©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2025; 14(3): 103347
Published online Sep 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i3.103347
Published online Sep 25, 2025. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v14.i3.103347
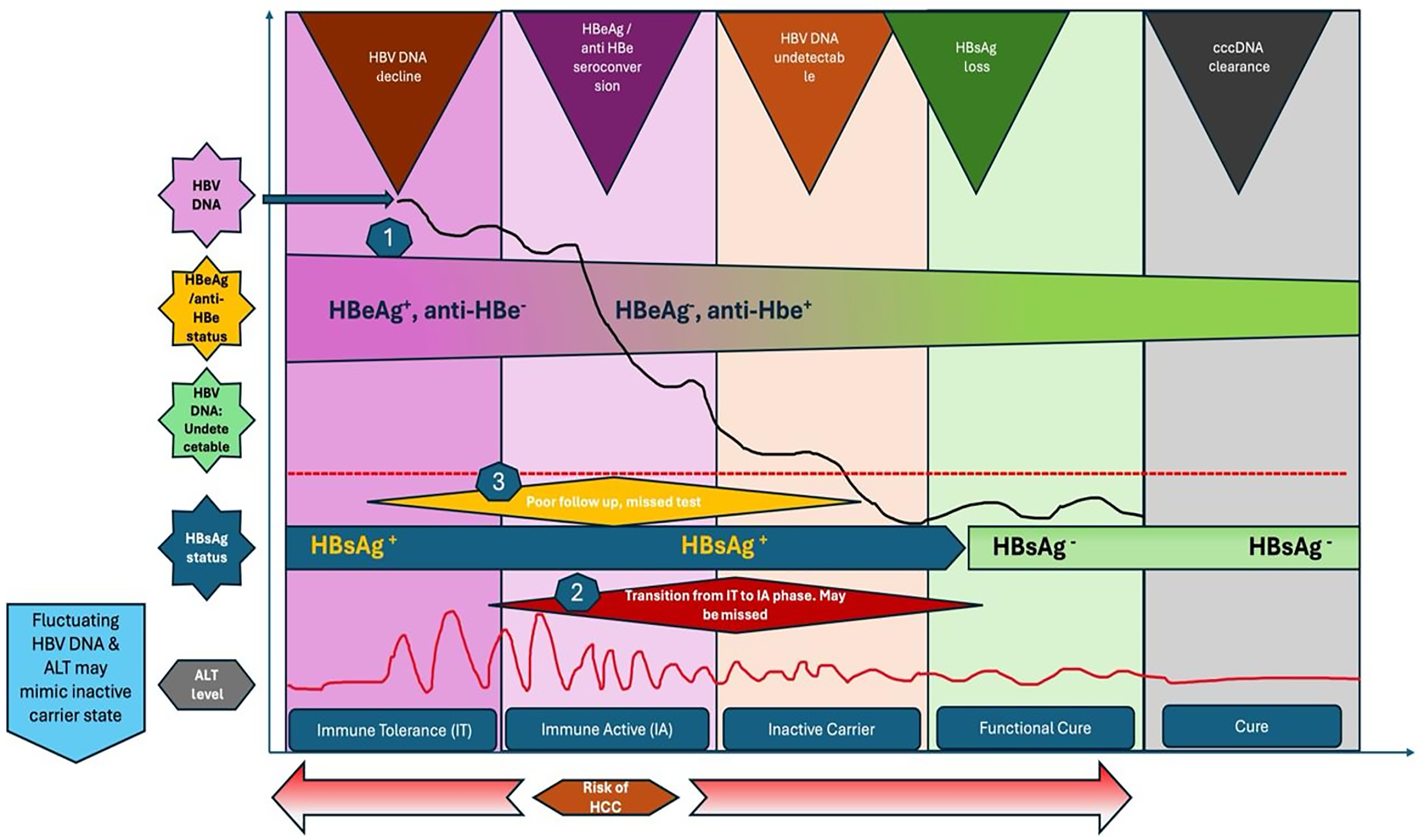
Figure 1 The natural history of hepatitis B virus presents certain challenges related to clinical management and treatment.
Key concerns include: (1) Variations in hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA levels during the inactive (immune tolerant) phase, which can lead to missed treatment opportunities; (2) Difficulty in identifying the transition from the inactive (immune tolerant) phase to the active (immune active) phase, increasing the risk of reactivation and clinical flare-ups; and (3) Inadequate follow-up and testing can elevate the risk of undetected hepatocellular carcinoma. These factors emphasize the importance of vigilant monitoring and timely intervention in the management of HBV. IT: Immune tolerant; IA: Immune active; ALT: Alanine aminotransaminase; HCC: Hepatocellular cancer; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HBeAg: Hepatitis B e antigen; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen.
- Citation: Manrai M, Jha AA, Pachisia AV, Dawra S. Chronic hepatitis B: Is it time for expanded antiviral treatment? World J Virol 2025; 14(3): 103347
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v14/i3/103347.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v14.i3.103347