©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Methodol. Dec 20, 2025; 15(4): 105516
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105516
Published online Dec 20, 2025. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105516
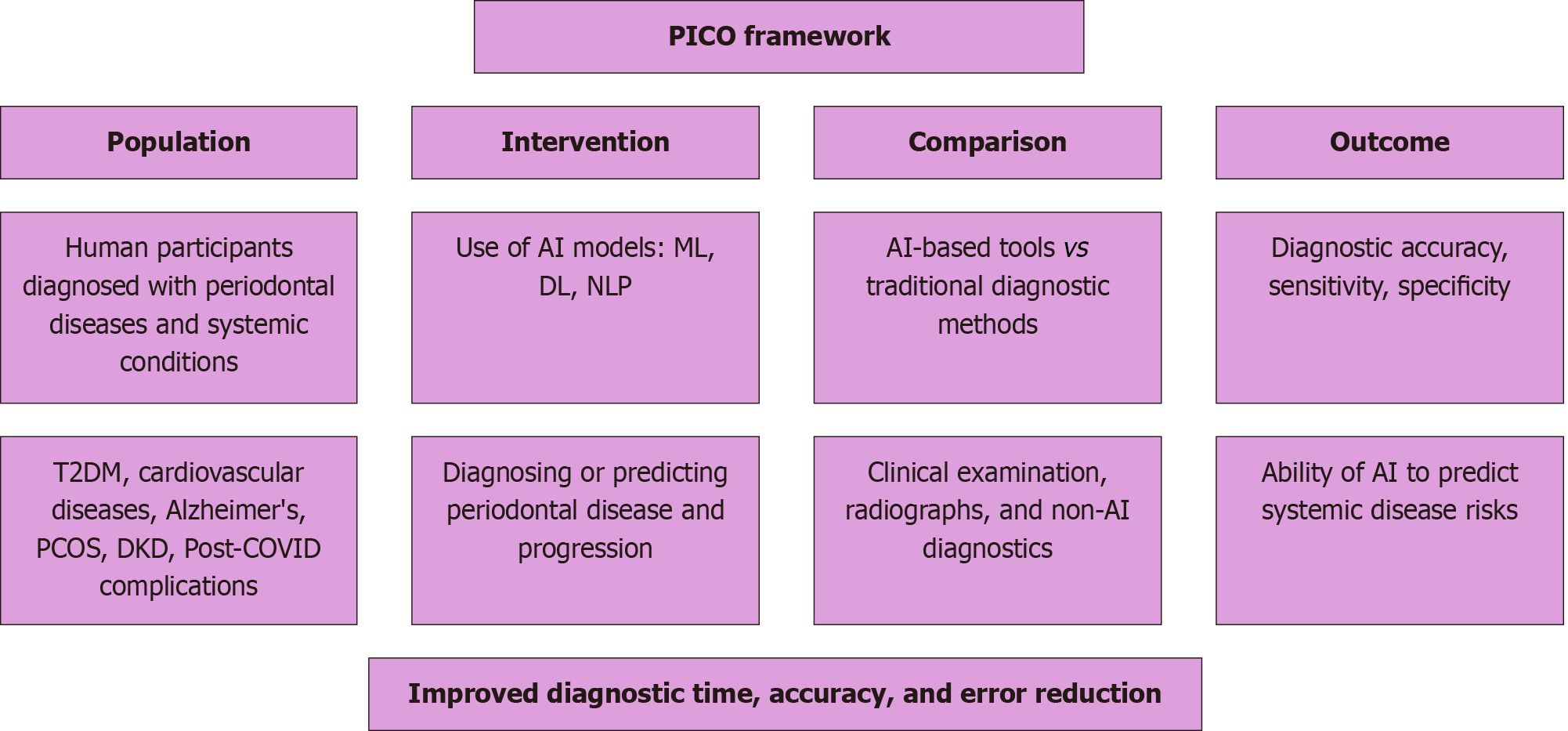
Figure 1 The Population, intervention, control, outcome and study design framework for systematic review.
