©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Methodol. Mar 20, 2026; 16(1): 107927
Published online Mar 20, 2026. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v16.i1.107927
Published online Mar 20, 2026. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v16.i1.107927
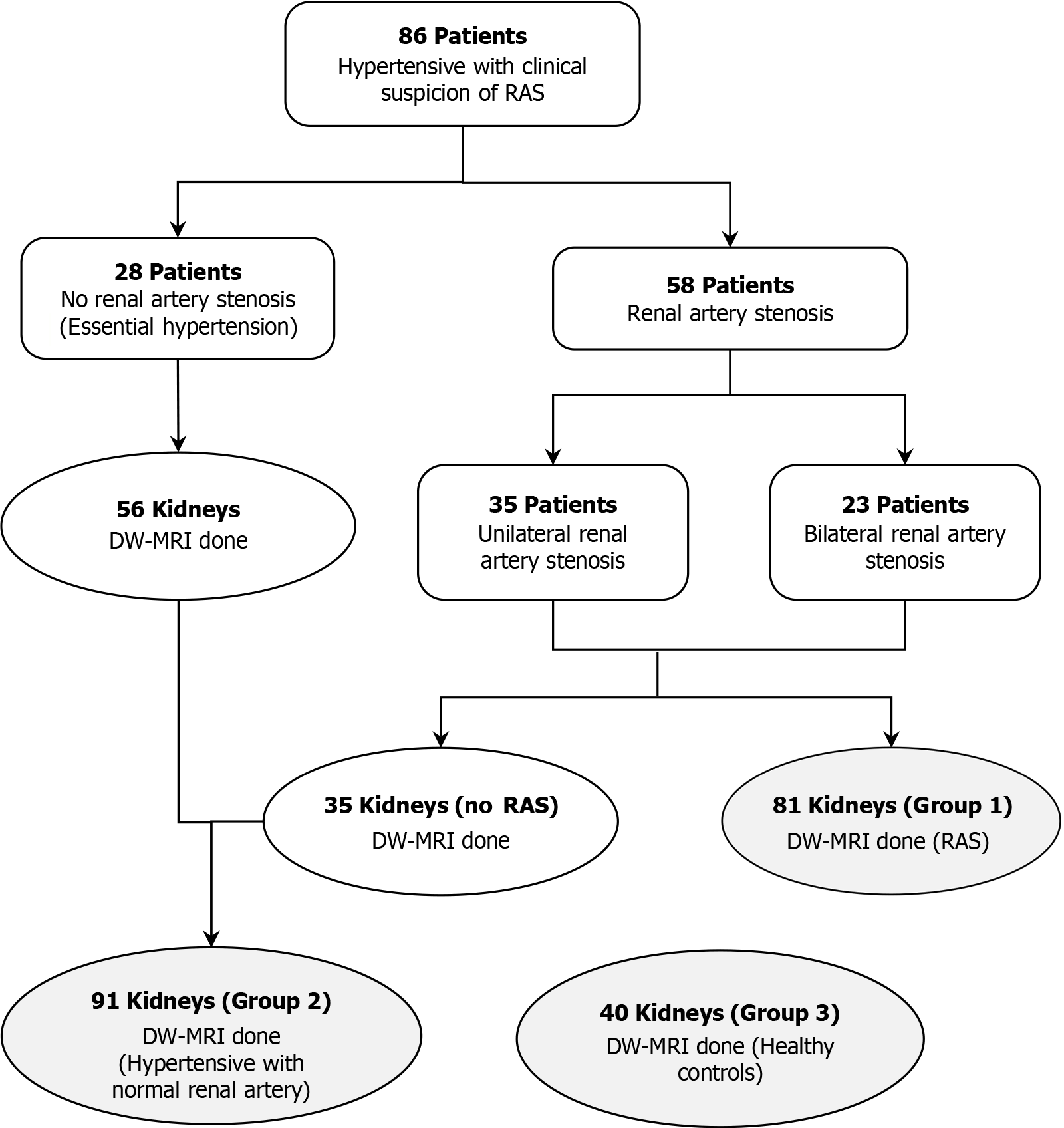
Figure 1 Flowchart of the study.
