©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Transplant. Mar 18, 2026; 16(1): 114162
Published online Mar 18, 2026. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.114162
Published online Mar 18, 2026. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.114162
Figure 1
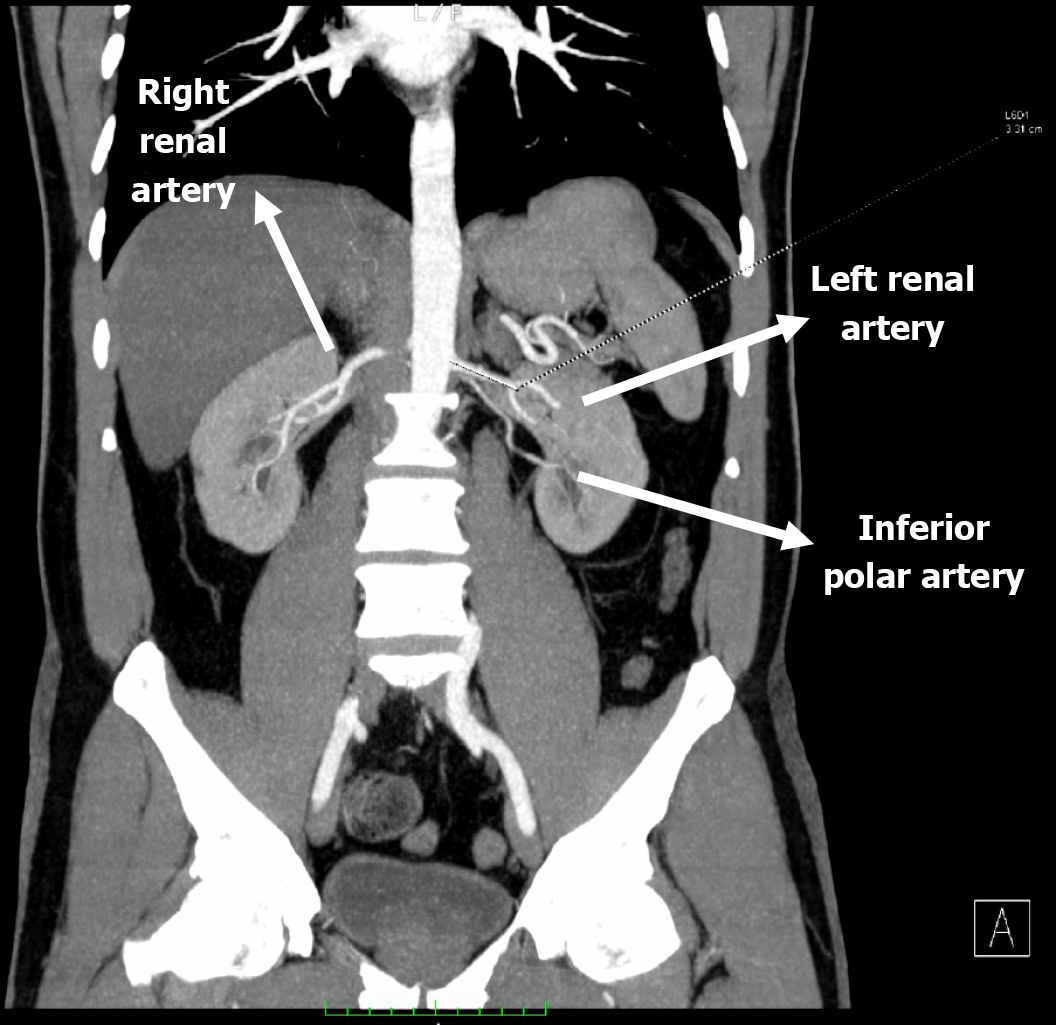
Computed tomography angiography scan depicted the anatomical configuration of the donor renal arteries.
