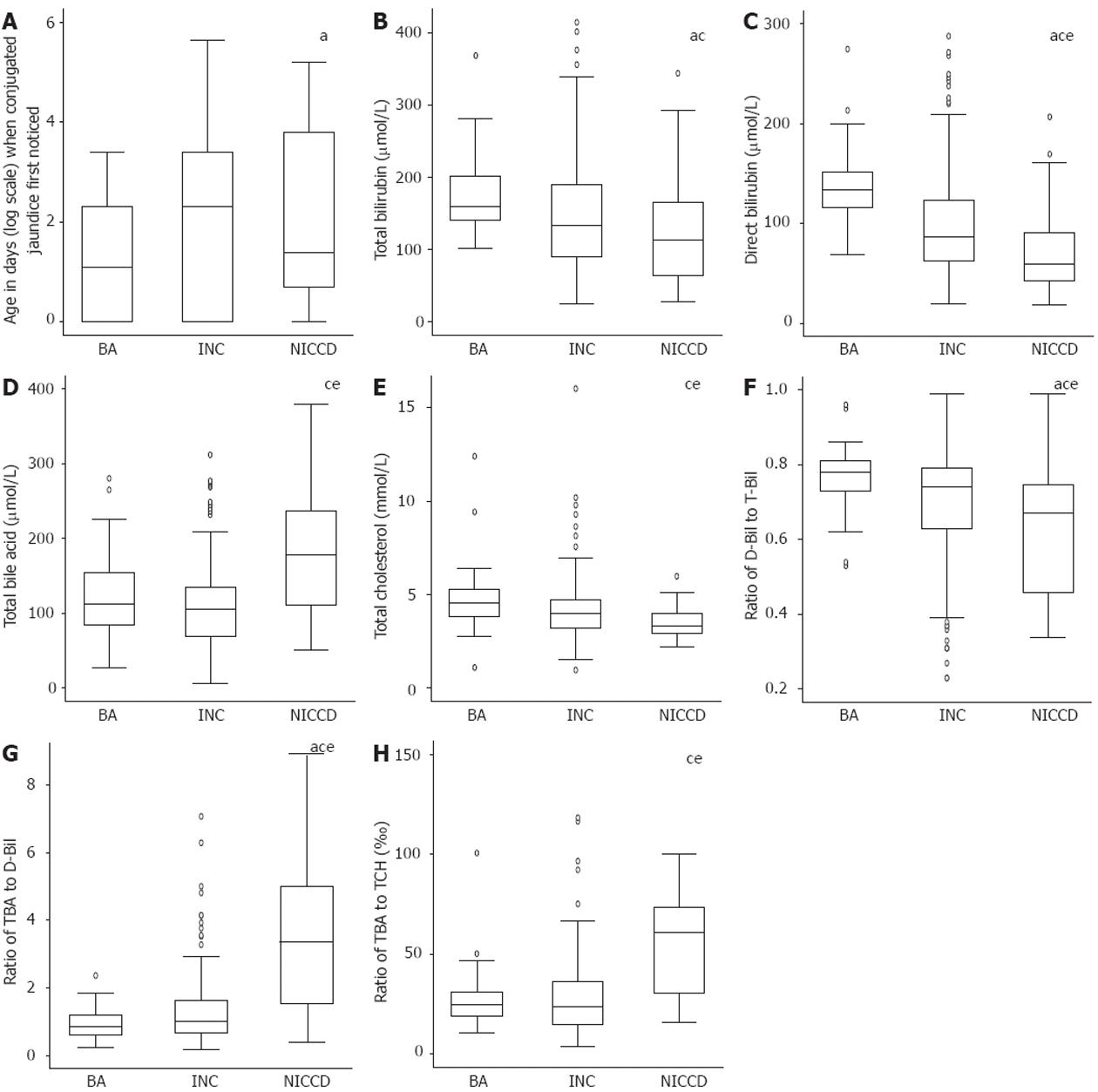
Figure 1 Comparison of the age when conjugated jaundice was first noticed (A), biochemistry indices (B-E), and ratios of some biochemical indices (F-H) in patients with neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency, idiopathic neonatal cholestasis and biliary atresia.
aP < 0.05 between BA and INC; cP < 0.05 between BA and NICCD; eP < 0.05 between INC and NICCD. Normal range: T-Bil (2-20 μmol/L), D-Bil (0-6 μmol/L), total bile acids (< 40 μmol/L), and TCH (3.12-5.20 mmol/L). NICCD: Neonatal intrahepatic cholestasis caused by citrin deficiency; BA: Biliary atresia; INC: Idiopathic neonatal cholestasis; TBA: Total bile acid; T-Bil: Total bilirubin; D-Bil: Direct bilirubin; TCH: Total cholesterol.
- Citation: Wang JS, Wang XH, Zheng YJ, Fu HY, Chen R, Lu Y, Fang LJ, Saheki T, Kobayashi K. Biochemical characteristics of neonatal cholestasis induced by citrin deficiency. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(39): 5601-5607
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i39/5601.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5601