©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2007; 13(27): 3699-3704
Published online Jul 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i27.3699
Published online Jul 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i27.3699
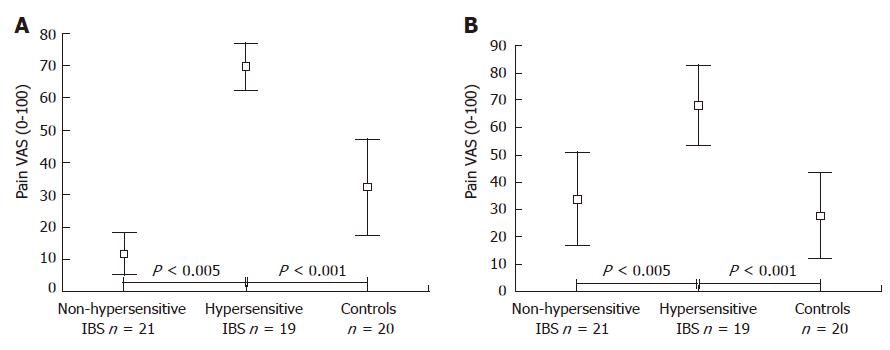
Figure 1 Pain intensity ratings (100 mm VAS) during tonic rectal (A) and tonic somatic (B) stimulation in non-hypersensitive and hypersensitive IBS patients and in healthy controls.
Hypersensitivity is defined by the 95% confidence interval of healthy controls. Means (symbol), 95% confidence intervals (whisker) are shown.
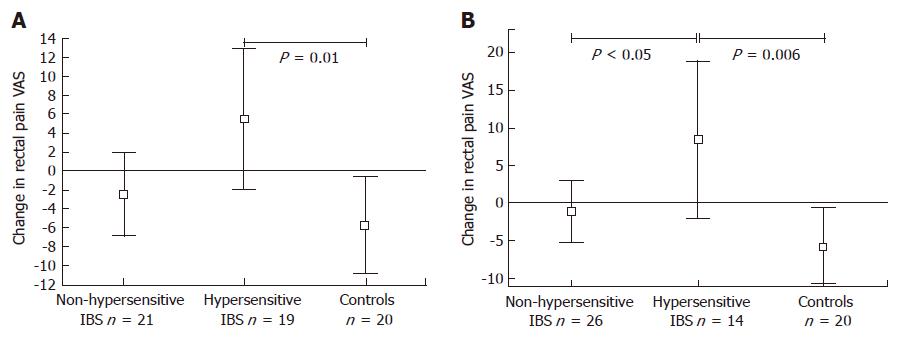
Figure 2 Change in rectal pain intensity scored on a VAS 0-100 during heterotopic stimulation in IBS subgroups and controls.
Means (symbol), 95% confidence intervals (whisker) are shown in patients hypersensitive or not to tonic rectal (A) and both tonic rectal and somatic (B) stimulation. Hypersensitivity is defined by the 95% confidence interval of healthy controls.
- Citation: Wilder-Smith CH, Robert-Yap J. Abnormal endogenous pain modulation and somatic and visceral hypersensitivity in female patients with irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(27): 3699-3704
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i27/3699.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i27.3699