©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Transplant. Mar 18, 2026; 16(1): 114367
Published online Mar 18, 2026. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.114367
Published online Mar 18, 2026. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.114367
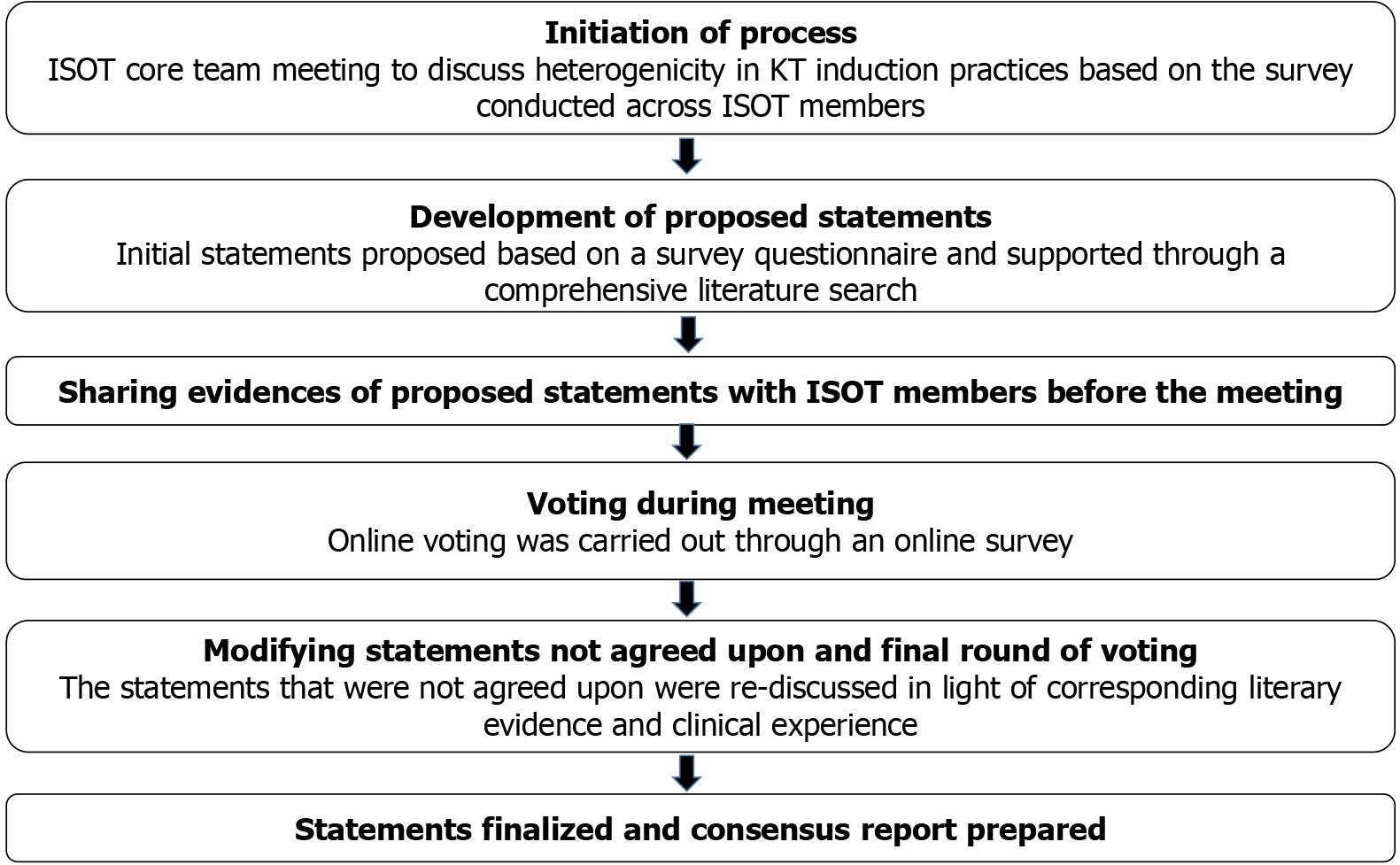
Figure 1 The modified Delphi process followed for formulating the consensus[8].