RAS: Renal artery stenosis; DW-MRI: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
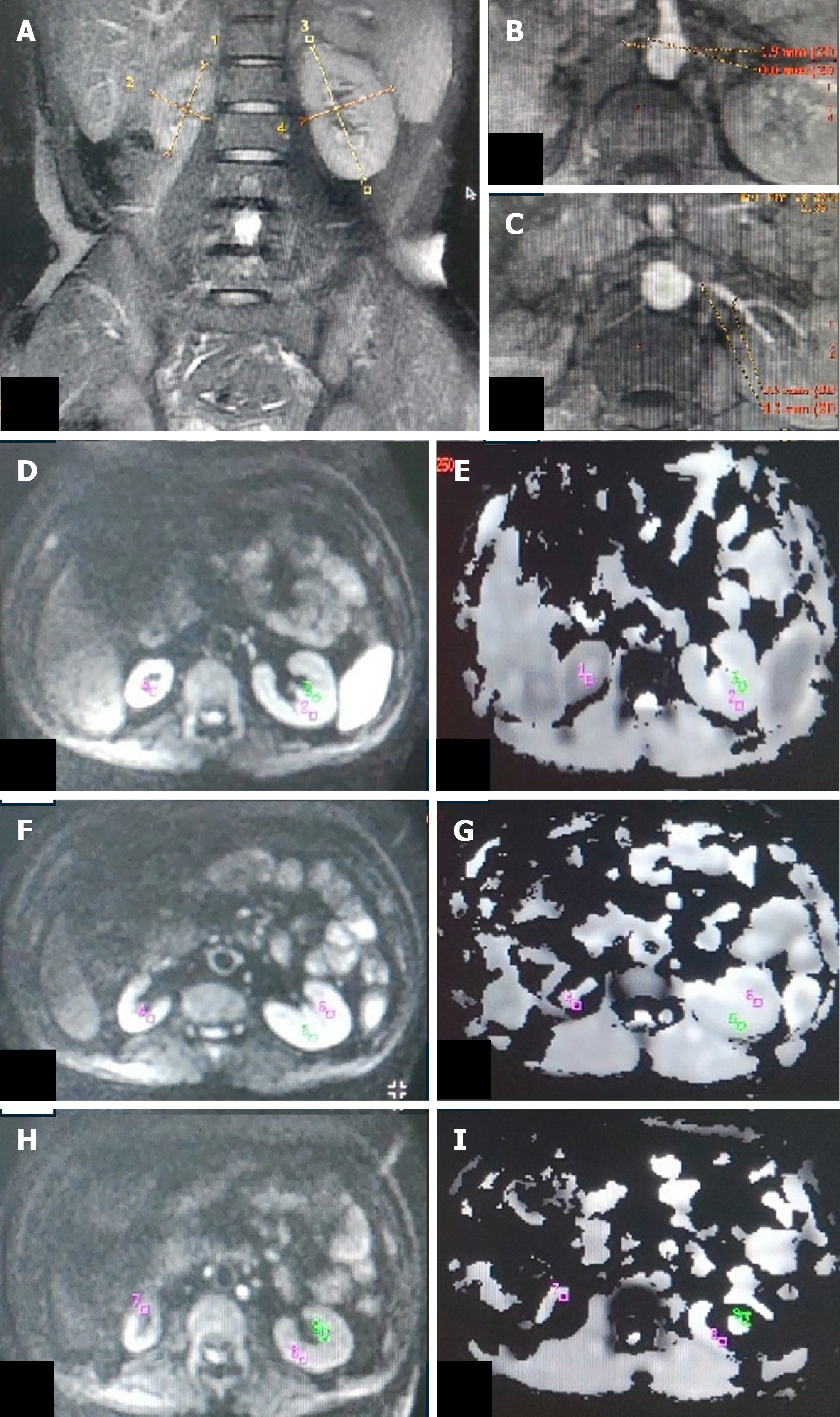
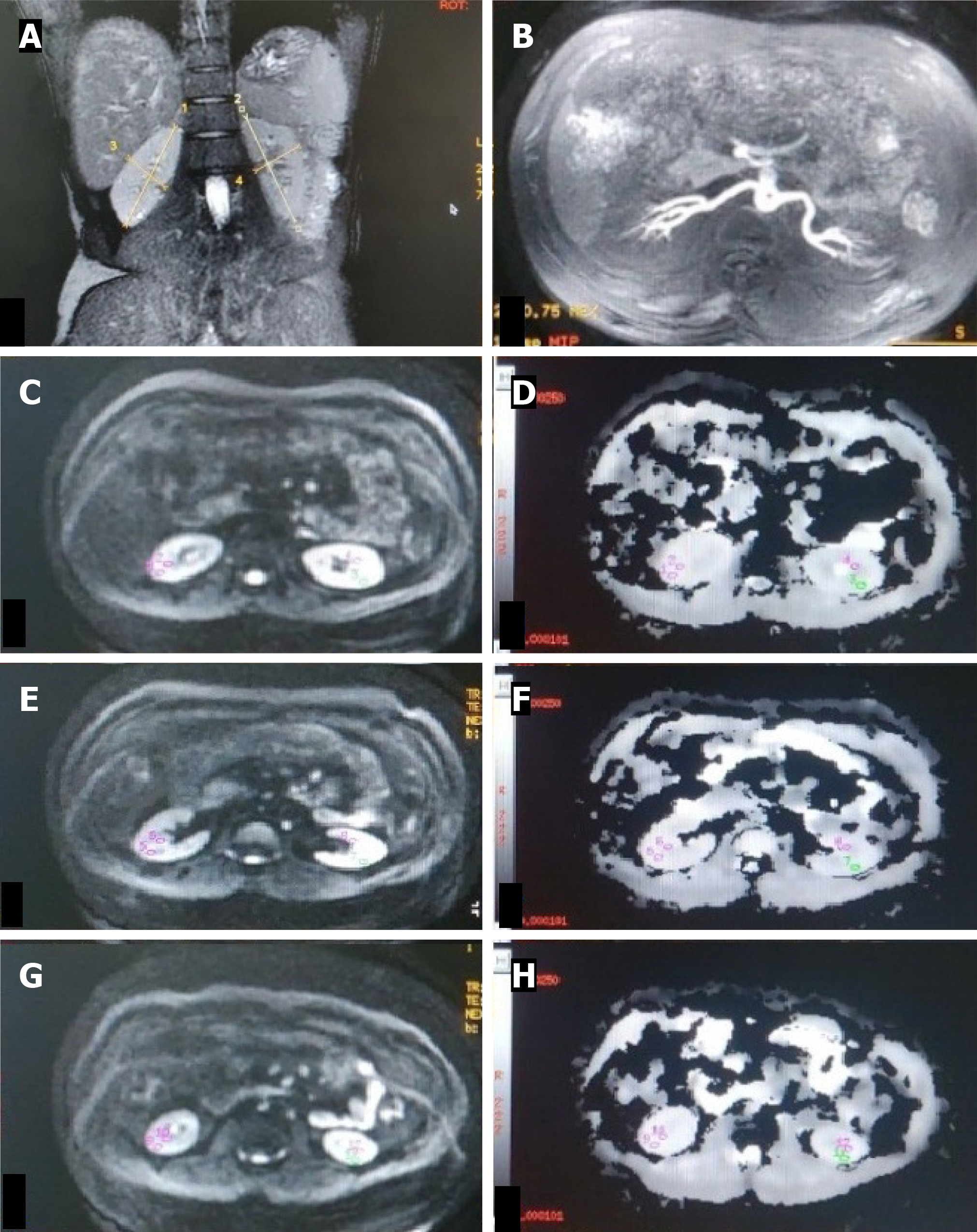
Figure 2 Bilateral renal artery stenosis.
