©The Author(s) 2026.
Artif Intell Gastroenterol. Jan 8, 2026; 7(1): 115498
Published online Jan 8, 2026. doi: 10.35712/aig.v7.i1.115498
Published online Jan 8, 2026. doi: 10.35712/aig.v7.i1.115498
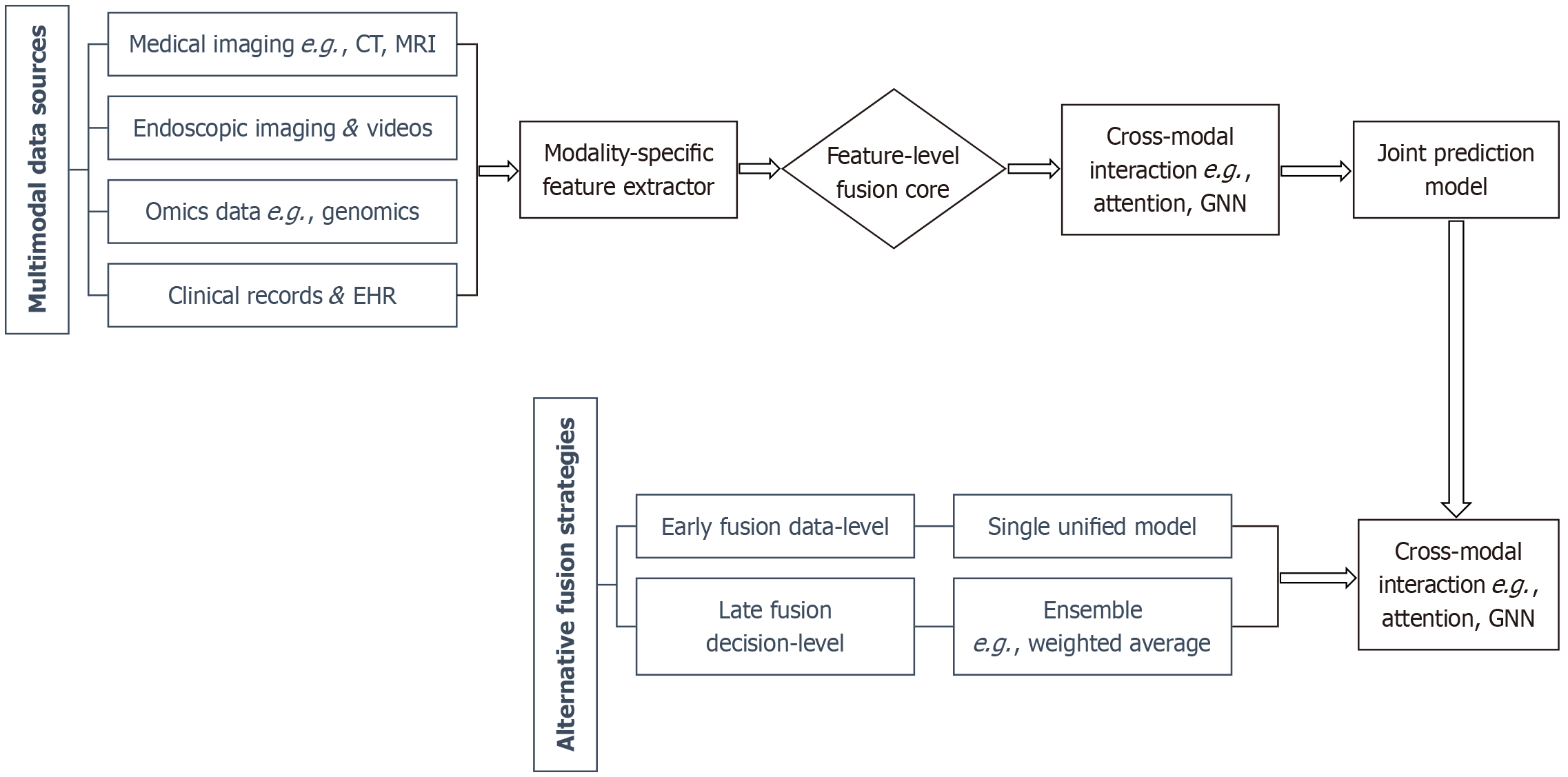
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of multimodal artificial intelligence fusion strategies for gastrointestinal tumors.
The model architectures for early, intermediate, and late fusion are compared. Intermediate (feature-level) Fusion (highlighted in blue), the predominant approach, involves processing each data modality through specialized networks, followed by integrating the extracted features to model cross-modal interactions for joint prediction. This architecture balances flexibility and the ability to capture complex, biologically meaningful interactions between data types, making it particularly suitable for personalized therapy applications. Early fusion combines raw data at the input stage, while late fusion aggregates decisions from separate models. CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; EHR: Electronic health record; GNN: Graph neural network.
- Citation: Nian H, Wu YB, Bai Y, Zhang ZL, Tu XH, Liu QZ, Zhou DH, Du QC. Multimodal artificial intelligence integrates imaging, endoscopic, and omics data for intelligent decision-making in individualized gastrointestinal tumor treatment. Artif Intell Gastroenterol 2026; 7(1): 115498
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2644-3236/full/v7/i1/115498.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.35712/aig.v7.i1.115498