ISOT: Indian Society of Organ Transplantation; KT: Kidney trans
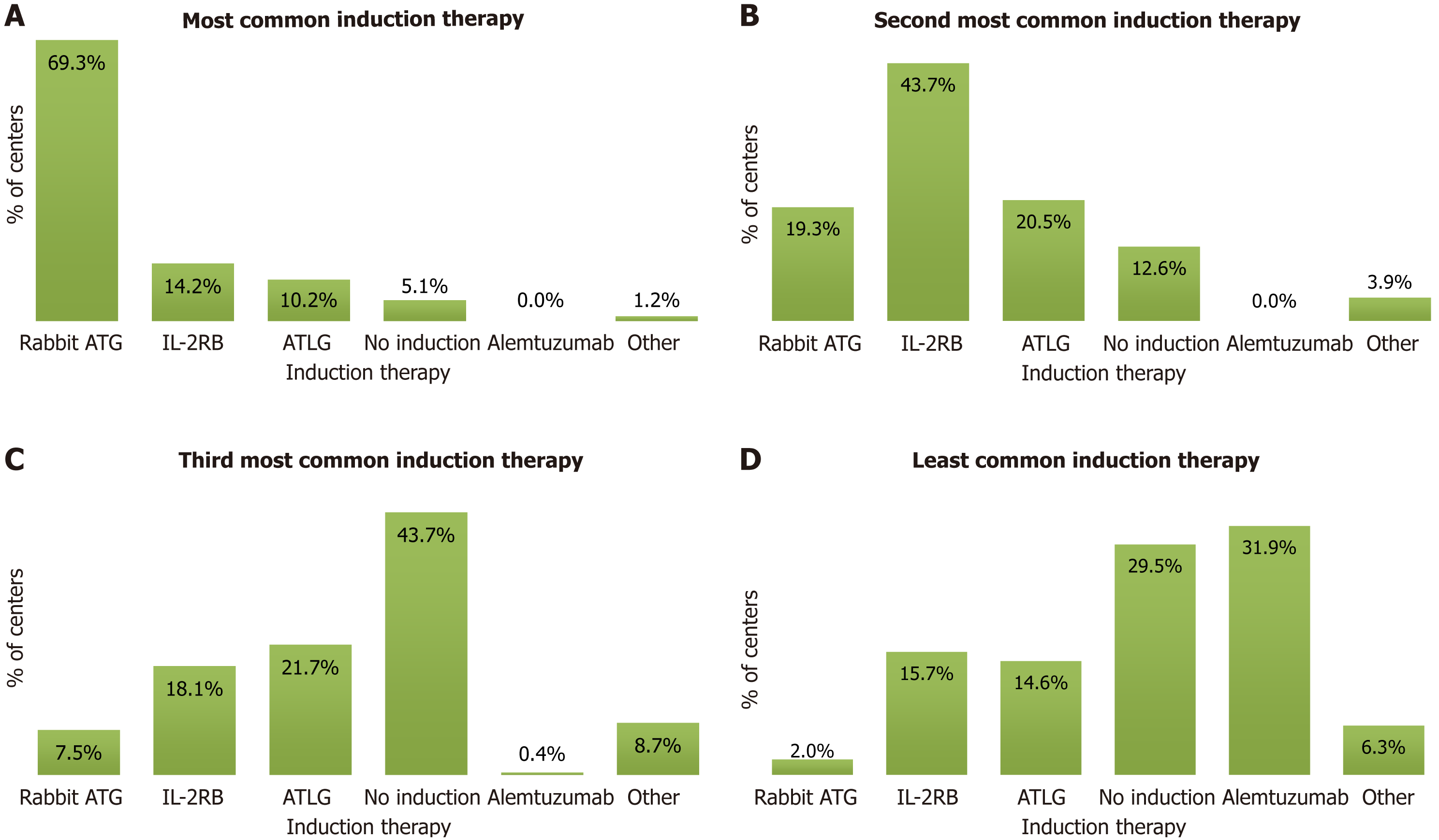
Figure 2 Distribution of induction therapy practices among kidney transplant centers in India.
