©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2006; 12(36): 5798-5804
Published online Sep 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5798
Published online Sep 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5798
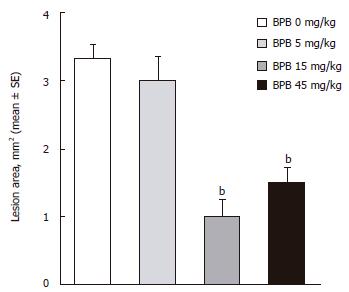
Figure 1 Effect of BPB on cysteamine-induced duodenal ulcers in rats.
bP < 0.001 vs BPB 0 mg/kg (cysteamine only) (Dunnett's test).
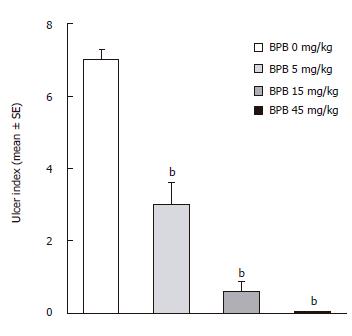
Figure 2 Effect of BPB on gastric mucosal damage induced by ethanol in rats.
bP < 0.01 vs BPB 0 mg/kg (ethanol only) (Dunnett's test).
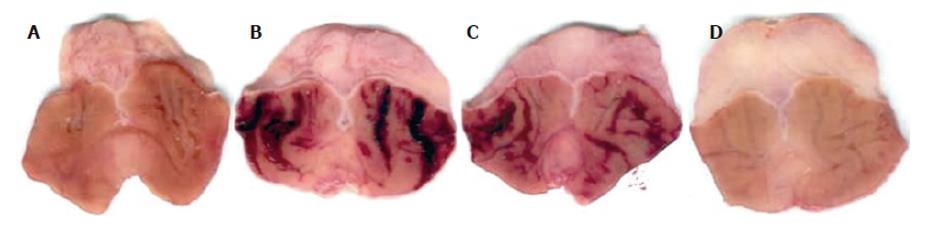
Figure 3 Morphological appearance of ethanol-induced band like hemorrhagic lesions in the stomach of rats.
A: Normal mucosa; B: Ethanol produced lesion; C: Pretreatment of rats with BPB 15 mg/kg; D: Pretreatment of rats with BPB 45 mg/kg.
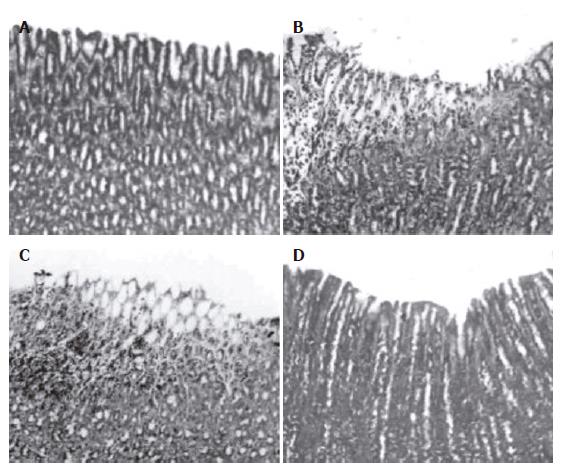
Figure 4 Light micrographs showing the effect of BPB on ethanol-induced gastric lesions of rats.
A: Normal mucosa; B: Ethanol produced lesion; C: Pretreatment of rats with BPB 15 mg/kg; D: Pretreatment of rats with BPB 45 mg/kg.
- Citation: Tariq M, Elfaki I, Khan HA, Arshaduddin M, Sobki S, Moutaery MA. Bromophenacyl bromide, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor attenuates chemically induced gastroduodenal ulcers in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(36): 5798-5804
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i36/5798.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5798