Copyright
©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2006; 12(27): 4428-4430
Published online Jul 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4428
Published online Jul 21, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4428
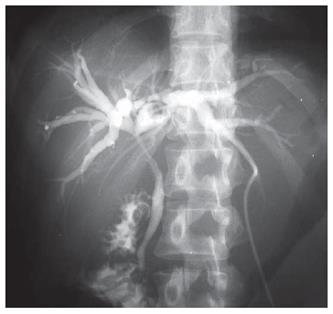
Figure 1 Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiograms showing a stricture of the common bile duct and bilateral hepatic ducts, although the bile duct wall was smooth.
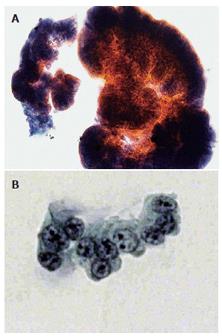
Figure 2 Microscopic cytology showing atypical columnar cells with variously-sized round nuclei with granular chromatin and prominent nucleoli.
A: Papanicolaou stain, × 200; B: Papanicolaou stain, × 400.
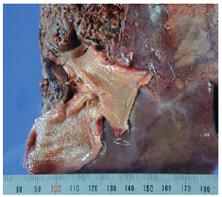
Figure 3 Gross features of the resected specimen showing the absence of a neoplastic lesion, with smooth mucosa in the right hepatic lobe and extrahepatic bile duct.
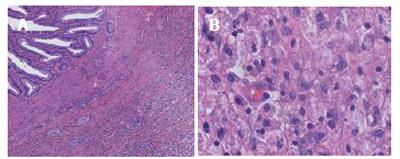
Figure 4 Microscopic view showing marked infiltration of foamy macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils in the lamina propria of the bile duct mucosa.
A: HE × 200; B: HE × 400.
- Citation: Kawate S, Ohwada S, Ikota H, Hamada K, Kashiwabara K, Morishita Y. Xanthogranulomatous cholangitis causing obstructive jaundice: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(27): 4428-4430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i27/4428.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4428