©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 15, 2004; 10(14): 2109-2112
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2109
Published online Jul 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2109
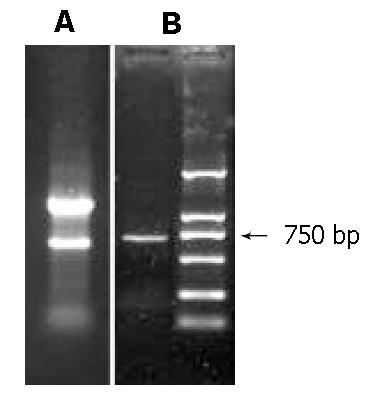
Figure 1 Amplification of Peroxiredoxin I by RT-PCR.
A: total RNAs were isolated from mouse intestinal epithelia; three bands were visualized on agarose gel, which represented the main ribosome RNA of the cells. B: amplification of the coding region of peroxiredoxin I applying RT-PCR.
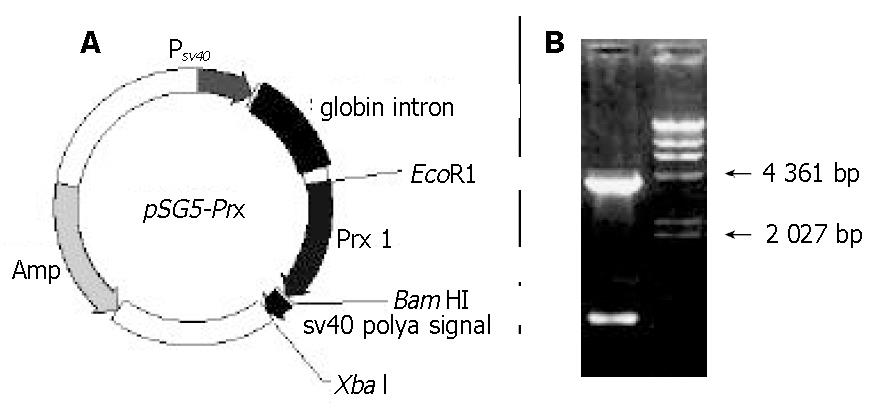
Figure 2 Recombinant expression vector pSG5-Prx.
A: diagrams of the expression vector pSG5-Prx. B: electrophoresis map of this vector (EcoR I and BamH I). λ/HindIII marker was loaded to estimate the relative molecular weight of the expression vector.
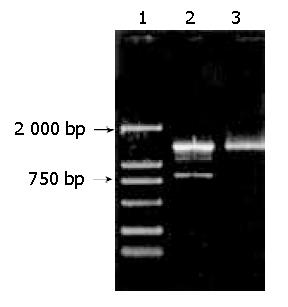
Figure 3 Detection of the transcription of recombinant vector pSG5-Prx by RT-PCR.
Total RNAs isolated from transfected cells were applying for RT-PCR analysis with primers P2 and P3. Lane 1: DNA marker DL 2000, Lane 2: RT-PCR product, Lane 3: PCR product using purified recombinant vector as template.
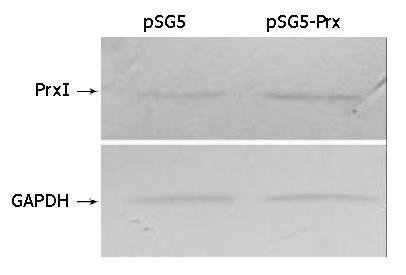
Figure 4 Immunoblotting of peroxiredoxin I of transfected and normal IEC-6 cell.
- Citation: Zhang B, Su YP, Wang T, Wang FC, Ai GP, Xu H, Wang JP, Huang YS, Jiang JX. Cloning and expression of mouse peroxiredoxin I in IEC-6 Cells. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(14): 2109-2112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i14/2109.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2109