PICO: Population, intervention, control, outcome; AI: Artificial intelligence; ML: Machine learning; DL: Deep learning; NLP: Natural language processing; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus; PCOS: Polycystic ovary syndrome; DKD: Diabetic kidney disease; COVID: Coronavirus disease.
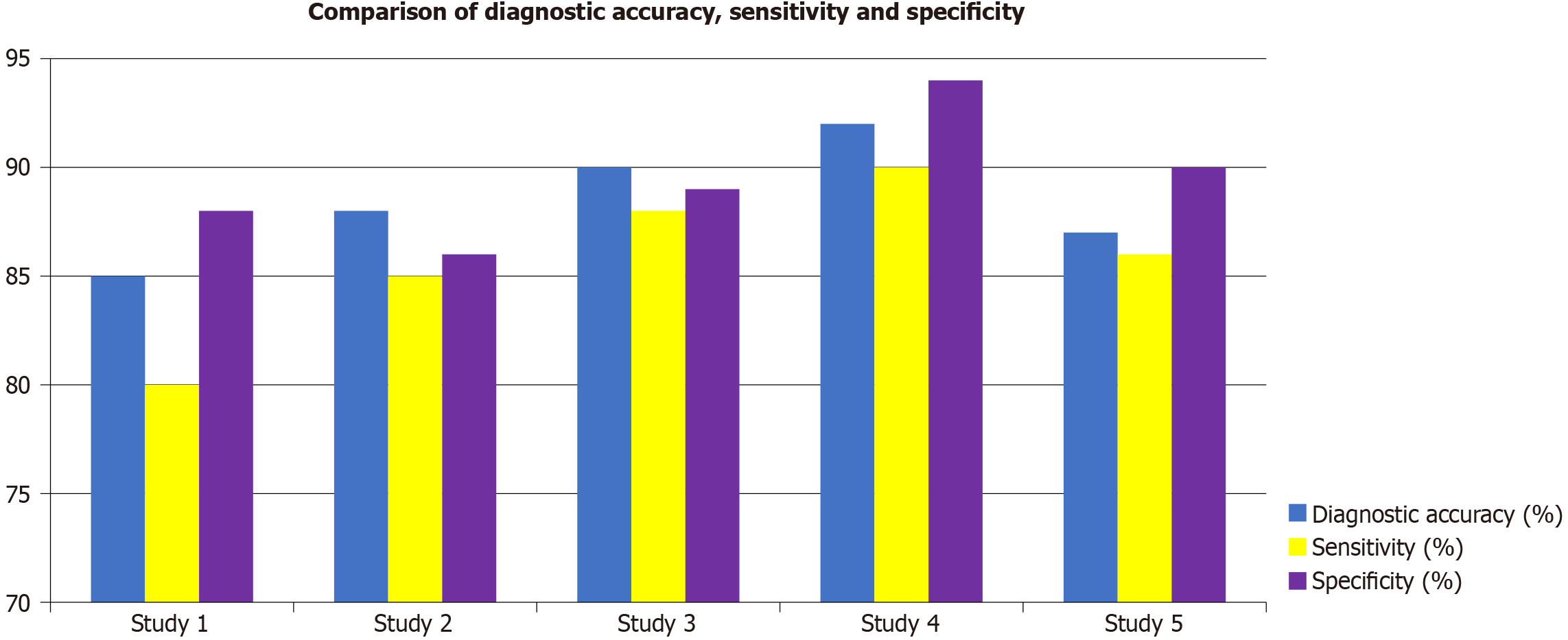
Figure 2
Comparison of diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity across five studies.
