©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2006; 12(28): 4529-4535
Published online Jul 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4529
Published online Jul 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4529
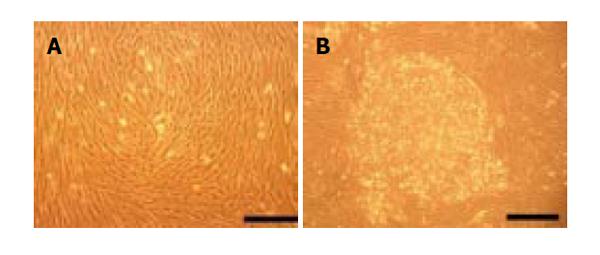
Figure 1 Putative PSC isolated from adult pancreas.
A: Morphology of cultivated putative PSCs; B: Cells aggregate when saturated. bar = 100 μm.
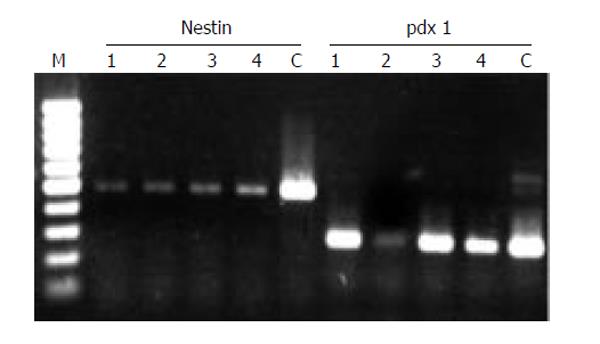
Figure 2 Nestin and pdx-1 expressed in putative PSCs after 5 passages of cultivation.
cDNA oriented from 4 individual donors (lane No. 1 to 4), 100 bp marker (M) and the plasmid cloned human nestin and pdx-1 gene with positive control (C) were shown.
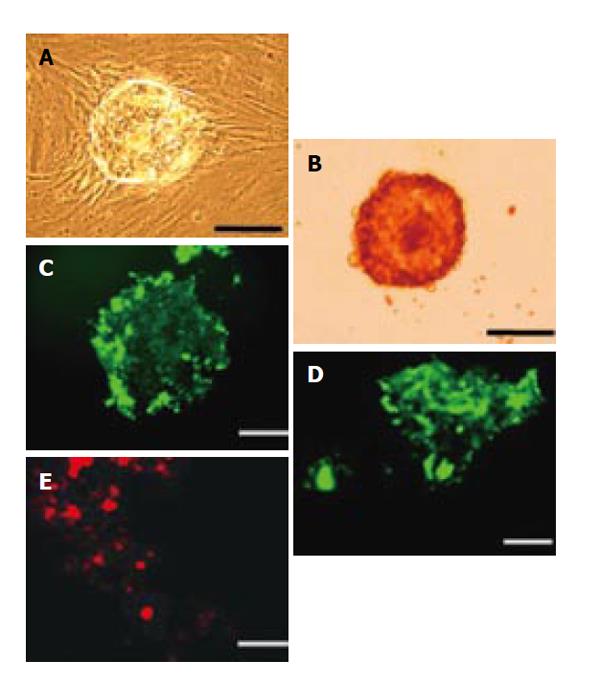
Figure 3 The differentiation of putative PSCs (4 wk).
A: Growth in Matrigel™; B: Dithizone stain; C-E: Immunohistochemistry staining by anti-insulin (C), glucagon (D) and somatostatin (E) immunoglobulins. bar = 100 μm.
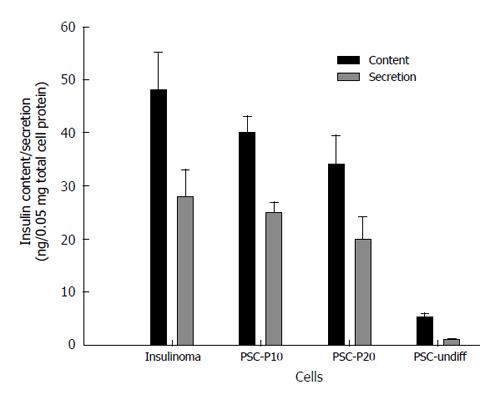
Figure 4 Measurement of Insulin content and secretion in differentiated putative PSCs.
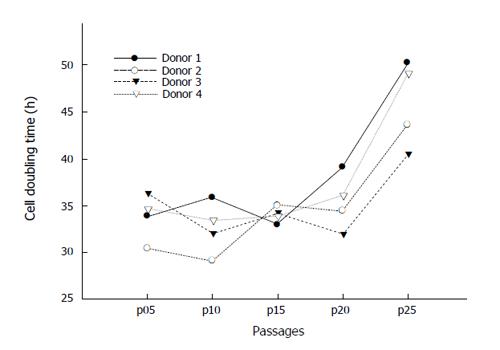
Figure 5 Cell doubling time of putative PSC.
- Citation: Lin HT, Chiou SH, Kao CL, Shyr YM, Hsu CJ, Tarng YW, Ho LLT, Kwok CF, Ku HH. Characterization of pancreatic stem cells derived from adult human pancreas ducts by fluorescence activated cell sorting. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(28): 4529-4535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i28/4529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4529