©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2005; 11(30): 4693-4696
Published online Aug 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4693
Published online Aug 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4693
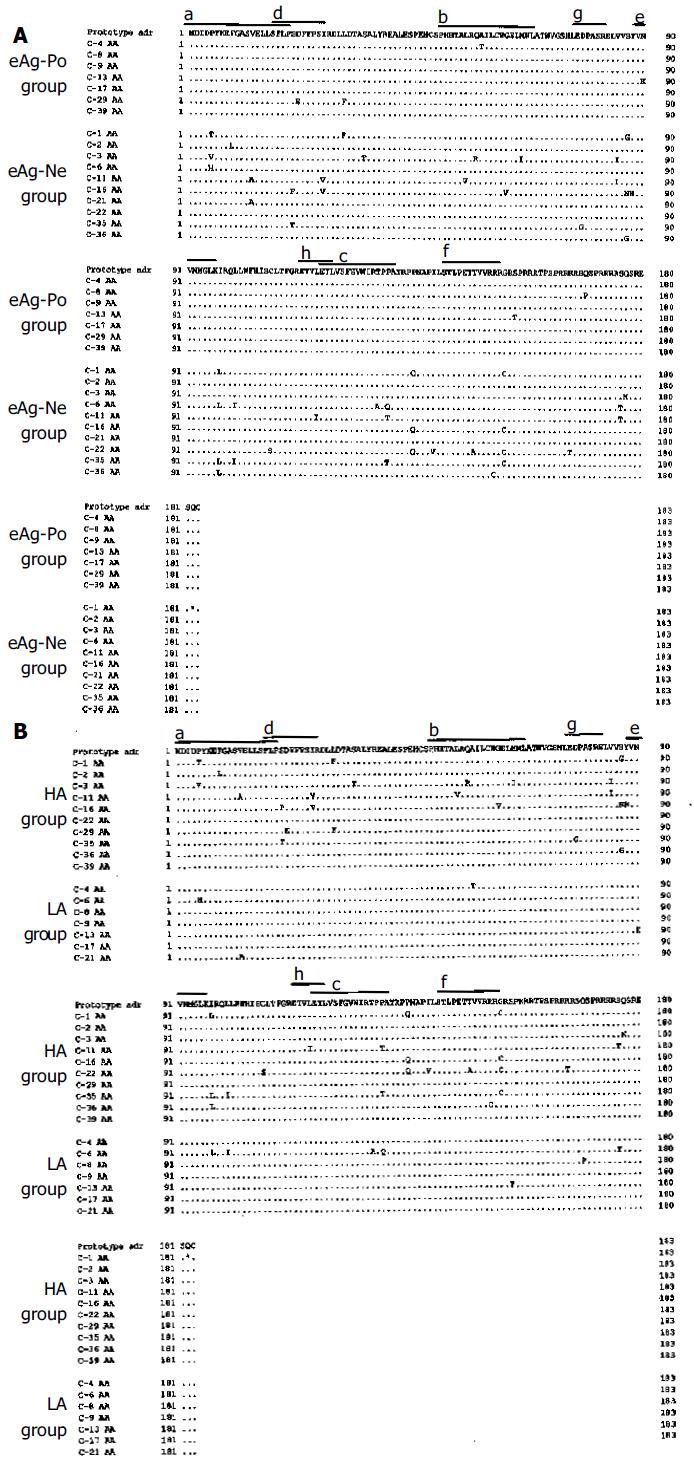
Figure 1 Comparison of core amino acid sequences between eAg-Po and eAg-Ne groups.
(A) and between HA and LA groups (B). The top line is the core amino acid sequence of the HBV adr subtype. Core amino acid sequences of the HA group are C-1, C-2, C-3, C-11, C-16, C-22, C-29, C-35, C-36, and C-39, and those of the LA group are C-4, C-6, C-8, C-9, C-13, C-17, and C-21, Each dot denotes an identical match to the top sequence. An asterisk denotes that this codon is a stop codon. a,b,c are HLA class II-restricted T cell recognition sites. d, e, f are HLA class I-restricted CTL epitopes. g, h are the lesion exposed at the surface of HBcAg.
- Citation: Tanaka H, Ueda H, Hamagami H, Yukawa S, Ichinose M, Miyano M, Mimura K, Nishide I, Zhang BX, Wang SW, Zhou SO, Li BH. Mutations in hepatitis B virus core regions correlate with hepatocellular injury in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(30): 4693-4696
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i30/4693.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4693