A-D: Survey responses to the query regarding the most common (A), second most common (B), third most common (C), and least common (D) induction therapies used by kidney transplant centers across India. ATG: Anti-thymocyte globulin; IL-2RA: Interleukin-2 receptor antagonist; ATLG: Anti-T-lymphocyte globulin.
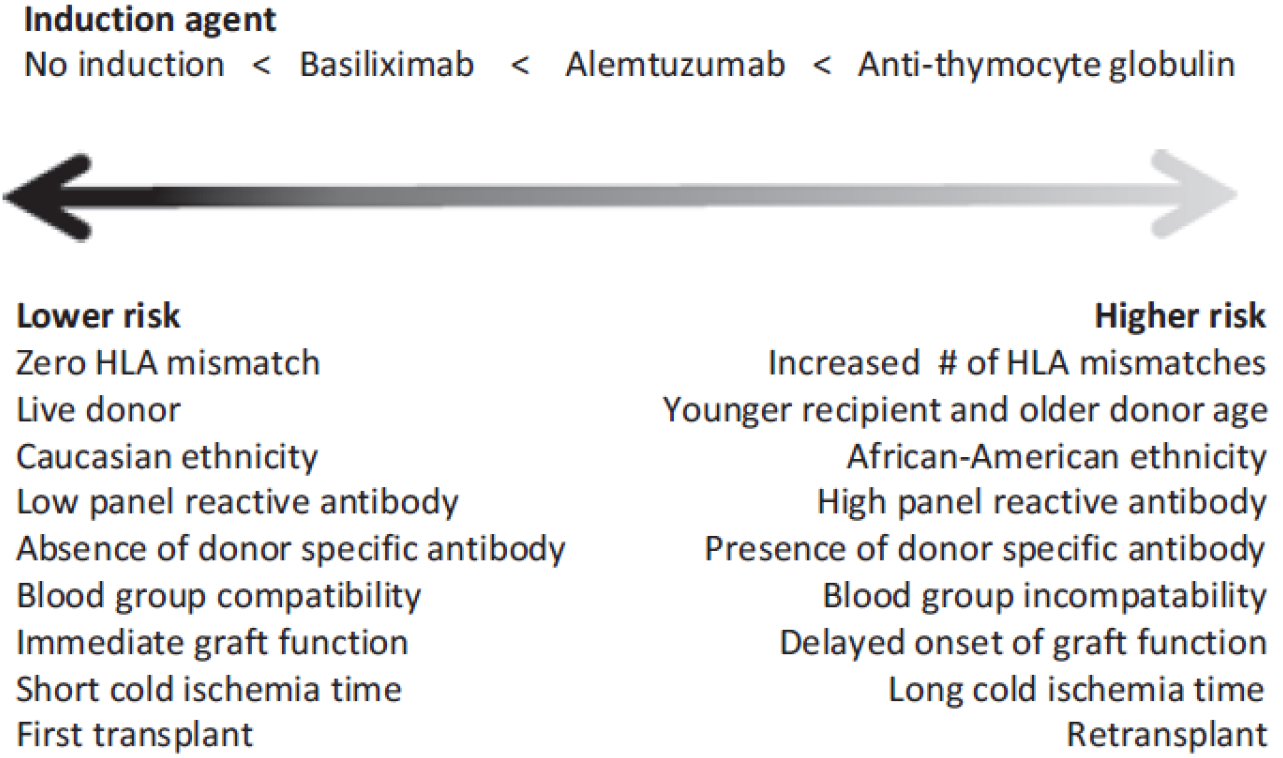
Figure 3 Preferred induction therapy based on immunological risk assessment[7].
HLA: Human leucocyte antigen.