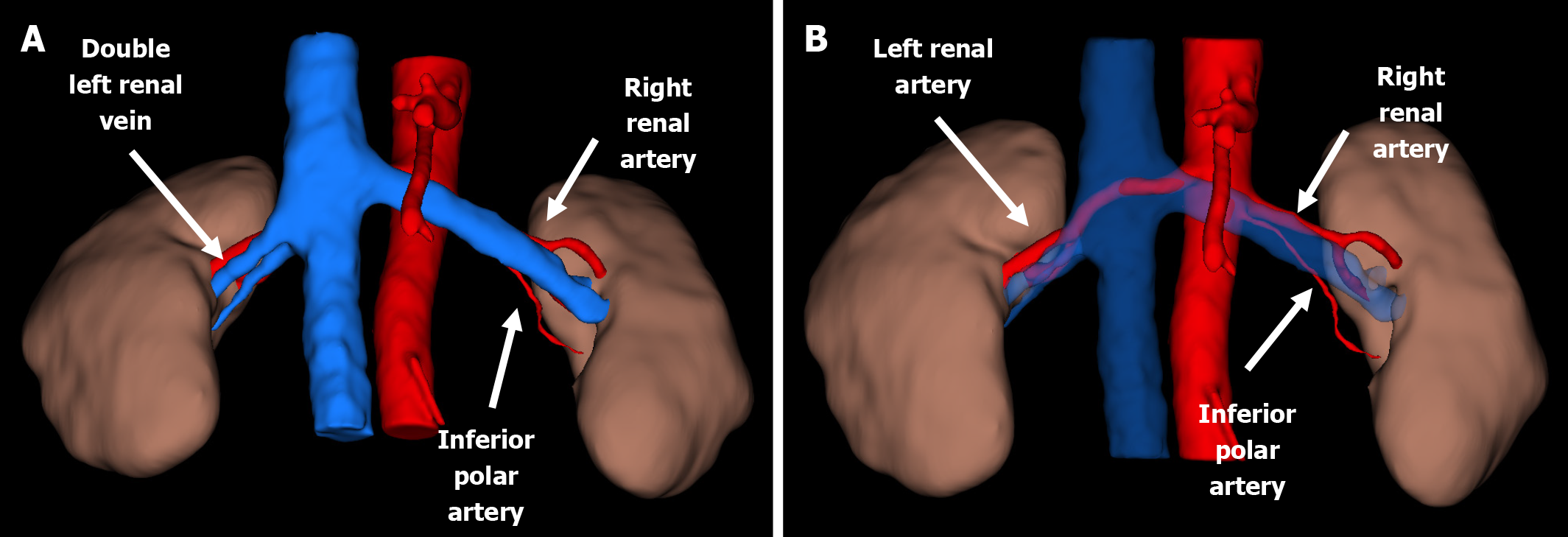
Figure 2 Three-dimensional reconstruction of computed tomography angiography illustrating the anatomical configuration of the donor renal arteries.
A: Anterior view; B: Anterior view with the left renal vein digitally removed to highlight the left renal arteries.
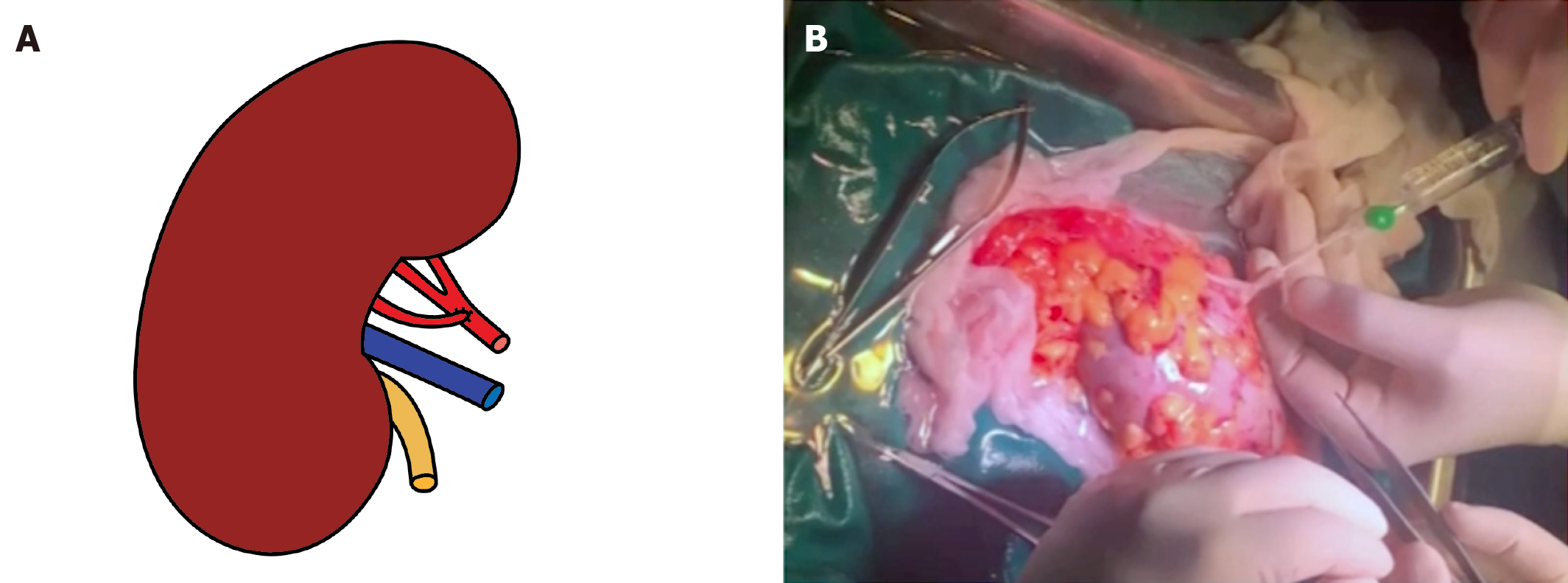
Figure 3 Back-table preparation showed transposition of the inferior polar artery into the main renal artery.
