©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2005; 11(6): 922-925
Published online Feb 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i6.922
Published online Feb 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i6.922
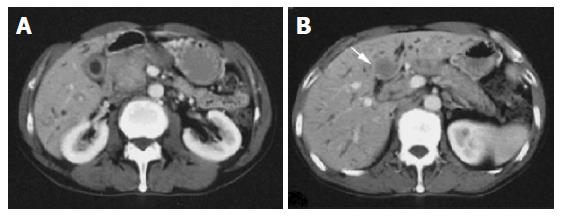
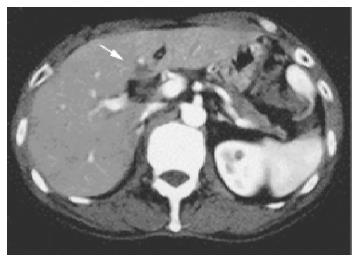
Figure 1 A: CT demonstrated dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts, swelling of the pancreatic head, thickening of the gallbladder wall; B: CT revealed the liver mass, which was not enhanced by contrast medium.
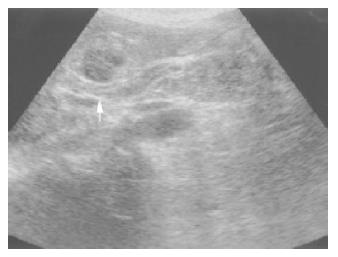
Figure 2 Ultrasonography demonstrated hypoechoic liver mass.
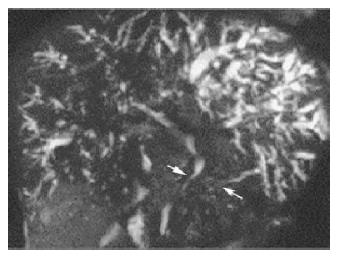
Figure 3 MRCP showed stricture of the common bile duct with marked dilatation of the intrahepatic bile duct and irregular narrowing of the pancreatic duct.
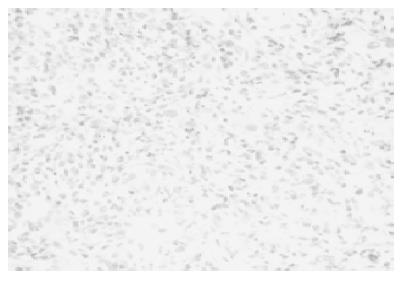
Figure 4 Biopsy specimens from the liver mass showed lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells, and a number of eosinophils.
It did not contain normal liver tissue or malignant cells.
Figure 5 CT revealed that the pancreatic swelling almost resolved 1 mo after the treatment.
Liver masses decreased.
Figure 6 MRCP demonstrated the normalized bile duct 6 mo after the treatment.
- Citation: Sasahira N, Kawabe T, Nakamura A, Shimura K, Shimura H, Itobayashi E, Asada M, Shiratori Y, Omata M. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver and peripheral eosinophilia in autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(6): 922-925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i6/922.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i6.922