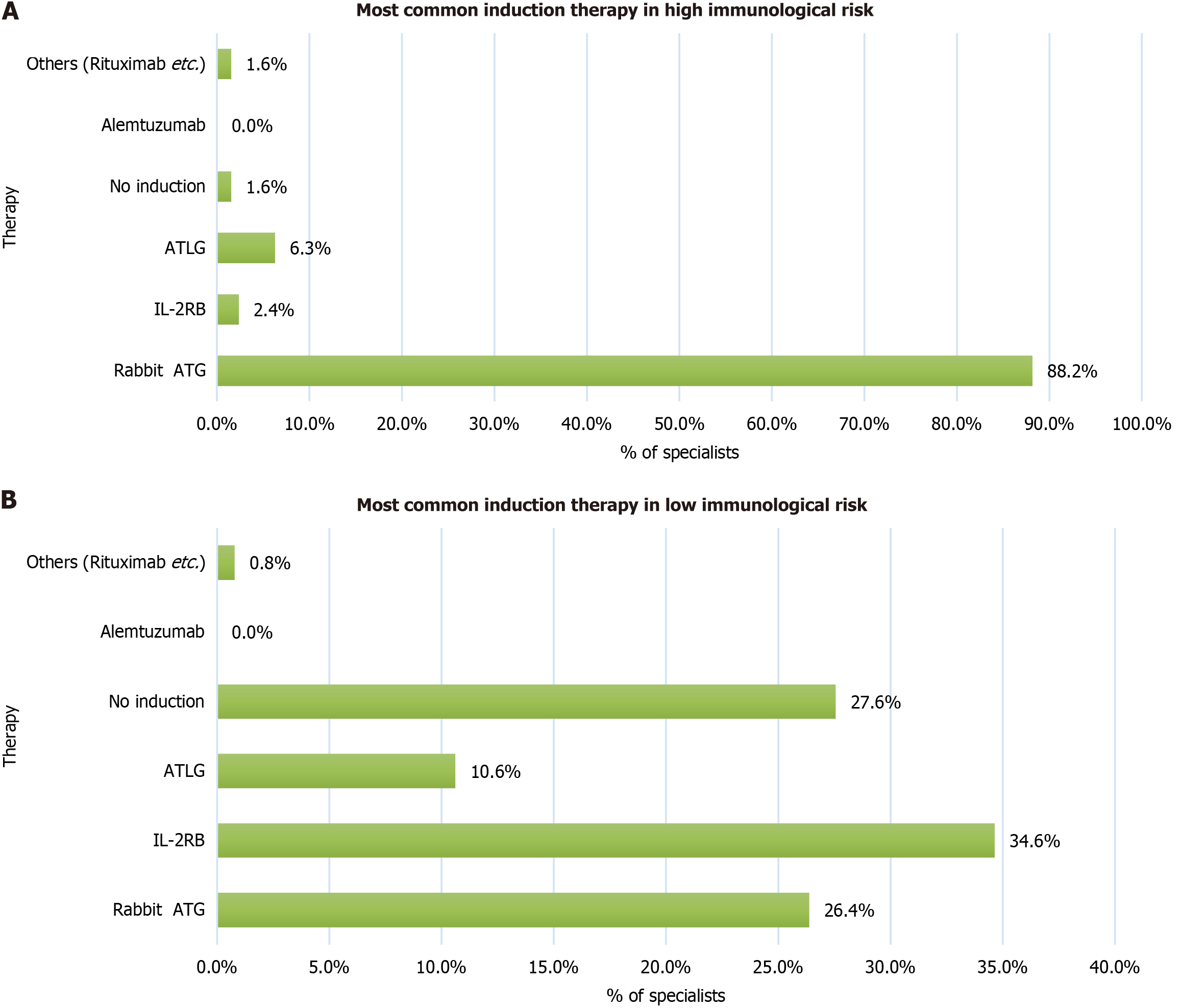
Figure 4 Preferred induction therapy by immunologic risk category.
A and B: Induction therapy preferred by specialists for recipients with high (A) and low (B) immunological risk. ATLG: Anti-human-T-lymphocyte immunoglobulin; IL-2RB: Interleukin-2 receptor anatagonists; ATG: Anti-thymocyte globulin.
