©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2008; 14(6): 948-950
Published online Feb 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.948
Published online Feb 14, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.948
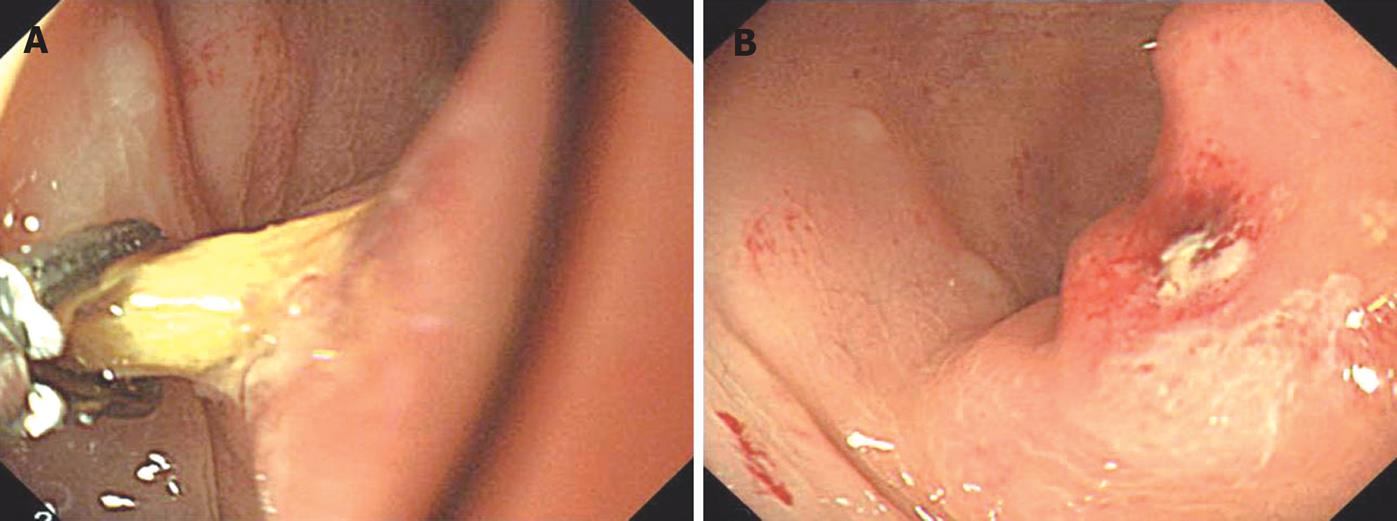
Figure 1 A: The endoscopic appearance of the toothpick in the sigmoid colon and removal of the toothpick was achieved using foreign-body extraction forceps.
B: The endoscopic appearance of impacted colonic mucosa after removal of toothpick.
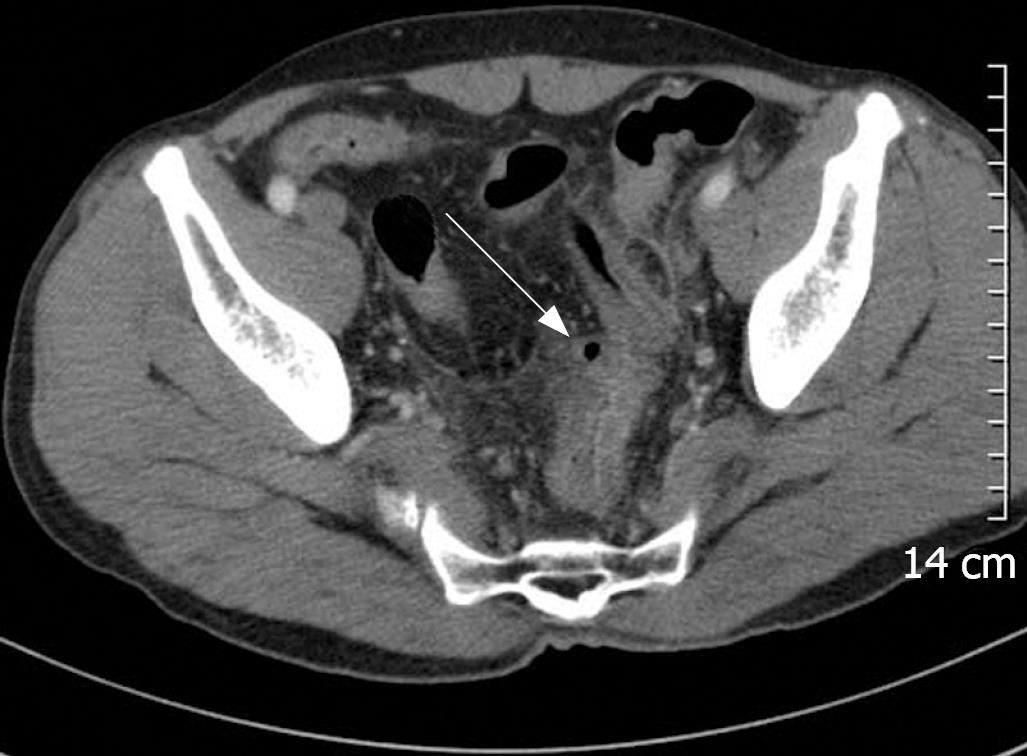
Figure 2 Initial abdominal CT shows severe wall thickening, pericolic fat infiltration and peritoneal thickening in the distal sigmoid colon.