A: T2W magnetic resonance (MR) image (coronal plane) showing atrophic right kidney (6.1 cm) and normal-sized left kidney (9.0 cm); B and C: Non-contrast MR angiography (INHANCE) in axial plane depicting diffuse stenosis of the right renal artery (B) and severe stenosis of the left renal artery at the ostium (C); D-I: Diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DW-MRI) image (D, F, H) in the axial plane with corresponding ADC map (E, G, I) of bilateral kidneys showing manually drawn region-of-interest (ROI) placed in the upper (D, E), middle (F, G) and lower (H, I) pole regions of the bilateral kidney. On the right side, as the kidney is atrophic, the ROI was placed in the corticomedullary region, whereas on the left, the ROI was placed separately in the cortex and medulla. Mean corticomedullary ADC of the right kidney was 1.19 × 10-3 mm2/s. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the left kidney were 169 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.76 × 10-3 mm2/s, respectively.
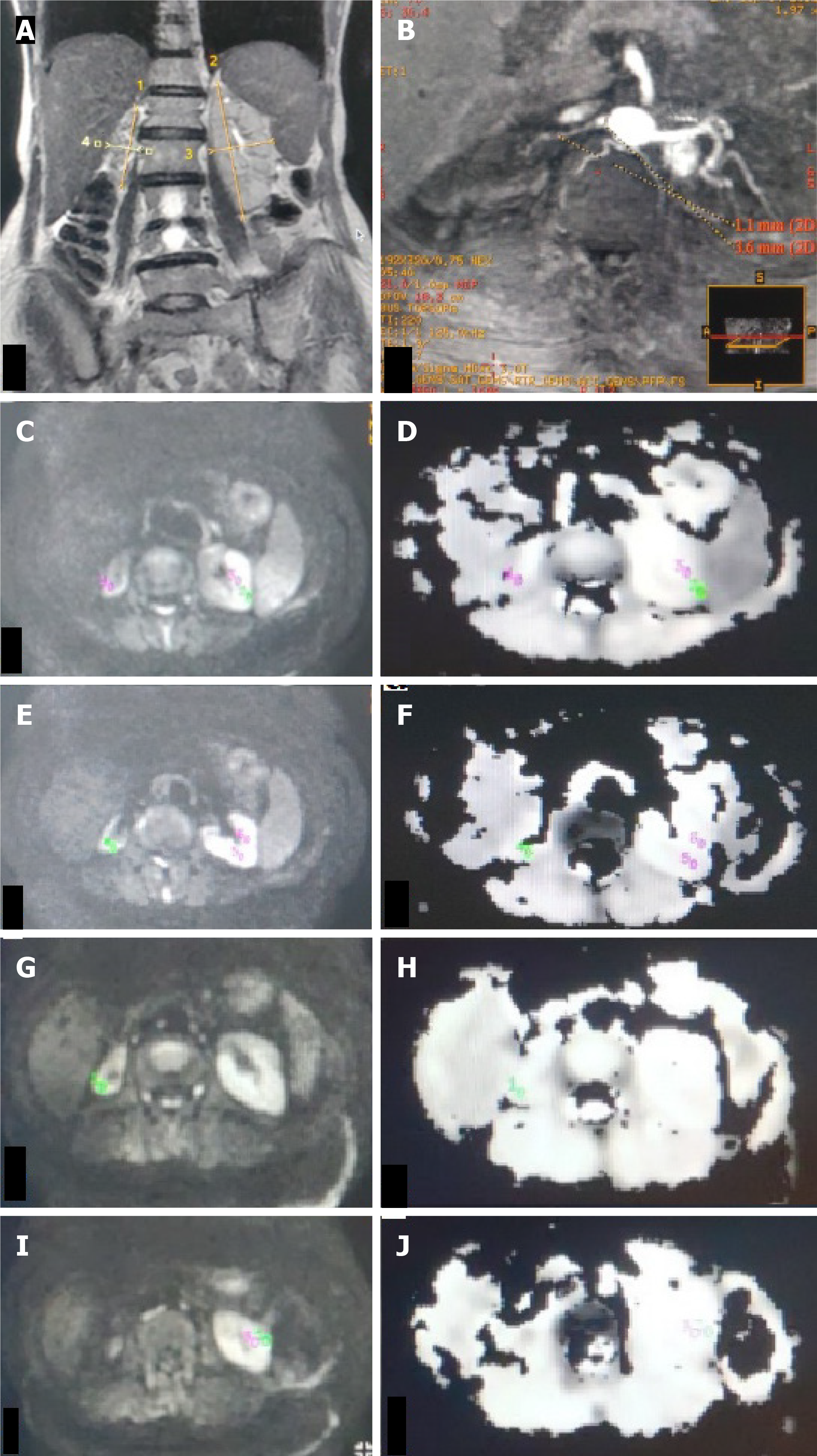
Figure 3 Unilateral renal artery stenosis with small-sized kidney.