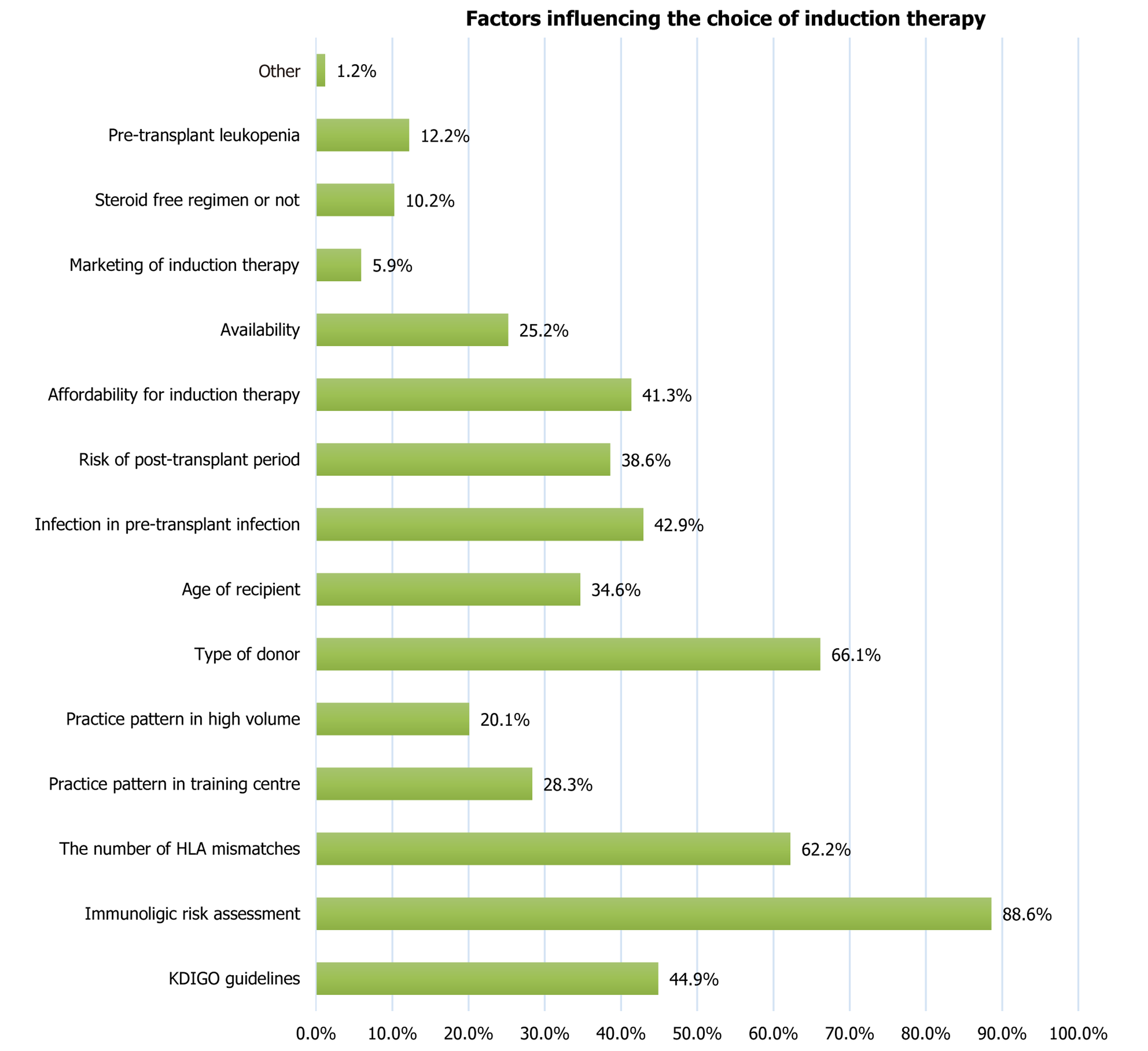
Figure 5 Factors influencing the choice of induction therapy.
HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; KDIGO: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes.