In the serosal surface, a small air-containing cavity lined by thin epithelium (arrow) is noted, which is consistent with a pseudodiverticulum.
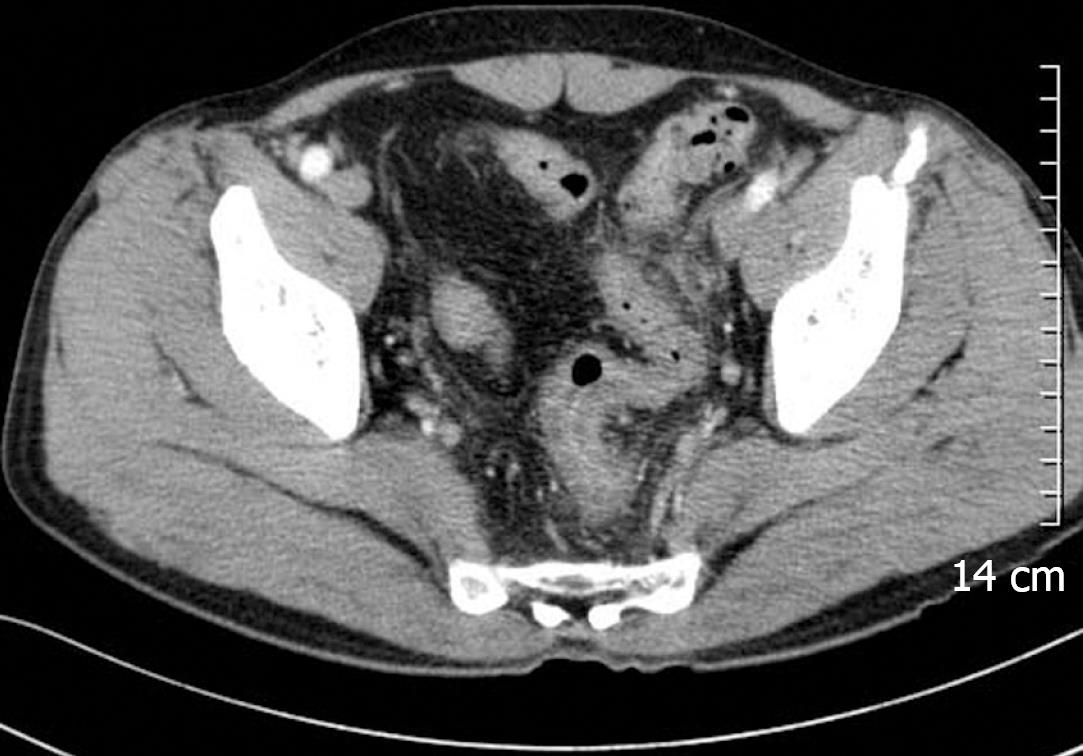
Figure 3 Follow-up CT shows improvement of sigmoid colonic inflammation and disappearance of the pseudodiverticulum.
- Citation: Chung YS, Chung YW, Moon SY, Yoon SM, Kim MJ, Kim KO, Park CH, Hahn T, Yoo KS, Park SH, Kim JH, Park CK. Toothpick impaction with sigmoid colon pseudodiverticulum formation successfully treated with colonoscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(6): 948-950
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i6/948.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.948