A: Schematic Illustration; B: Perioperative image.
Figure 4
Anatomical configuration of the renal allograft in the right iliac fossa, showing end-to-side anastomosis of the renal vein to the external iliac vein and end-to-side anastomose of the main renal artery to the external iliac artery.
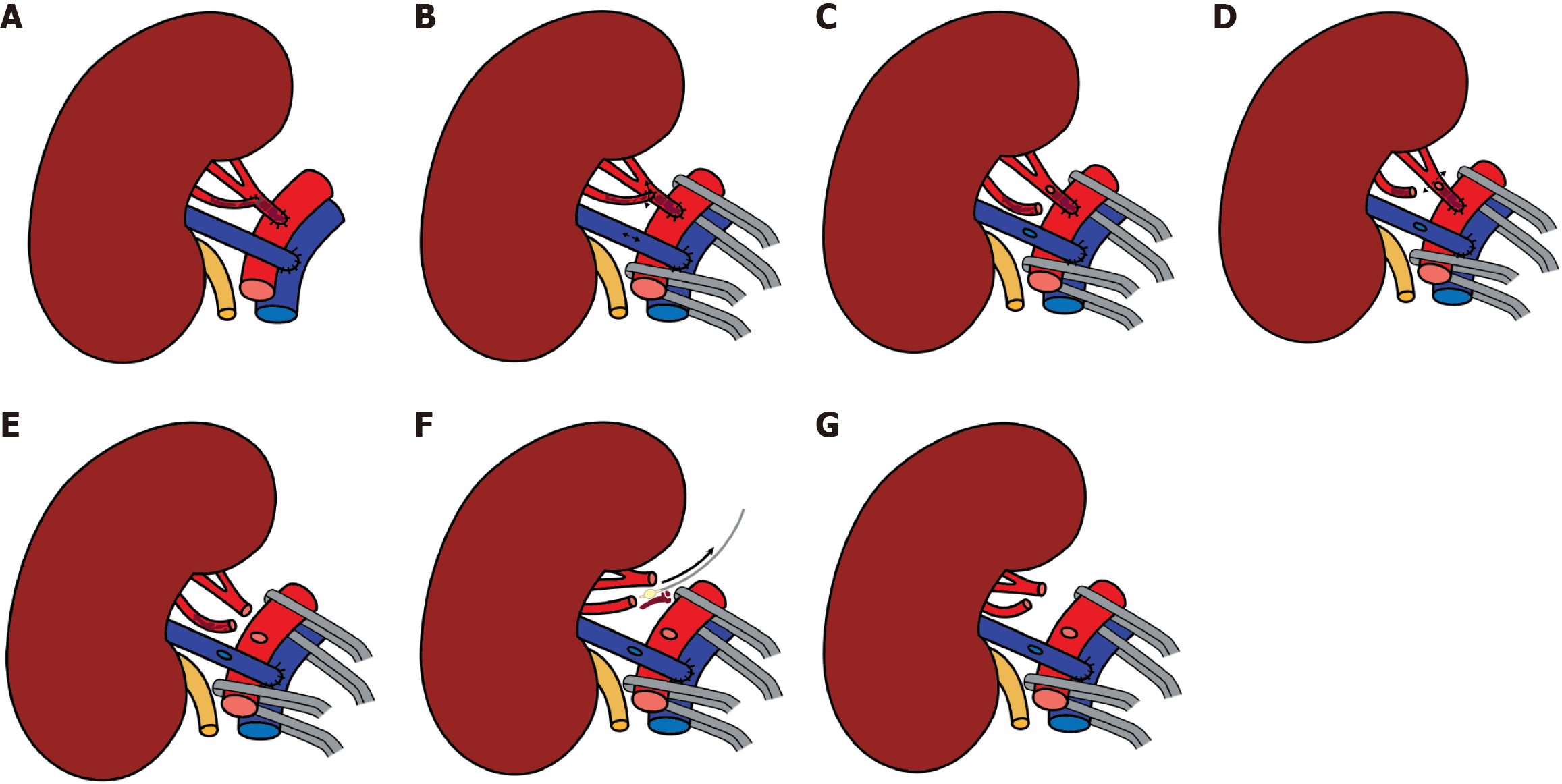
Figure 5 Steps of arterial thrombectomy of the main and inferior polar renal arteries.
