©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2005; 11(22): 3479-3484
Published online Jun 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3479
Published online Jun 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3479
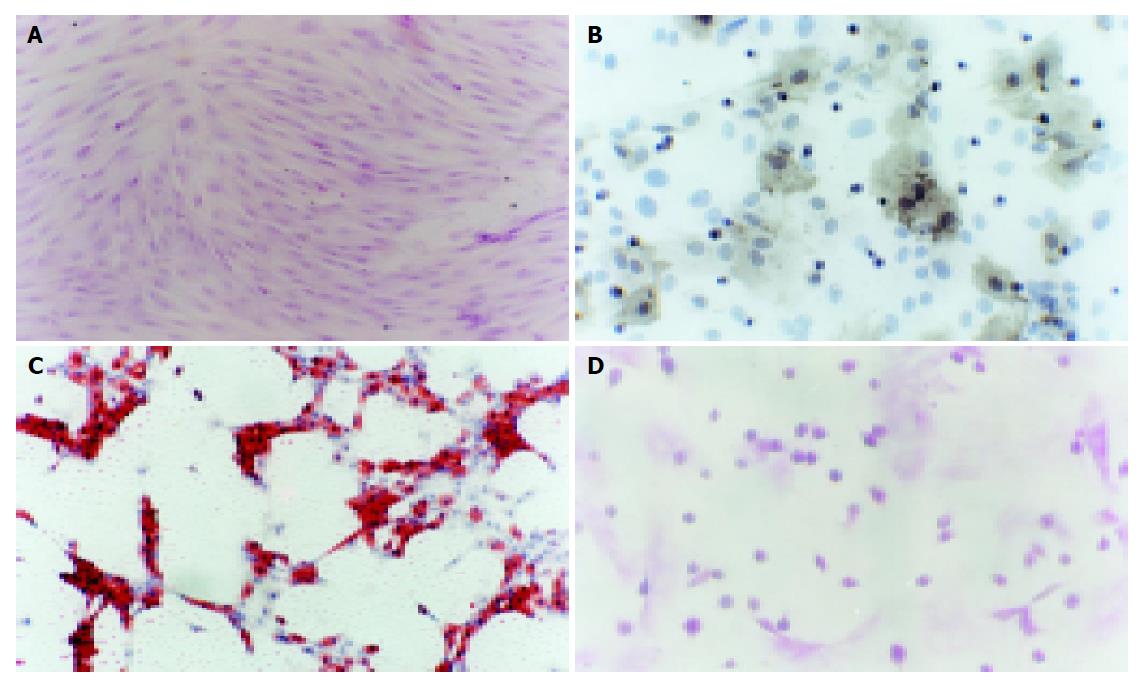
Figure 1 Different morphology and differentiation of rat MSCs.
A: Morphology of rat MSCs stained with HE. The cells were fibroblast-like and grew as a whirlpool (×100); B: Appearance of osteocytes 21 d after induction. The positive cells were observed by stain for alkaline phosphatase. The gray parts were cytoplasm stained for alkaline phosphatase. The cells differentiated MSCs into osteocytes. The blue ones were nuclei stained with hematoxylin (×400); C: Oil red-O positive cells 6 d after adipogenic differentiation of rat MSCs. The red parts were lipid-rich vacuoles, the blue ones were nuclei stained with hematoxylin (×100); D: Cells stained by PAS. Glycogen storage was seen as accumulated magenta staining. The small round cells and epithelioid cells had magenta staining in the region (×200).
-
Citation: Kang XQ, Zang WJ, Song TS, Xu XL, Yu XJ, Li DL, Meng KW, Wu SL, Zhao ZY. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into hepatocytes
in vitro . World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(22): 3479-3484 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i22/3479.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3479