©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2005; 11(48): 7651-7656
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7651
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7651
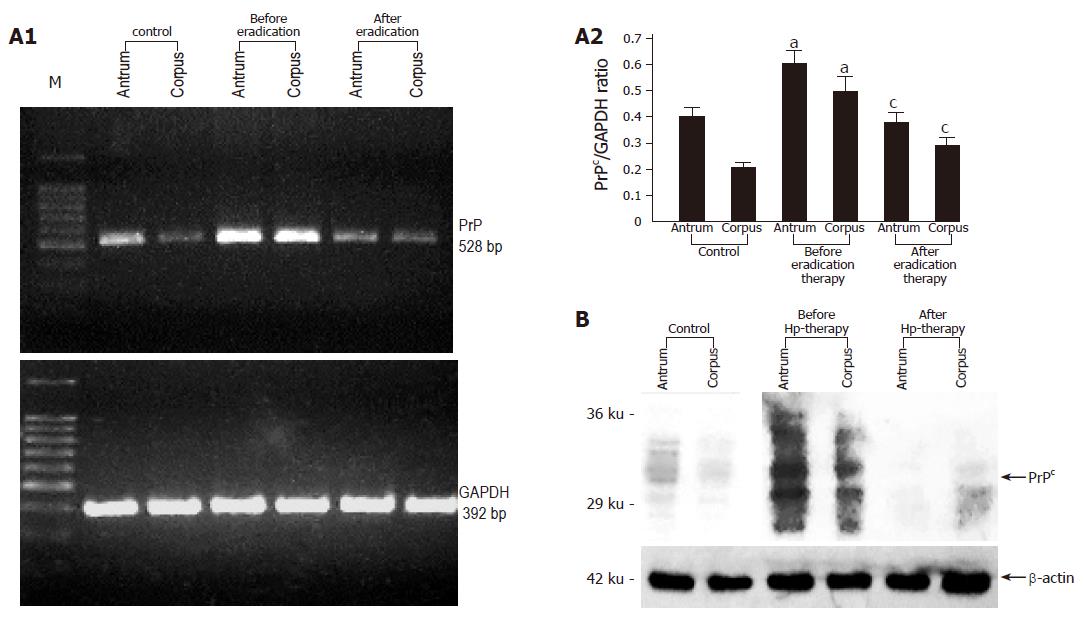
Figure 1 A: Representative RT-PCR and densitometric analysis showing PrPc mRNA expression in the gastric mucosa colonized with H pylori before and after successful eradication therapy (n = 10).
Data are expressed as means±SE. aP<0.05 vs the control group, cP<0.05 vs the expression before eradication therapy; B: Representative immunoblot analysis showing PrPc protein expression in the gastric mucosa colonized with H pylori before and after successful eradication therapy.
Figure 2 Protein expression of PrPc in two gastric cell lines (MKN45 and KATO III); the positive control is from bovine brain.
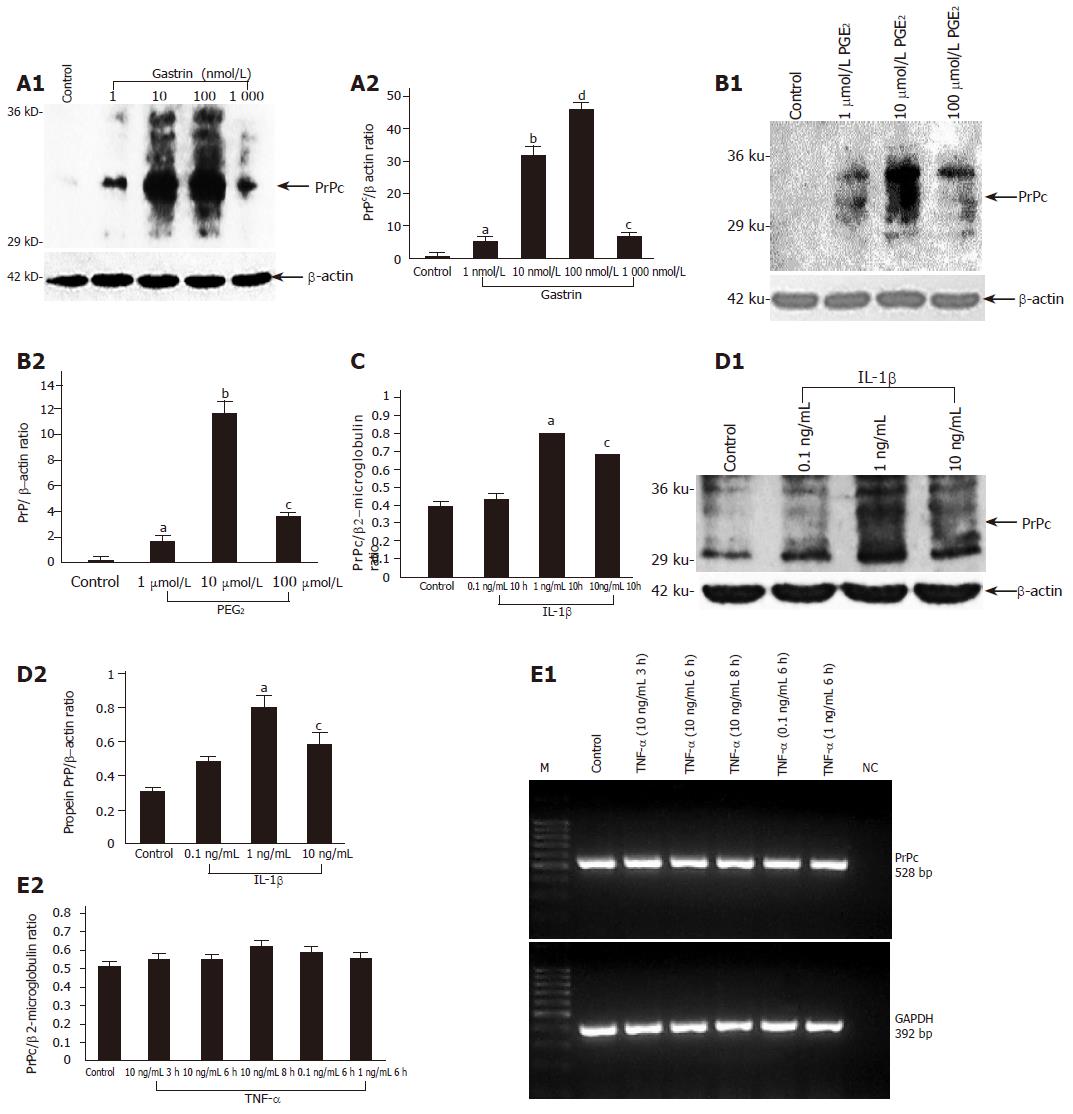
Figure 3 PrPc protein and mRNA expression in MKN45 cells incubated with increasing doses of gastrin (1-1 000 nmol/L) (A), PGE2 (1-100 µmol/L) aP<0.
05 vs control, bP<0.001 vs control, cP<0.05 vs control, dP<0.001 vs control (B), interleukin 1β (0.1-10 ng/mL) (C and D) or TNF-α (0.1-10 ng/mL) aP<0.05 vs control, bP<0.001 vs control, cP<0.05 vs control (E). Data represent means±SE of three independent experiments. At the mRNA level, the expression of PrPc was normalized to β2-microglobulin and at the protein level to β-actin.
- Citation: Konturek PC, Bazela K, Kukharskyy V, Bauer M, Hahn EG, Schuppan D. Helicobacter pylori upregulates prion protein expression in gastric mucosa: A possible link to prion disease. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(48): 7651-7656
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i48/7651.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7651