©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 1, 2004; 10(13): 1914-1917
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1914
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1914
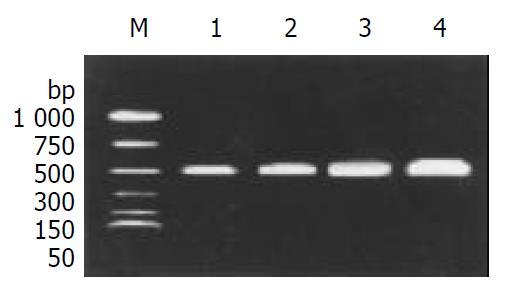
Figure 1 Analysis of TNF-α mRNA expression in UC mice after a 4-week treatment.
A 550-bp fragment was amplified by PCR. M: Marker; Lane 1: Group G IV (control); Lane 2: Group G I (TCME); Lane 3: Group G II (SASPE); Lane 4: Group G III (NSE). The primers used were: upstream, 5’-GGAGCTGCTCAGAGTAAATCAC-3’; and the downstream, 5’-GCACGAGTCACTCTCGTTTTC-3’[23].
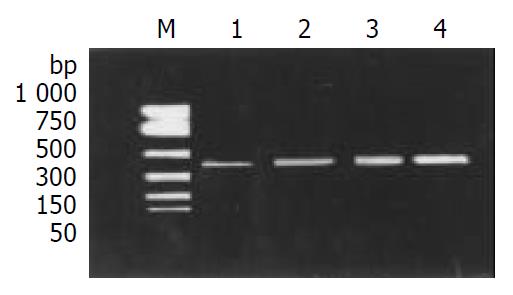
Figure 2 Analysis of IFN-γ mRNA expression in UC mice after a 4-week treatment.
A 430-bp fragment was amplified by PCR. M: Marker; Lane 1: Group G IV (control); Lane 2: Group G I (TCME); Lane 3: Group G II (SASPE); Lane 4: Group G III (NSE). The primers used were: upstream, 5’-TTTTGGGTCTCTTGGCTGTT-3’; and the downstream, 5’-CTCCTTTTTCGCTTCCCTGT-
- Citation: Guo SM, Tong HB, Bai LS, Yang W. Effect of traditional Chinese medicinal enemas on ulcerative colitis of rats. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(13): 1914-1917
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i13/1914.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1914