©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2007; 13(7): 1027-1031
Published online Feb 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1027
Published online Feb 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1027
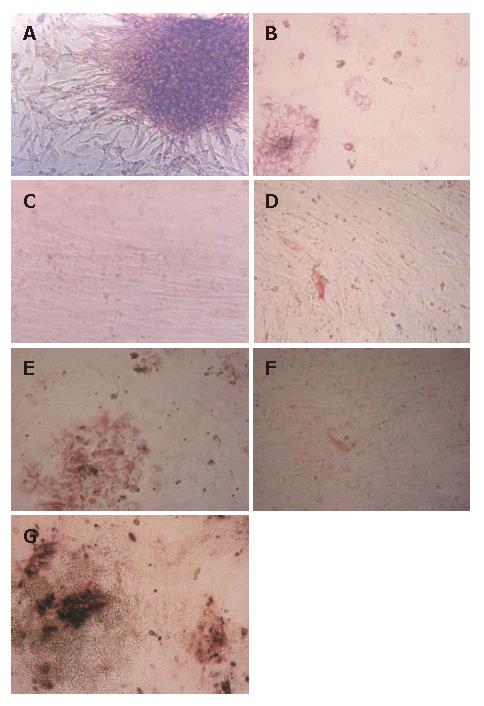
Figure 1 Morphology, PAS and S-P staining of the HFHs under light microscope.
A: Isolated HFHs formed epithelial-like spheroid and they were surrounded by fibroblast-like cells in culture after 48 h; B: HFHs were stained by PAS, the majorities of cultured cells were positive; C: HFHs state in vitro for 50 d; D: HFHs were positive for CK8 in hepatocytes in vitro for 50 d (S-P); E: HFHs expressed liver marker CK18 in vitro for 14 d (S-P); F: Only a few of hepatocytes were positive for CK18 in vitro for 50 d (S-P); G: HFHs expressed ALB in vitro for 14 d (S-P). (Original magnification, × 40).
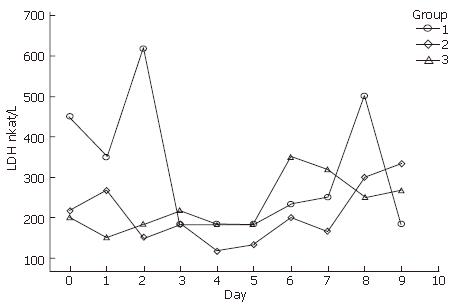
Figure 2 Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) released in primary human hepatocytes.
Figure 3 HBsAg (A) and HBeAg (B) in supernatant detected by ELISA (OD:optical denisity).
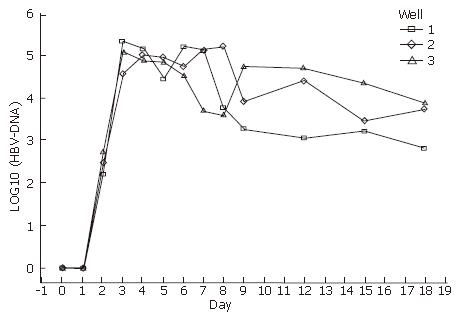
Figure 4 HBV-DNA in media detected by FQ-PCR.
Figure 5 Detection of HBcAg by immunohistochemistry staining (S-P).
A: The HBcAg positive in hepatocytes; B: Negative control for HBcAg. Original magnification, × 40.
- Citation: Lin M, Chen Q, Yang LY, Li WY, Cao XB, Wu JR, Peng YP, Chen MR. Hepatitis B virus infection and replication in primarily cultured human fetal hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(7): 1027-1031
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i7/1027.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1027