©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Transplant. Mar 18, 2026; 16(1): 111524
Published online Mar 18, 2026. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.111524
Published online Mar 18, 2026. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.111524
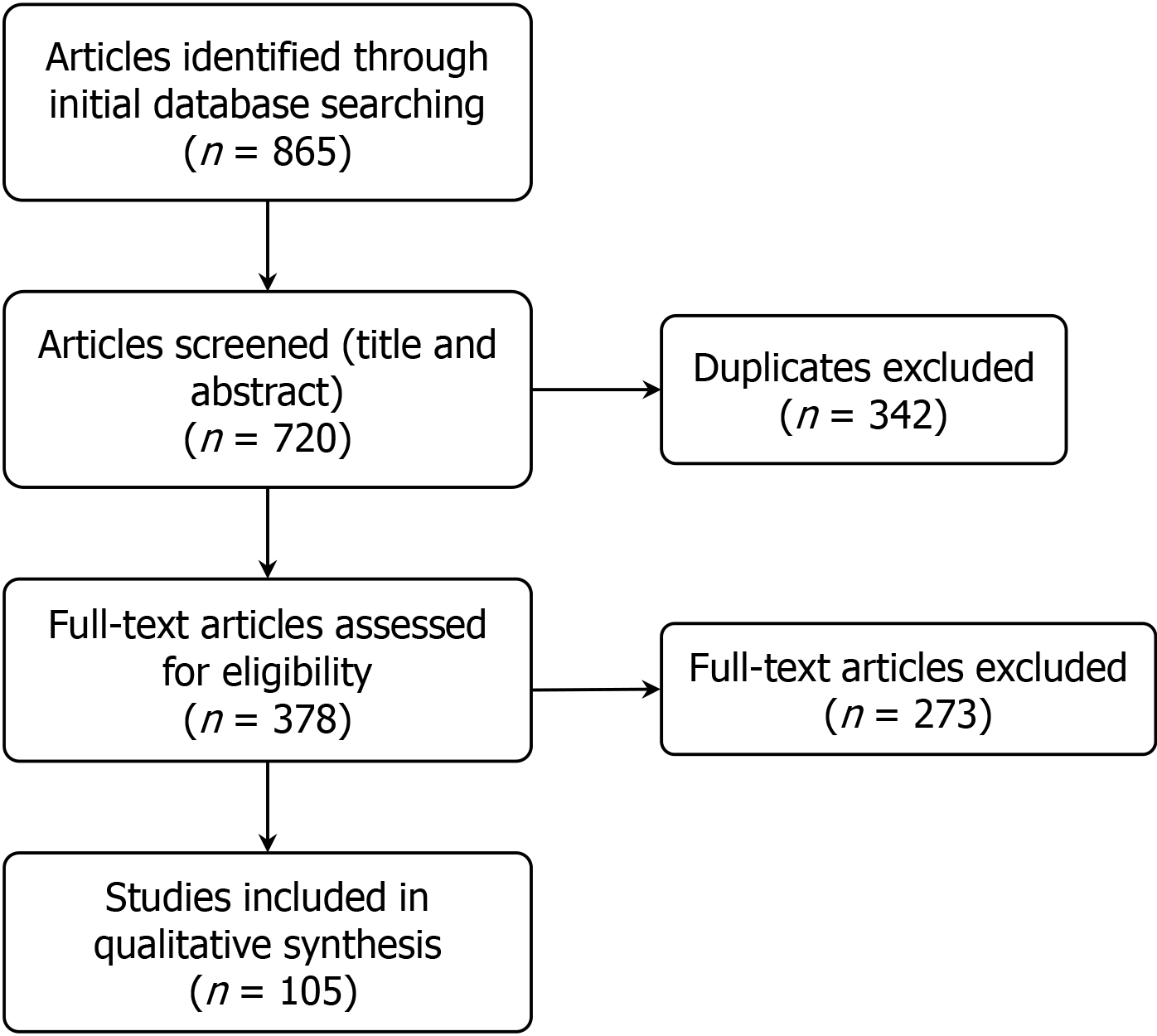
Figure 1
Flow diagram showing study methodology for selecting the articles.
