©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Nephrol. Sep 25, 2025; 14(3): 107582
Published online Sep 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i3.107582
Published online Sep 25, 2025. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v14.i3.107582
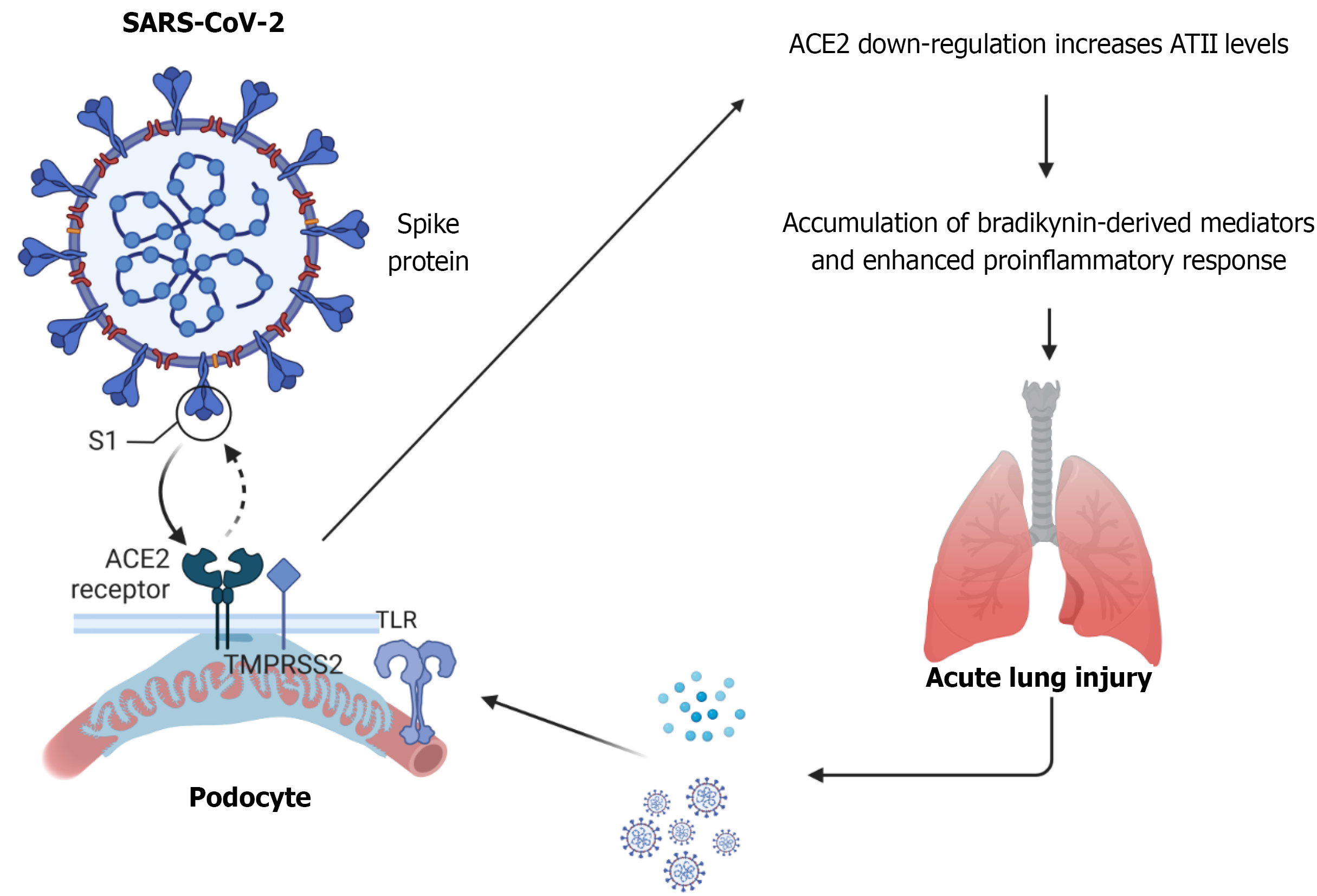
Figure 1 Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike (S1) protein binds to the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor on the surface of podocytes.
The transmembrane serine protease 2 facilitates viral entry by cleaving S1. Viral internalization leads to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) degradation, reducing its ability to convert angiotensin (AT)II into Ang 1-7. This results in excess ATII, which is associated with proinflammatory and vasoconstrictive effects. ACE2 downregulation promotes accumulation of bradykinin-derived mediators, further enhancing inflammation. ATII: A key component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. ATII induces inflammatory cascades by increasing adhesion molecules, cytokines, and chemokines release; it also promotes reactive oxygen species production, cell growth, and extracellular matrix remodeling. ATII/AT1R pathway activates protein phosphatase 2A, which in turn downregulates endothelial NO synthase phosphorylation, decreasing levels of NO and leading to endothelial dysfunction. Kinins, such as bradykinin (BK) and kallidin: Bioactive proinflammatory peptides that are released by kallikreins (serum proteases) from their precursors, kininogens, following tissue injury. ACE2: Inhibits conversion of ATII into Ang 1-7, and blocks breakdown of des-Arg9 bradykinin (des-Arg9 BK, an active metabolite of BK) into inactive fragments. Des-Arg9 BK exerts its biological effects, mainly the release of proinflammatory cytokines and recruitment of immune cells, as well as the increase in vascular permeability, by activating B1 receptors. The inflammatory response extends beyond the kidneys, contributing to acute lung injury, a key complication of severe coronavirus disease 2019. Infected lung cells release viral particles and inflammatory cytokines, which enter circulation and exacerbate systemic inflammation. These circulating factors further stimulate toll-like receptors on podocytes, triggering innate immune responses, inflammation and kidney injury. SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
- Citation: Gembillo G, Peritore L, Spadaro G, Cuzzola F, Calderone M, Messina R, Di Piazza S, Sudano F, Gambuzza ME, Princiotto M, Soraci L, Santoro D. Kidney involvement and anemia in COVID-19 infection. World J Nephrol 2025; 14(3): 107582
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v14/i3/107582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v14.i3.107582