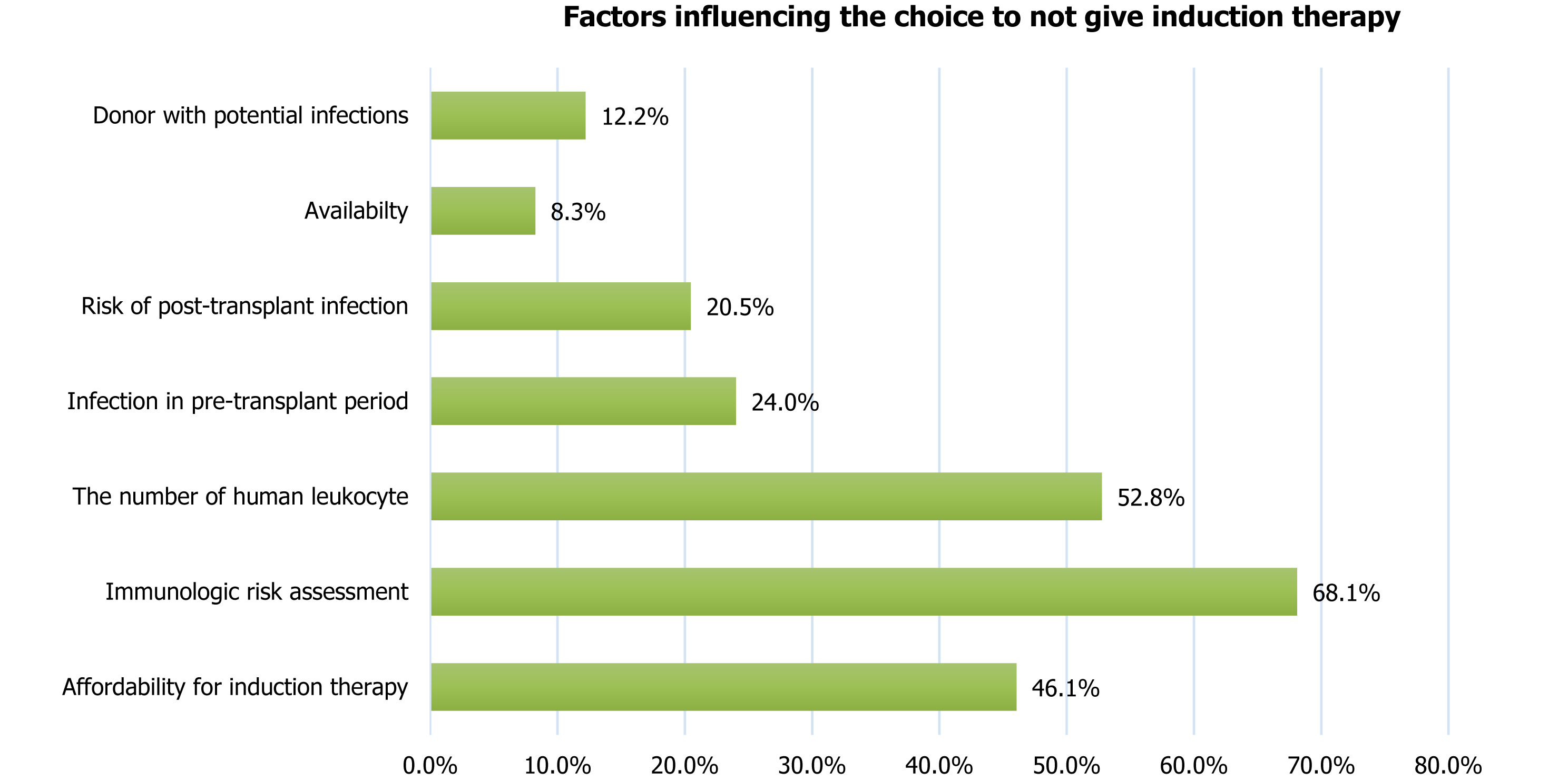
Figure 6
Factors considered by centers before deciding not to give induction therapy.
- Citation: Kute VB, Balwani MR, Shrimali JB, Pasari A, Kher V, Patel MP, Chafekar D, Guditi S, Das P, Siddaiah GM, Godara SM, Bhargava V, Gupta A, Ramteke V, Deshpande N, Tolani P, Prasad N, Patil RK, Mohanka R, Mahajan S, Sharma S, Banerjee S, Engineer DP, Agarwal D, Kashiv P, Lahiri A, Khullar D, Srivastava A. Induction therapy in kidney transplant recipients: A consensus statement of Indian Society of Organ Transplantation. World J Transplant 2026; 16(1): 114367
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v16/i1/114367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.114367