A: T2W magnetic resonance image (MRI) (coronal plane) showing atrophic right kidney (4 cm) and normal-sized left kidney (9.4 cm); B: Non-contrast MR angiography (INHANCE) in axial plane depicting diffuse stenosis of right renal artery; C-J: DW MRI image (C, E, G, I) in the axial plane with corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (D, F, H, J) of bilateral kidneys showing manually drawn region-of-interest (ROI) placed in the upper (C, D), middle (E, F) pole of bilateral kidneys, lower (G, H) pole region of right kidney and lower (I, J) pole region of left kidney. On the right side, as the kidney is atrophic, the ROI was placed in the corticomedullary region, whereas on the left, the ROI was placed separately in the cortex and medulla. Mean corticomedullary ADC of the right kidney was 1.43 × 10-3 mm2/s. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the left kidney were 194 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.91 × 10-3 mm2/s, respectively.
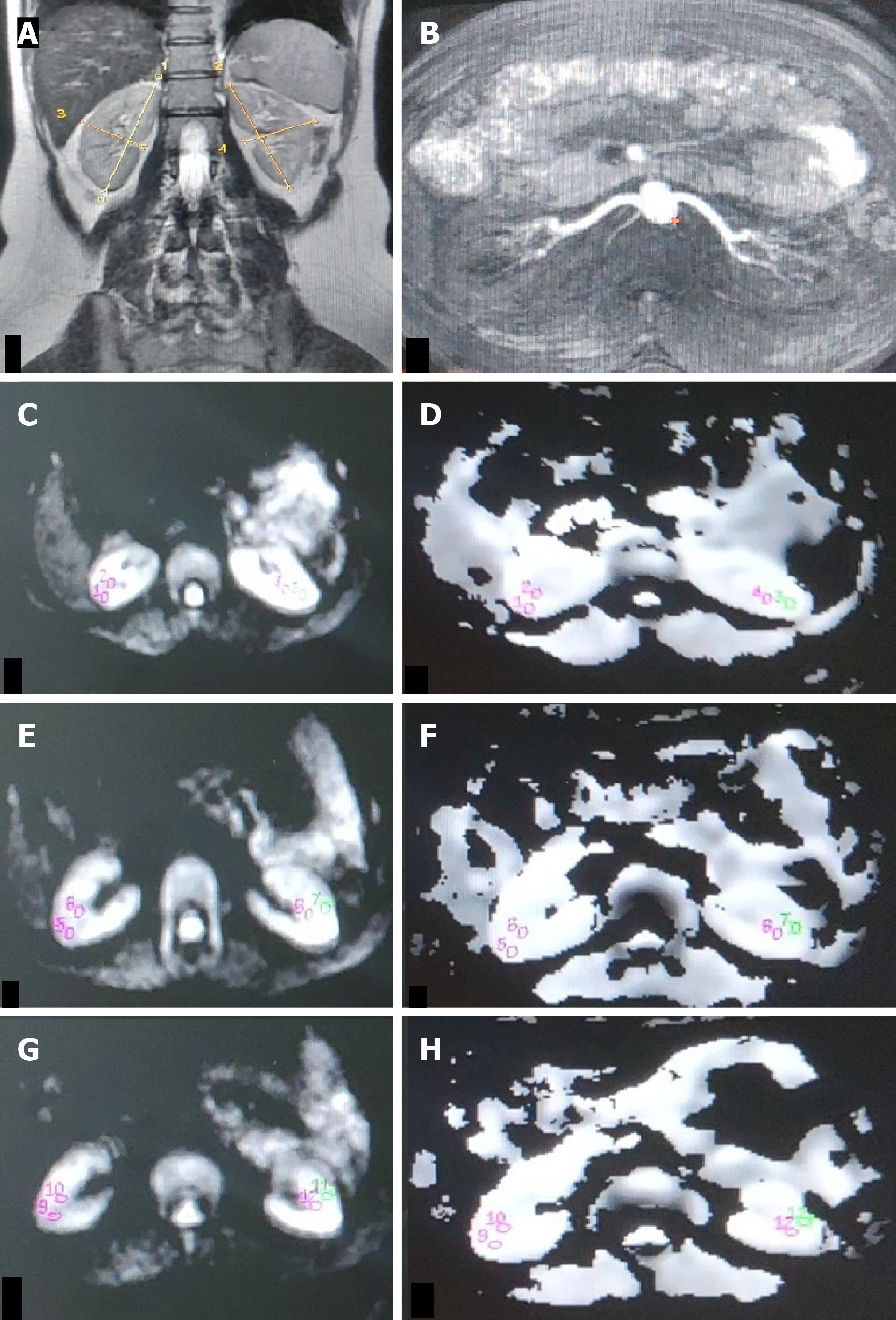
Figure 4 Hypertensive patient.
A: T2W magnetic resonance (MR) image (coronal plane) showing bilateral normal-sized kidneys (RK 8.9 cm, LK 8.9 cm); B: Non-contrast MR angiography (INHANCE) depicting bilateral normal renal arteries in the axial plane; C-H: Diffusion-weighted MR image (C, E, G) in the axial plane with corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (D, F, H) of bilateral kidneys showing manually drawn region-of-interest (ROI) placed in the upper (C, D), middle (E, F) and lower (G, H) pole regions of bilateral kidneys. The ROI is placed in the cortex and medulla on both sides. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the right kidney were 191 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.86 × 10-3 mm2/s. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the left kidney were 189 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.82 × 10-3 mm2/s, respectively.
Figure 5 Normal renal imaging.
A: T2W magnetic resonance (MR) image (coronal plane) showing bilateral normal-sized kidneys (RK 8.7 cm, LK 9.0 cm); B: Non-contrast MR angiography (INHANCE) depicting bilateral normal renal arteries in the axial plane; C-H: Diffusion-weighted MR image (C, E, G) in the axial plane with corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (D, F, H) of bilateral normal kidneys showing manually drawn region-of-interest (ROI) placed in the upper (C, D), middle (E, F) and lower (G, H) pole regions of bilateral kidneys. The ROI is placed in the cortex and medulla on both sides. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the right kidney were 589 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.82 × 10-3 mm2/s, respectively. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the left kidney were 19 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.85 × 10-3 mm2/s, respectively.