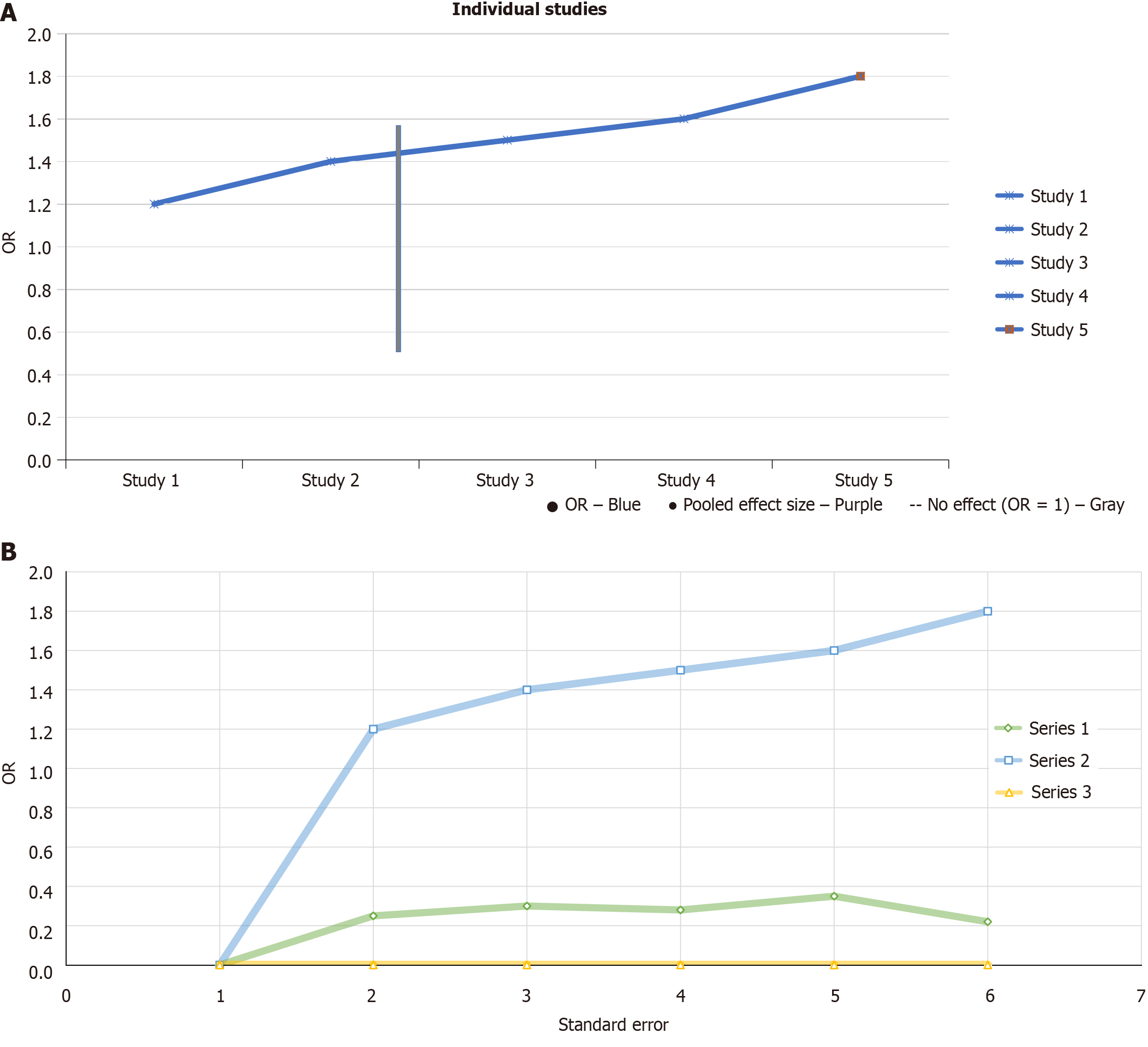
Figure 3 Artificial intelligence model of periodontal system interaction.
A: Forest plot of artificial intelligence models for periodontal-systemic interactions. Forest plot illustrating the odds ratios for individual studies and the pooled effect size in diagnosing periodontal-systemic interactions. The vertical dashed line represents no effect (odds ratios = 1), with confidence intervals shown by horizontal lines; B: Scatter plot visualizing publication bias in artificial intelligence models for diagnosing periodontal-systemic interactions. OR: Odds ratios.
