©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2005; 11(17): 2666-2669
Published online May 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i17.2666
Published online May 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i17.2666
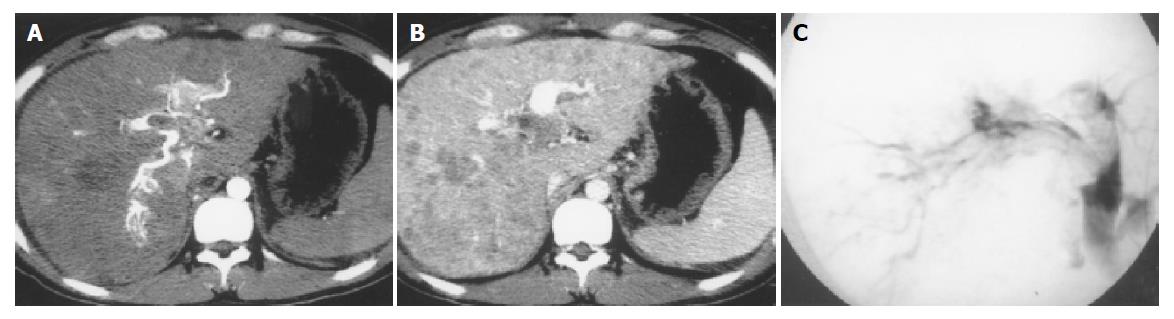
Figure 1 Diffuse pattern of HCC complicated with severe and central APS.
Earlier enhancement and stronger opacification of main portal trunk, left and right first-order branches, with thromboses in them; decreased enhancement degrees of HCC foci and spleen, and ascites were also displayed (A, B). DSA finding of the same patient (C).
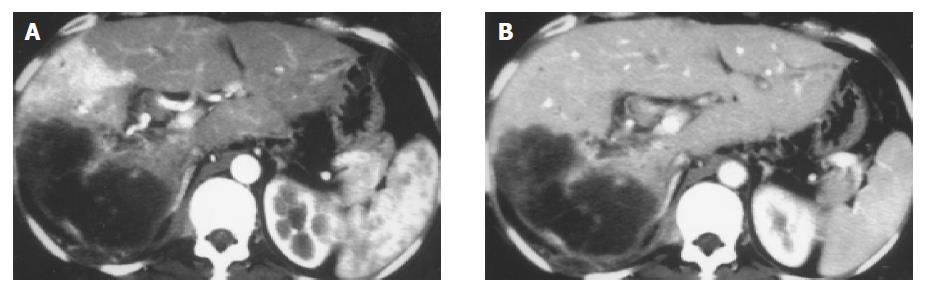
Figure 2 Massive pattern of HCC associated with mild and peripheral APS.
Transient wedge-shaped enhancement anterior to HCC foci at late hepatic arterial phase (A), becoming isoattenuation at portal vein phase (B); decreased enhancement degree of HCC focus was disclosed too. The APS was missed with DSA (not shown).
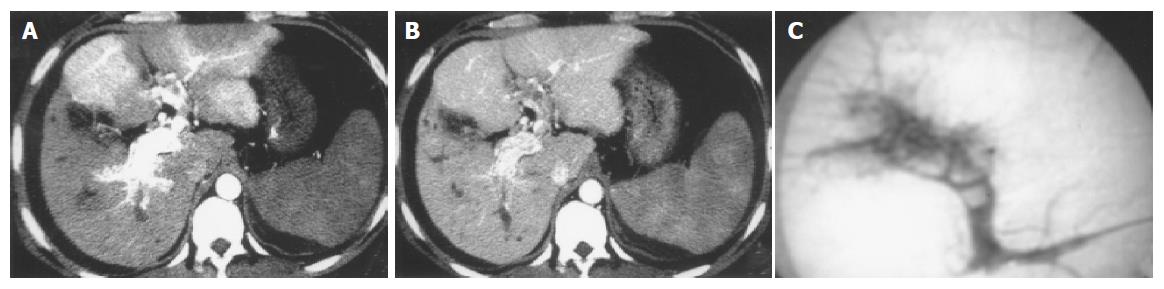
Figure 3 Massive pattern of HCC accompanied with severe, central and slight, peripheral APS.
Earlier enhancement and stronger opacification of main portal trunk, left and right first-order branches, with thromboses in them and transient patchy enhancement at late hepatic arterial phase (A), becoming isoattenuation at portal vein phase (B); decreased enhancement degrees of HCC focus and spleen, cirrhotic liver and ascites were also shown. DSA finding of the same patient (C).
- Citation: Luo MY, Shan H, Jiang ZB, Liang WW, Zhang JS, Li LF. Capability of multidetector CT to diagnose hepatocellular carcinoma-associated arterioportal shunt. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(17): 2666-2669
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i17/2666.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i17.2666