©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2007; 13(9): 1453-1457
Published online Mar 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1453
Published online Mar 7, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1453
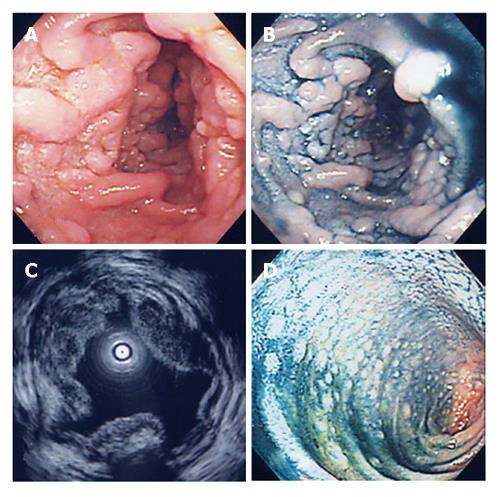
Figure 1 EGD (A), dye contrast EGD (B), EUS (C), and lower endoscopy (D) showing features of the lesions.
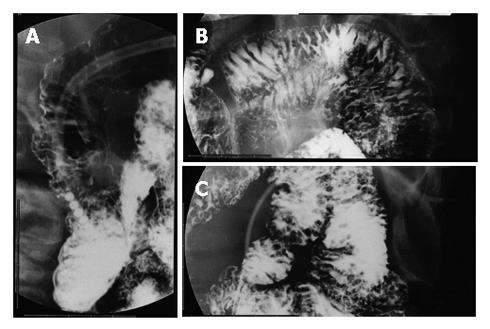
Figure 2 Fluoroscopic examinations showing many small round shaped defects in the second portion of the duodenum (A), jejunum (B), and ileum (C).
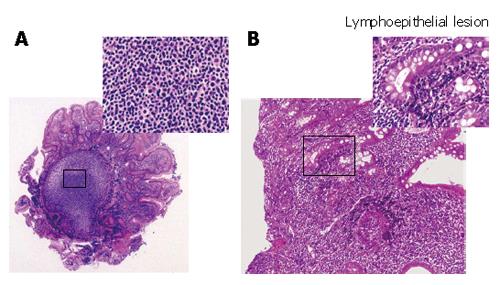
Figure 3 Follicular colonization (A) and many small lymphocytes and a few large lymphocytes in the duodenal tissues (B) in the biopsied specimens (HE, × 200)
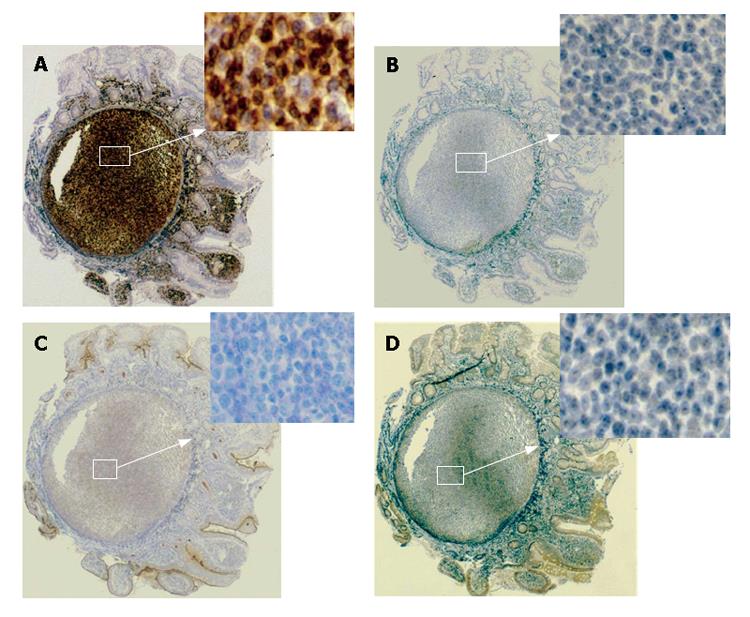
Figure 4 Immunohistological profiles of the lesions revealing positive staining for bcl-2 (A) and negative staining for CD5 (B), CD10 (C), and CyclinD1 (D).
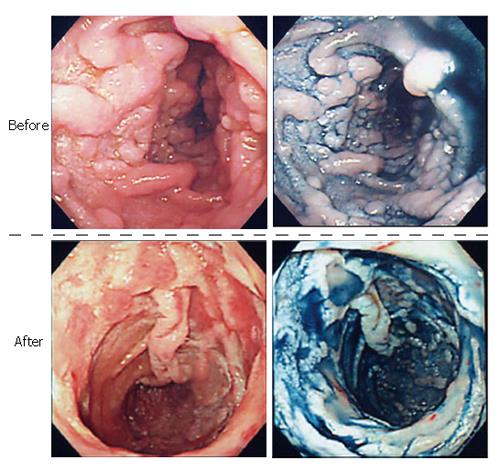
Figure 5 Endoscopic features of the lesions before and after the treatment.
- Citation: Hirata N, Tominaga K, Ohta K, Kadouchi K, Okazaki H, Tanigawa T, Shiba M, Watanabe T, Fujiwara Y, Nakamura S, Oshitani N, Higuchi K, Arakawa T. A case of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma forming multiple lymphomatous polyposis in the small intestine. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(9): 1453-1457
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i9/1453.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i9.1453