©2009 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2009; 15(35): 4449-4452
Published online Sep 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4449
Published online Sep 21, 2009. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.4449
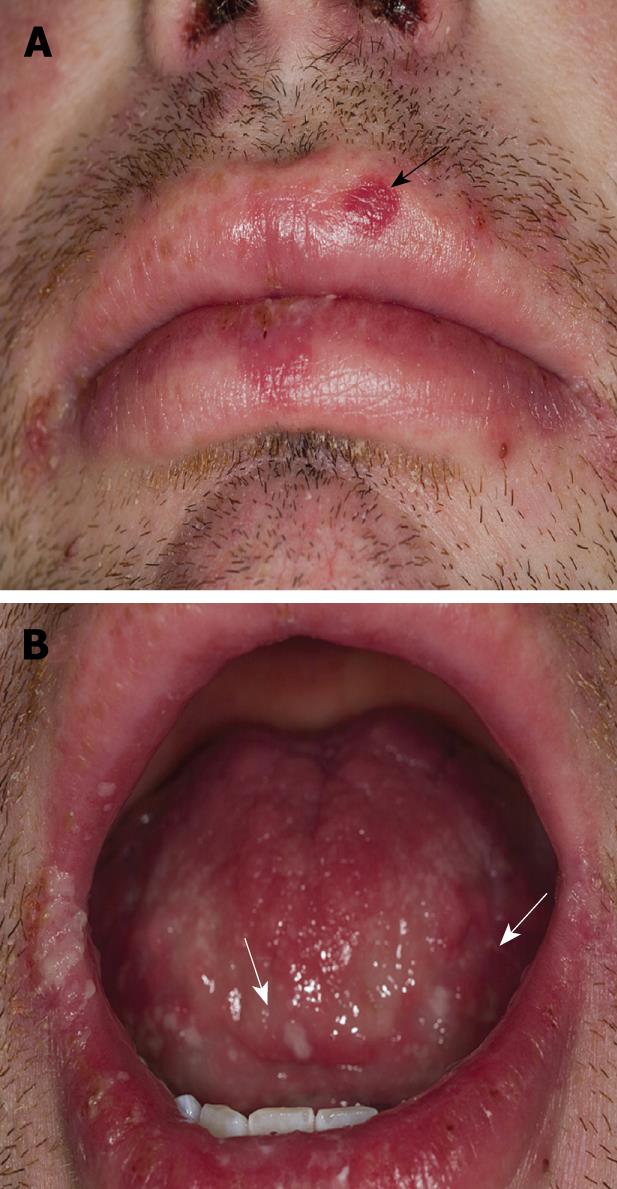
Figure 1 Mucosal lesions.
A: Lip involvement with target-lesion on left upper lip progressing to a bullae (black arrow); B: Tongue desquamation demonstrated as white plaques (white arrows).
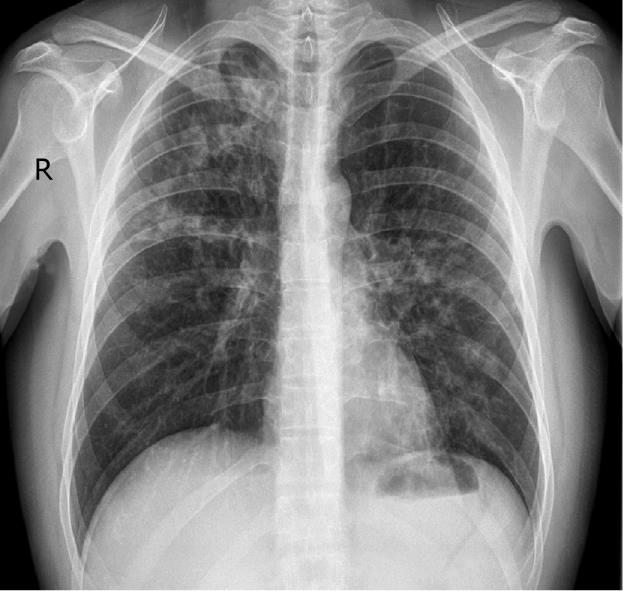
Figure 2 Chest X-Ray.
Patchy bilateral alveolar infiltrates consistent with bronchialpneumonia.
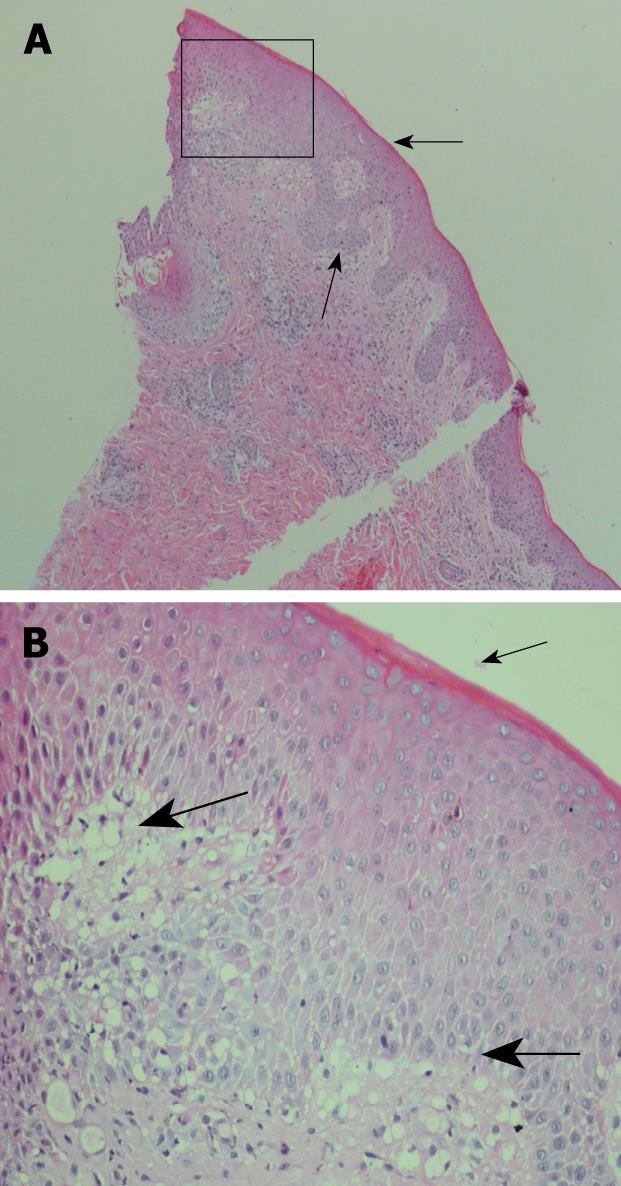
Figure 3 Histology of skin biopsies.
The epidermis shows mild irregular acanthosis with a small amount of overlying compact keratin (thin arrow). There is superficial dermal oedema associated with vacuolar change of the basal layer of the epidermis (thick arrow). Within the dermis is a mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate. The findings are consistent with erythema multiforme. A: 25 × magnification; B: Insert at 100 × magnification.
- Citation: Salama M, Lawrance IC. Stevens-Johnson syndrome complicating adalimumab therapy in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15(35): 4449-4452
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v15/i35/4449.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.4449