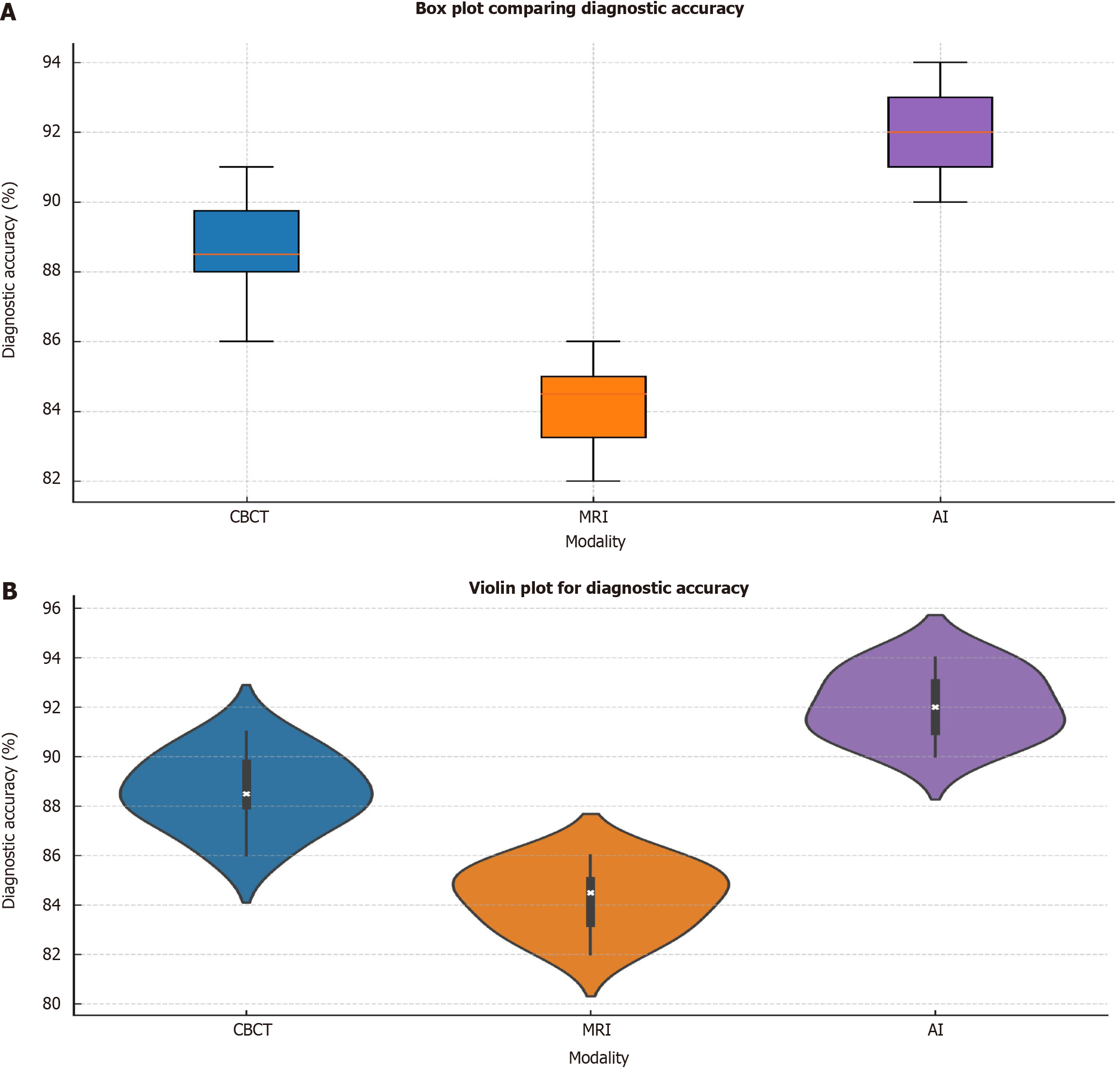
Figure 4 Diagnostic accuracy of cone beam computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and artificial intelligence models.
