©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2005; 11(16): 2502-2507
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2502
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2502
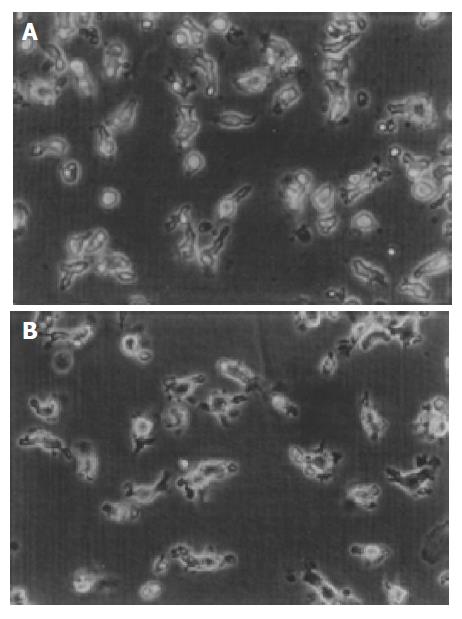
Figure 1 Morphology of DCs.
A: Morphology of DCs derived from cord blood at d 14 was irregular and with cytoplasm projections. B: After being pulsed with whole tumor cell lysates, the dendritic processes of DCs being more typical (phase contrast microscope, 20×5.5).
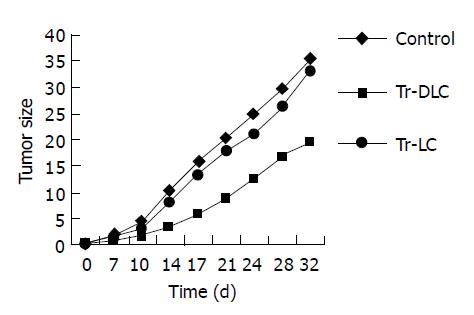
Figure 2 Growth curves of human hepatocarcinoma BEL-7402 cells in SCID mice treated with DC-primed lymphocytes (Tr-DLC), unprimed lymphocytes (Tr-LC) and in control group respectively.
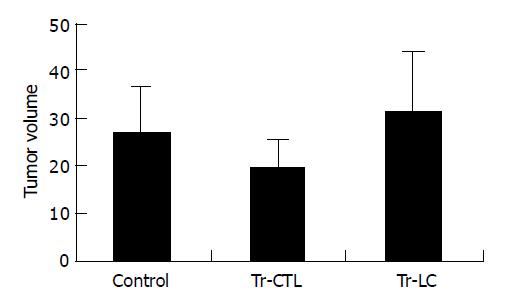
Figure 3 All mice were killed after 32 d of tumor cell injection and tumor volumes measured ex vivo and presented as mean±SD after evolution (5 mice/group).
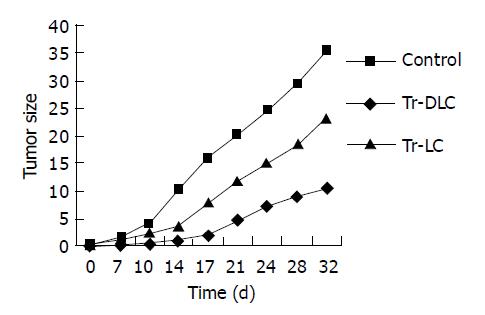
Figure 4 Growth curves of human hepatocarcinoma cell BEL-7402 in SCID mice vaccinated with DC-primed lymphocytes (Im-DLC), unprimed lymphocytes (Im-LC) and in control group respectively.
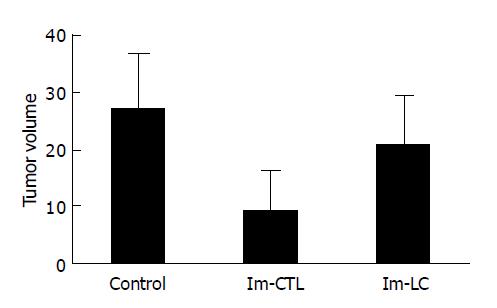
Figure 5 All mice were killed after 32 d of tumor cell challenge and tumor volumes were measured ex vivo and presented as mean±SD after evolution (5 mice/group).
-
Citation: Su ZJ, Chen HB, Zhang JK, Xu L. Effects of dendritic cells from cord blood CD34+ cells on human hepatocarcinoma cell line BEL-7402
in vitro and in SCID mice. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(16): 2502-2507 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i16/2502.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2502