©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2005; 11(39): 6096-6103
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6096
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6096
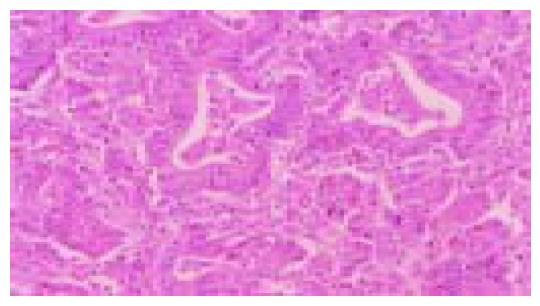
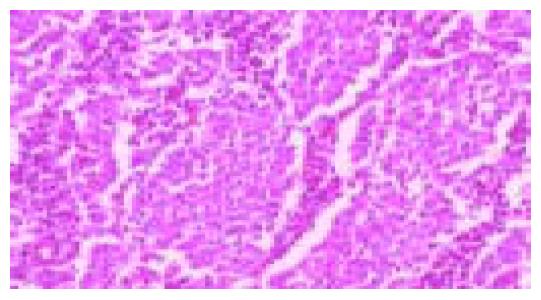
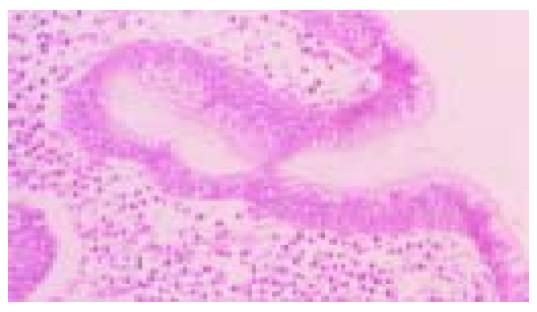
Figure 1 Moderately differentiated, intestinal-type (tub2) adenocarcinoma.
Irregular neoplastic tubular structures are seen throughout the field (hematoxylin and eosin stain).
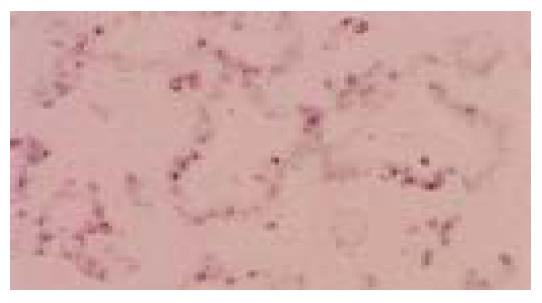
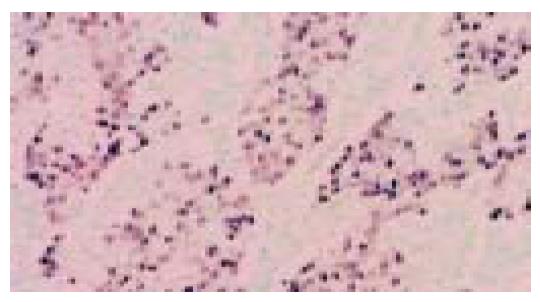
Figure 2 Same case as in Figure 1.
EBER-1 nuclear positivity is limited to neoplastic cells lining the tubular structures (in situ hybridization).
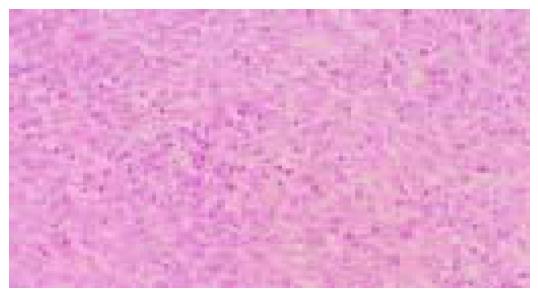
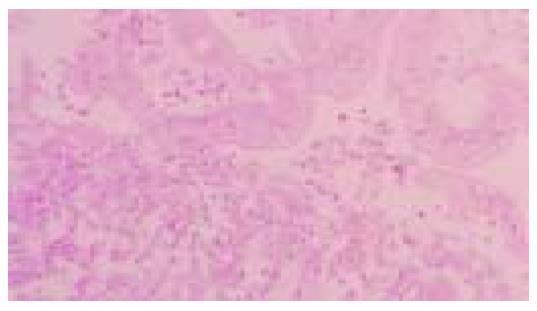
Figure 3 Diffuse-type (por1) adenocarcinoma.
Sheets of neoplastic cells are distributed in an indistinct pattern (hematoxylin and eosin stain).
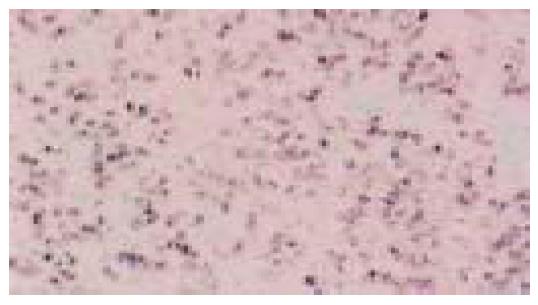
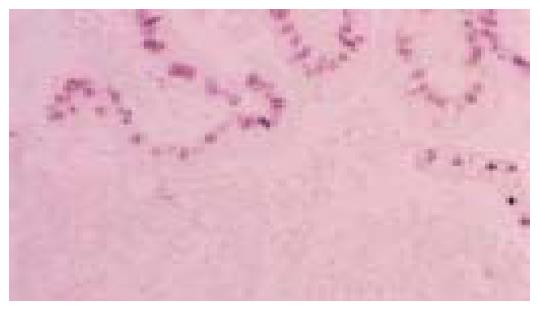
Figure 4 Same case as in Figure 3.
A uniform nuclear signal of EBER-1 is seen in neoplastic cells (in situ hybridization)
Figure 5 Poorly differentiated, LEL carcinoma.
Clusters of neoplastic cells are separated by lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate
Figure 6 Same case as in Figure 5.
An EBER-1-positive signal is detected in the nuclei of neoplastic cells (in situ hybridization
Figure 7 Lining gastric epithelium shows regenerative changes characterized by nuclear growth without atypia.
There are few neoplastic cells in the underlying lamina propria (hematoxylin and eosin stain)
Figure 8 Same case as in Figure 7.
The EBER-1-positive nuclear signal is restricted to regenerative epithelium. Note the EBER-1 nuclear negativity of neoplastic cells infiltrating the lamina propria (in situ hybridization
Figure 9 Lining gastric epithelium shows high-grade dysplasia, characterized by cell stratification and crowding, increased nuclear/cytoplasm ratio, nuclear atypia, and prominent eosinophilic nucleoli (hematoxylin and eosin stain).
Figure 10 Same case as in Figure 9.
Dysplastic epithelium is intensely positive for the EBER-1 nuclear signal (in situ hybridization)
- Citation: Herrera-Goepfert R, Akiba S, Koriyama C, Ding S, Reyes E, Itoh T, Minakami Y, Eizuru Y. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma: Evidence of age-dependence among a Mexican population. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(39): 6096-6103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i39/6096.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6096