A: Box plot comparing diagnostic accuracy across cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and artificial intelligence (AI) modalities. This highlighting the median, interquartile range, and variability for each. AI shows the highest median accuracy, with CBCT and MRI showing lower but similar accuracy levels; B: Violin plot showing the distribution of diagnostic accuracy across CBCT, MRI, and AI modalities. CBCT: Cone beam computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; AI: Artificial intelligence.
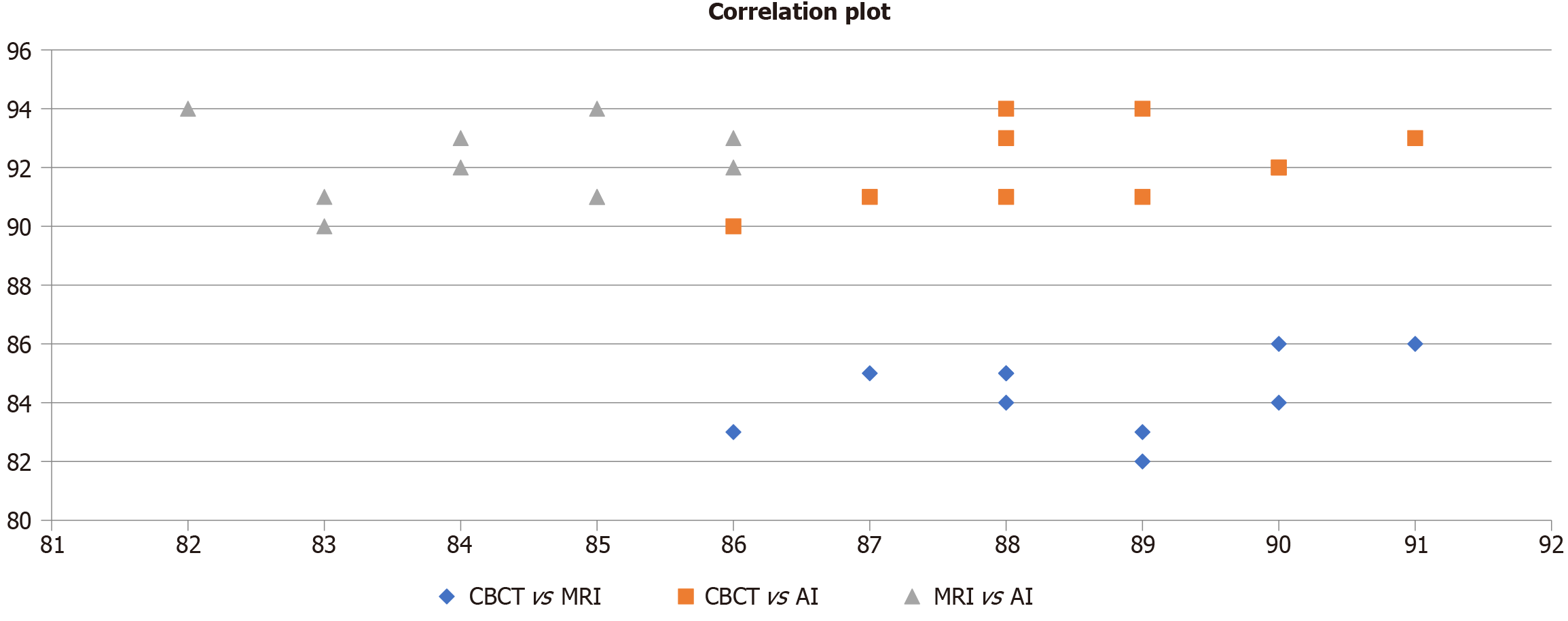
Figure 5 Correlation between diagnostic accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity across cone beam computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and artificial intelligence modalities.
CBCT: Cone beam computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; AI: Artificial intelligence.
- Citation: Das N, Gade KR, Addanki PK. Artificial intelligence for early diagnosis and risk prediction of periodontal-systemic interactions: Clinical utility and future directions. World J Methodol 2025; 15(4): 105516
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v15/i4/105516.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v15.i4.105516