©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2006; 12(42): 6779-6785
Published online Nov 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6779
Published online Nov 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6779
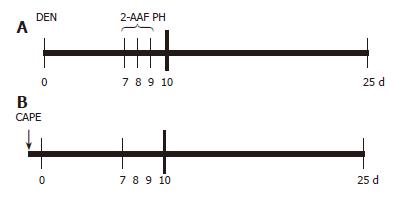
Figure 1 CAPE administration protocol.
A: Carcinogenic treatment (CT): at time 0 the rats were treated with 200 mg/kg of DEN; on d 7, 8 and 9, 2-AAF was administered by gavage at doses of 20 mg/kg per day, a PH was performed at d 10 and rats were sacrificed at d 25; B: CAPE (↓) was administered 12 h before DEN.
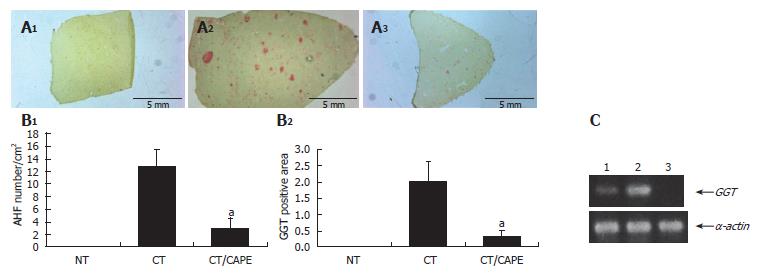
Figure 2 Effect of CAPE on GGT expression.
A: GGT histochemically stained sections (1) non-treated group (NT), (2) carcinogenic treatment group (CT), (3) CT plus CAPE before DEN; B: CAPE effect on number/cm2 of AHF and percentage of GGT+ area/tissue. The differences of AHF number and area after the effect of CAPE in these groups were compared with the respective control group (CT + vehicle) and obtained values were significant by t with aP < 0.05. Twelve histological liver sections per rat from each treatment were randomly selected. NT (n = 3), CT (n = 4), CT plus CAPE (n = 7); C: The RT-PCR assay was used to determine GGT mRNA expression. L1: Control NT; L1: CT group; L1: CT plus CAPE. The series of the extreme right represents α-actin transcripts as control. This experiment was performed with a pool of total RNA isolated from 3 animals.
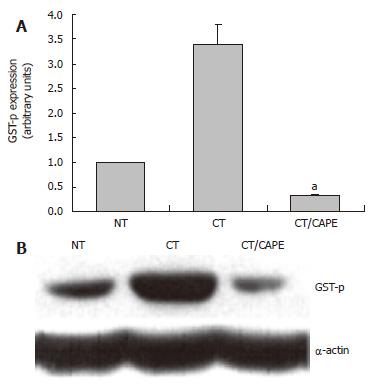
Figure 3 The effect of CAPE on GSTp protein expression.
Western blot was used to analyze the expression of the GSTP protein marker. A: Densitometric analysis of GSTP in: Control NT, CT and CT plus CAPE given before DEN. Results were statistically significant with aP < 0.05; B: Representative Western blot.
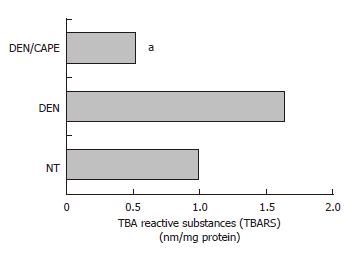
Figure 4 Effect of CAPE on LPX levels induced by DEN.
LPX was determined by detection of malonyldialdehyde concentration and expressed as TBARS. DEN increased TBARS levels detected at 12 h. CAPE administered 12 h before the initiator, clearly reduced the TBARS induced by DEN. Six hundred microgram of liver homogenates of each treated group were used, group NT, DEN (12 h after) and DEN plus CAPE (24 h after CAPE administration). Results were statistically significant with aP < 0.05.
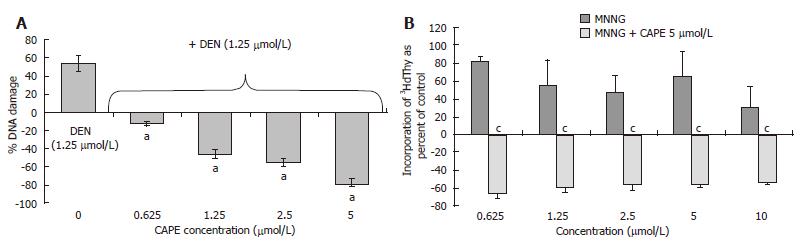
Figure 5 CAPE protects from genotoxic damage caused by DEN and MNNG in PHC.
A: DEN at 1.25 μmol/L concentration induced 3HdT incorporation and this dose was tested with several concentrations of CAPE (0.625, 1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10 μmol/L). CAPE decreased DEN genotoxic damage to levels even below the control; B: Curve concentration of MNNG from 0.625-10 μmol/L. One dose of 5 μmol/L of CAPE protects from genotoxic damage caused by MNNG in PHC. Data incorporation of 3HdT was estimated as dpm/mg of DNA and results are expressed as percent of control samples, the zero data represent 3HdT incorporation of basal level of control group. Results were obtained from 3 replicates of at least 3 animals. aP < 0.05 vs DEN only; cP < 0.05 vs MNNG only.
- Citation: Carrasco-Legleu CE, Sánchez-Pérez Y, Márquez-Rosado L, Fattel-Fazenda S, Arce-Popoca E, Hernández-García S, Villa-Treviño S. A single dose of caffeic acid phenethyl ester prevents initiation in a medium-term rat hepatocarcinogenesis model. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(42): 6779-6785
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i42/6779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i42.6779