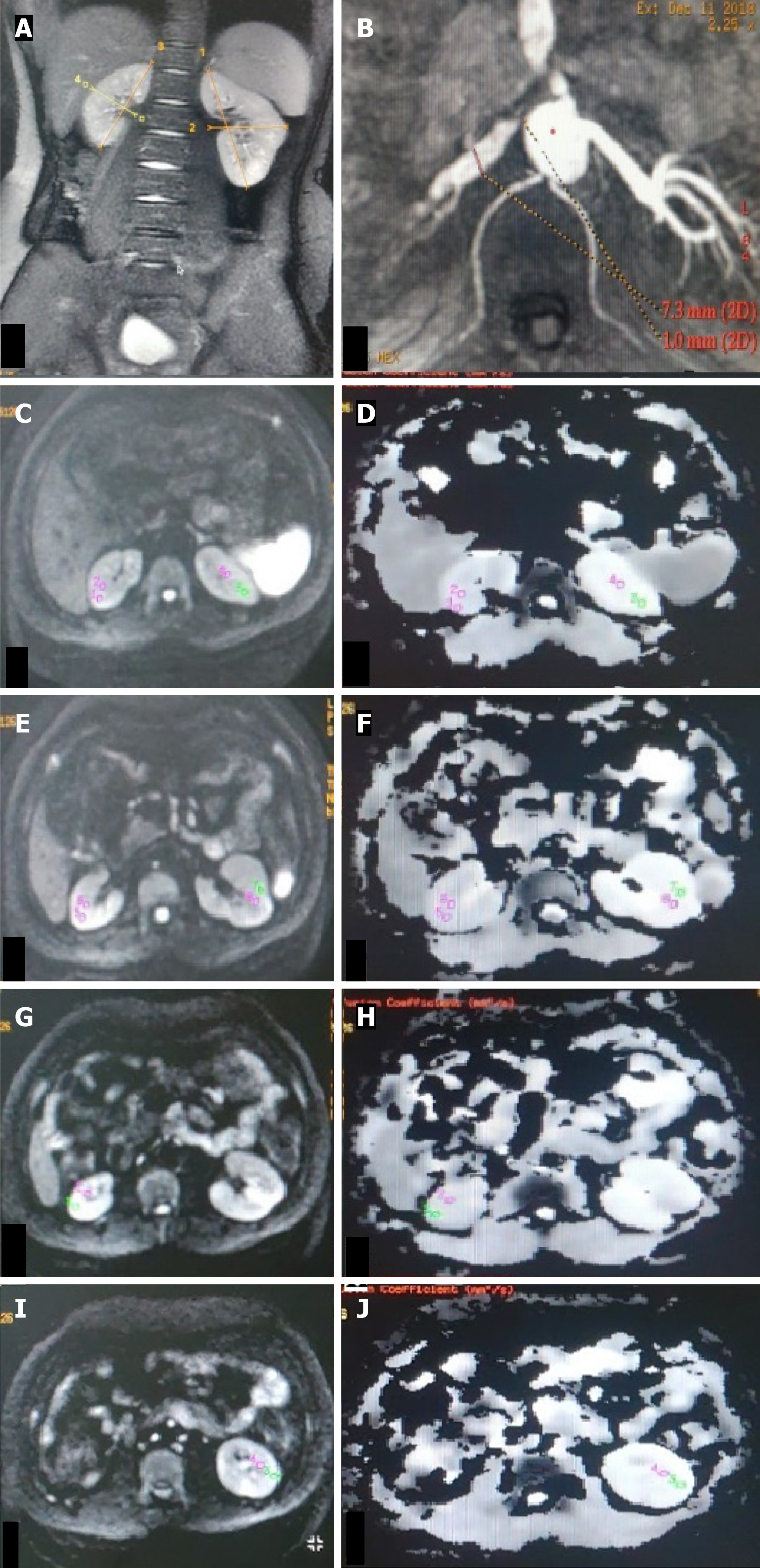
Figure 6 Unilateral renal artery stenosis with normal-sized kidney.
