©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2011; 17(21): 2658-2662
Published online Jun 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i21.2658
Published online Jun 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i21.2658
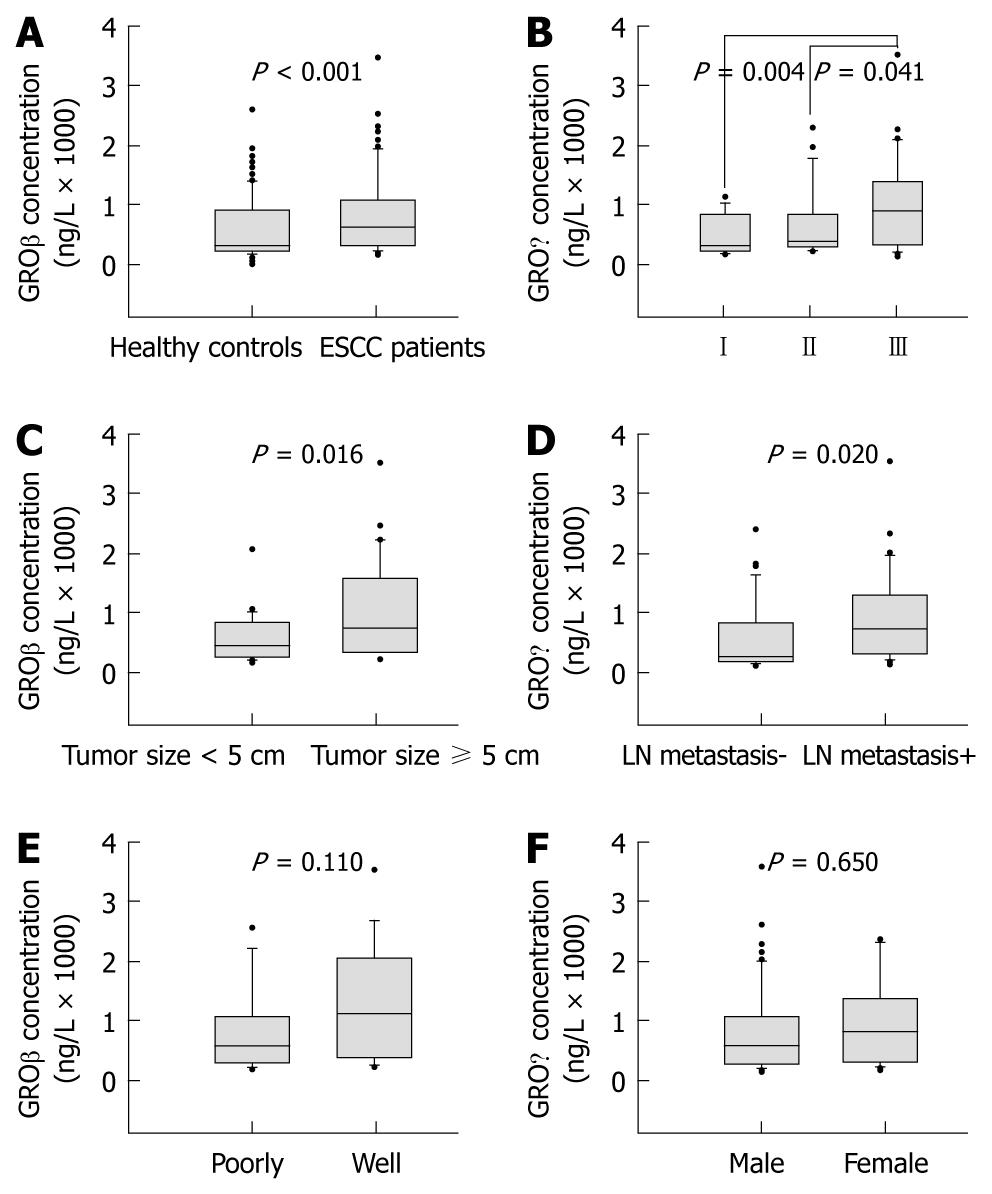
Figure 1 Correlations between serum growth-related gene product β level and clinicopathological parameters in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Serum growth-related gene product β (GROβ) levels were measured in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients (n = 72) and healthy volunteers (n = 83) using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Serum levels of GROβ were significantly increased in ESCC patients (A). Serum levels of GROβ were correlated positively with tumor-node-metastasis stage (B), tumor size (C), and lymph node (LN) metastasis (D), but not with histological grade (E) or gender (F) in ESCC patients. The boxes represent the distribution of the 25th and 75th percentile data (the line in the box is the median, and the dots are the outlying points).
- Citation: Dong QM, Zhang JQ, Li Q, Bracher JC, Hendricks DT, Zhao XH. Clinical significance of serum expression of GROβ in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(21): 2658-2662
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i21/2658.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i21.2658