A: Thrombosed principal and accessory renal arteries; B-D: Dismantling of the arterial anastomosis; E and F: Thrombectomy of both arteries; G: Renal arteries cleared of thrombus.
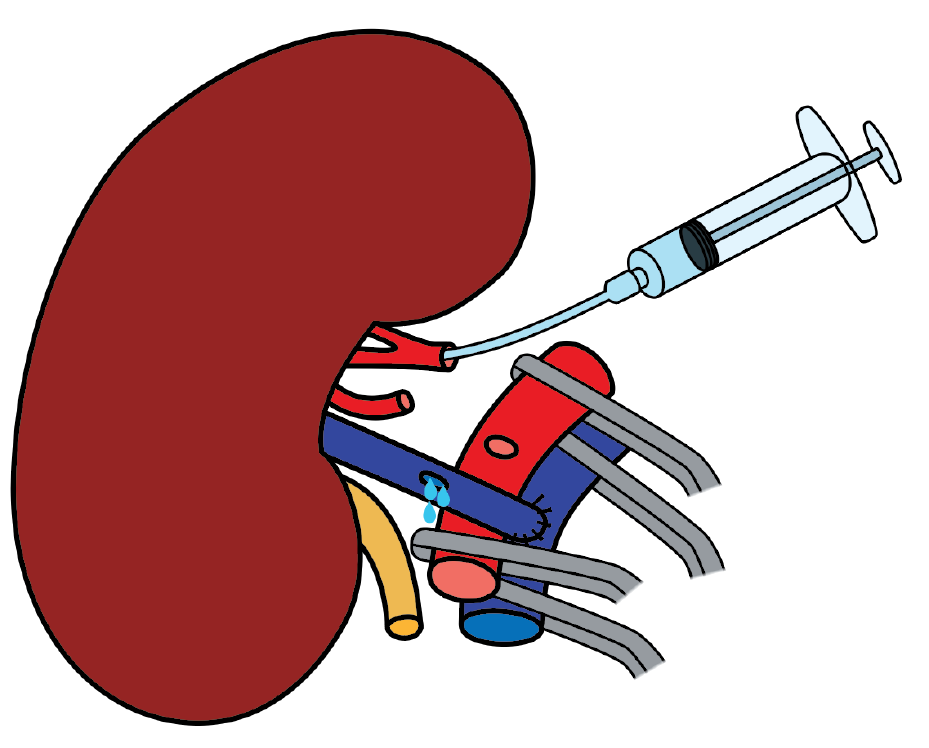
Figure 6
Cold perfusion of the kidney using heparinized saline combined with a vasodilator solution through a venotomy.
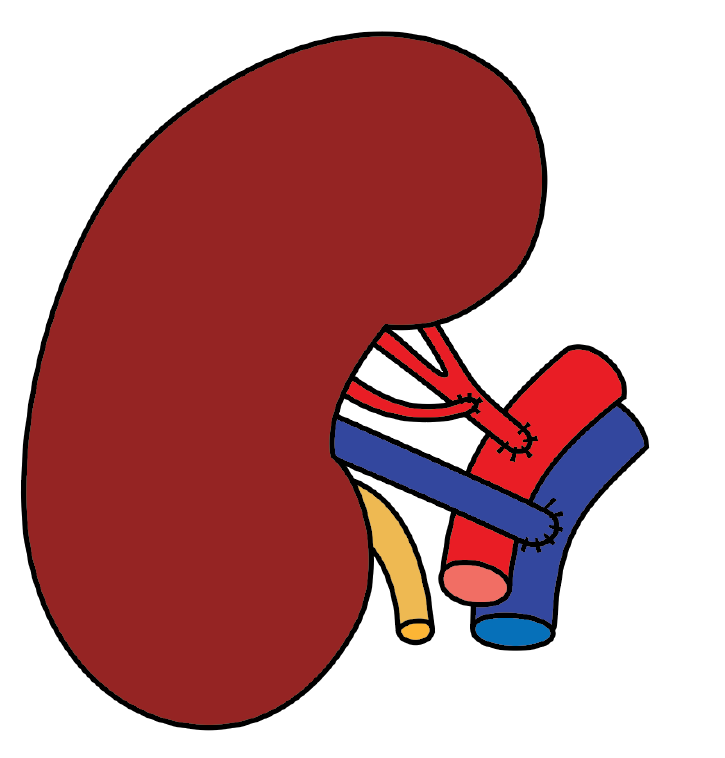
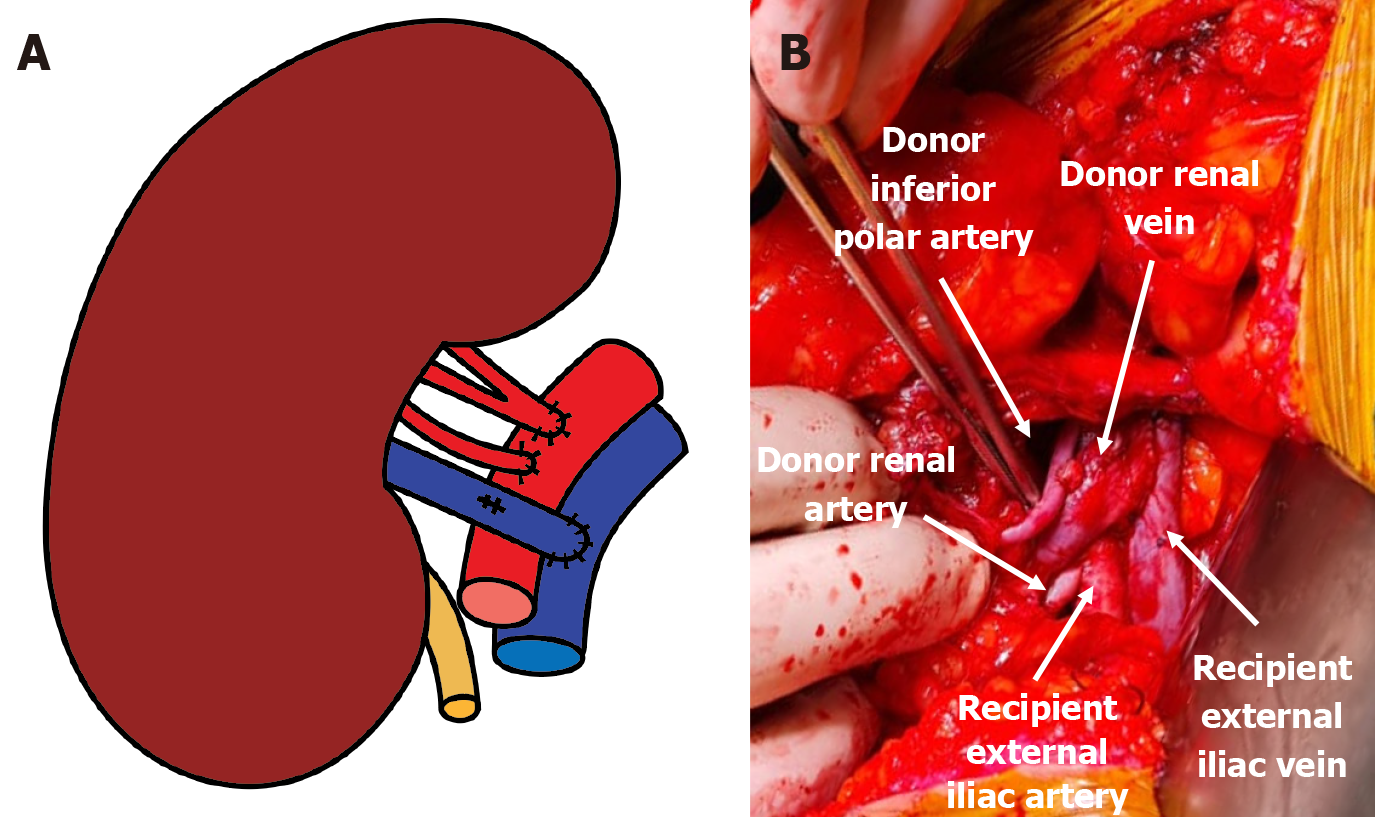
Figure 7 Anatomical configuration of the renal allograft in the right iliac fossa, showing end-to-side anastomosis of the renal vein to the external iliac vein, and separate end-to-side anastomoses of the main renal artery and the inferior polar artery to the external iliac artery.
A: Schematic illustration; B: Peri-operative photograph.
- Citation: Lekehal B, Ait Youssef N, Lekehal M, Jdar A, El Hassani AEA, Belyazid I, Bakkali T, Bounssir A. Acute graft thrombosis in a patient with factor V Leiden mutation: A case report and review of literature. World J Transplant 2026; 16(1): 114162
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v16/i1/114162.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.114162