A: T2W magnetic resonance (MR) image (coronal plane) showing bilateral normal-sized kidneys (RK 8.6 cm, LK 10.7 cm); B: Non-contrast MR angiography (INHANCE ) in axial plane depicting severe right renal artery stenosis at the ostium; C-H: Diffusion-weighted MR image (C, E, G, I) in the axial plane with corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (D, F, H, J) of bilateral kidneys showing manually drawn region-of-interest (ROI) placed in the upper (C, D), middle (E, F) pole of bilateral kidneys, lower (G, H) pole of the right kidney and lower (I, J) pole region of left kidney. The ROI is placed in the cortex and medulla on both sides. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the right kidney were 165 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.63 × 10-3 mm2/s, respectively. Mean cortical ADC and medullary ADC values of the left kidney were 198 × 10-3 mm2/s and 1.84 × 10-3 mm2/s, respectively.
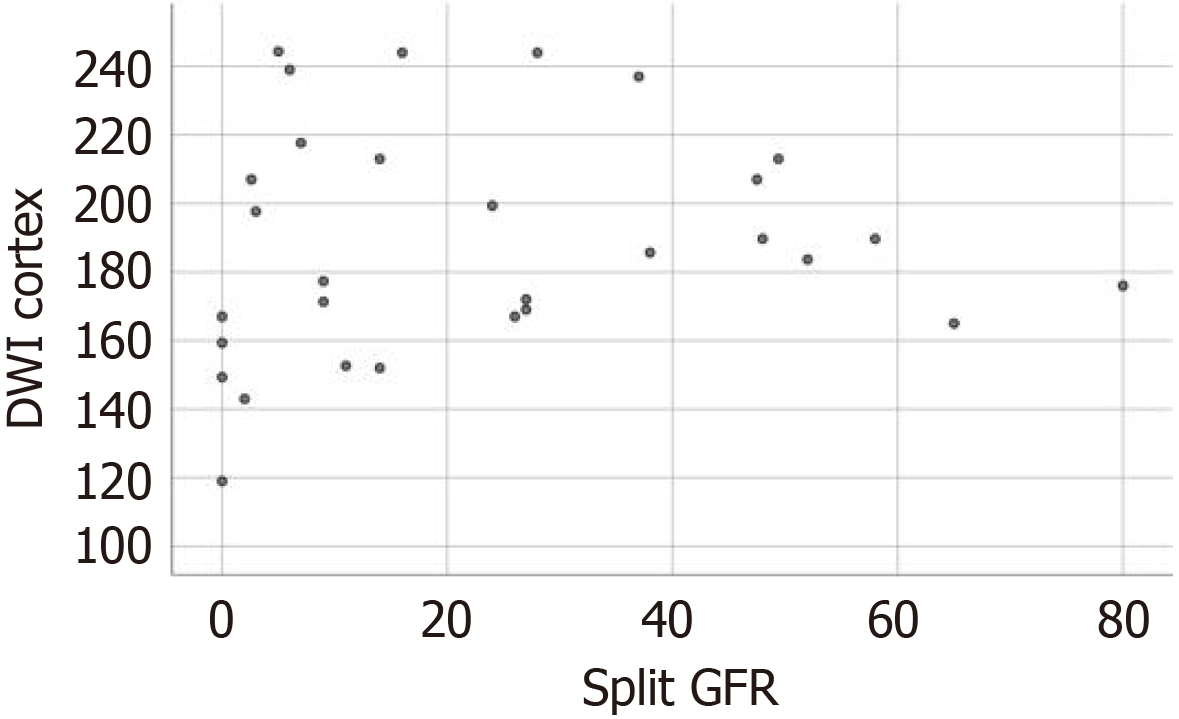
Figure 7 Scatter plot representing the relationship between renal apparent diffusion coefficient values (× 10-3 mm2/s) and the split GFR (mL/minute).
GFR: Glomerular filtration rate.
- Citation: Lal H, Agarwal S, Ponmalai K, Prasad R, Bhadauria DS, Gambhir S, Mandal S, Kumar S, Yadav P, Jowel P. Apparent diffusion coefficient of kidneys with non-contrast magnetic resonance angiography for functional and anatomical assessment in renal artery stenosis. World J Methodol 2026; 16(1): 107927
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v16/i1/107927.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v16.i1.107927