©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2006; 12(35): 5599-5605
Published online Sep 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i35.5599
Published online Sep 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i35.5599
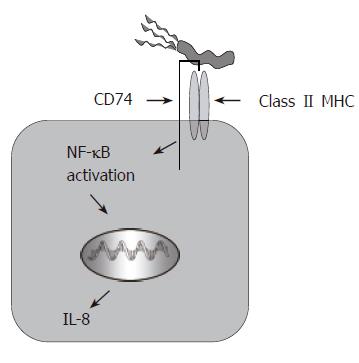
Figure 1 H pylori binds to CD74 on gastric epithelial cells and induces NF-κB activation and IL-8 production.
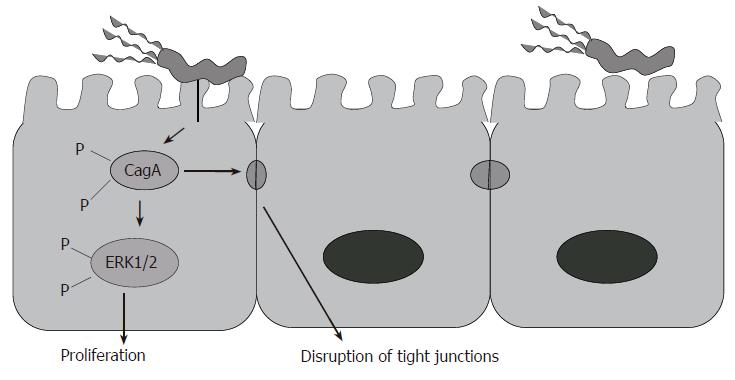
Figure 2 CagA is injected into the cell by a type IV secretion system where it is phosphorylated and induces ERK1/2 phosphorylation and increased cell proliferation.
CagA also induces disruption of the tight junctions between adjacent cells.
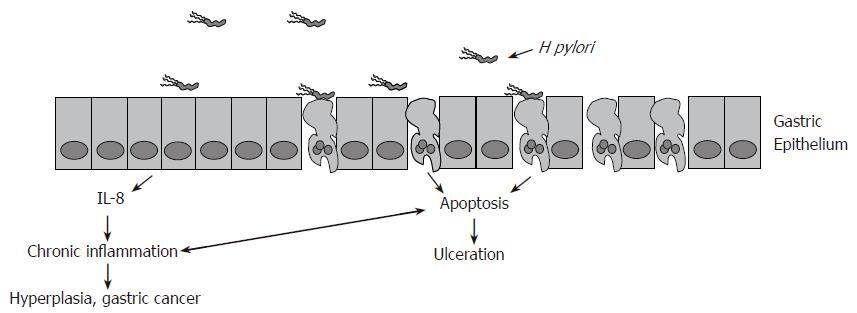
Figure 3 H pylori induces chronic inflammation leading to either ulceration or malignant outgrowths.
-
Citation: Beswick EJ, Suarez G, Reyes VE.
H pylori and host interactions that influence pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(35): 5599-5605 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i35/5599.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i35.5599