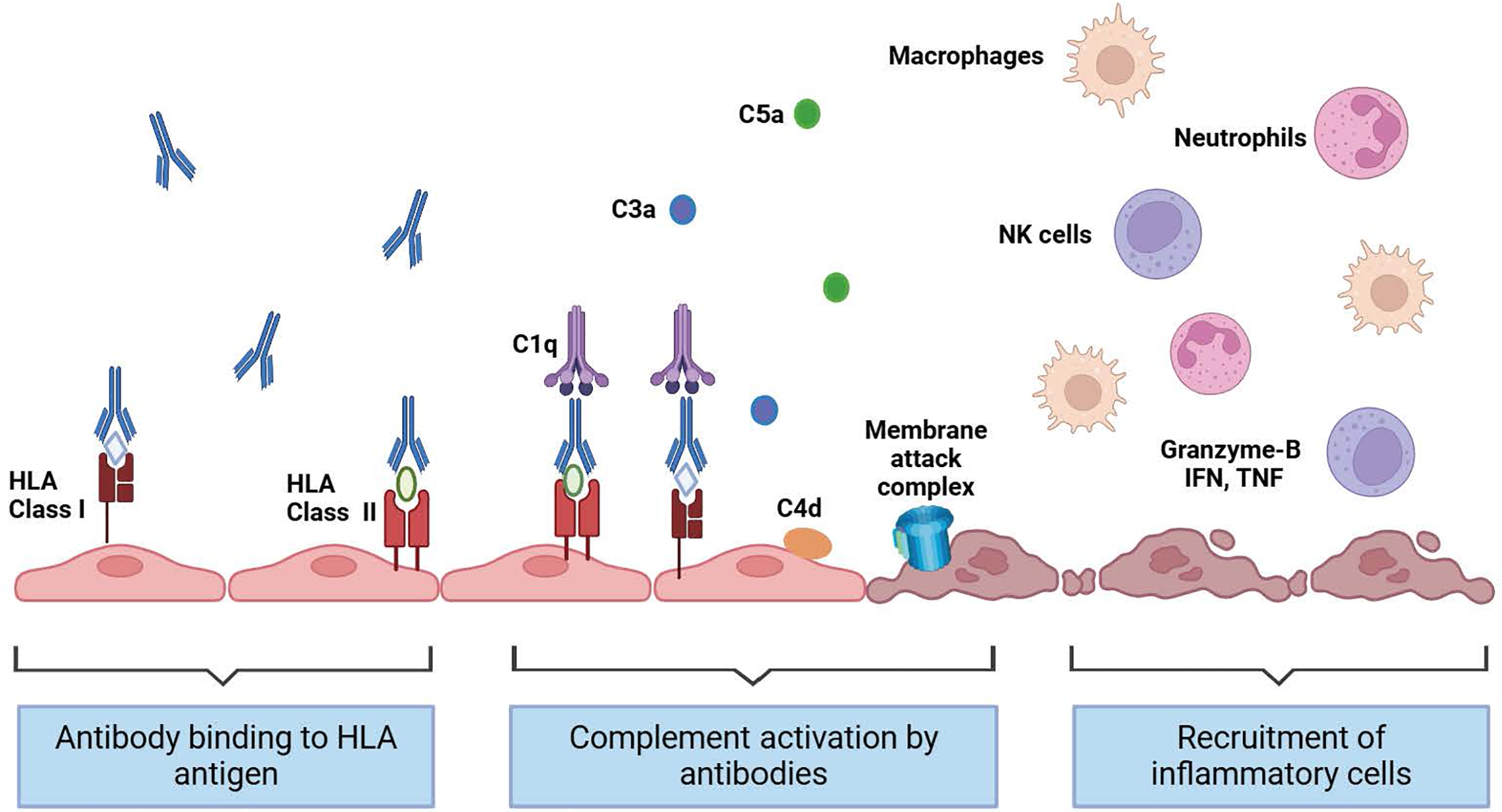
Figure 2 Mechanism of antibody-mediated rejection.
(Source: Biorender.com). NK cells: Natural killer cells; IFN: Interferon; TNF: Tumour necrosis factor; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen.
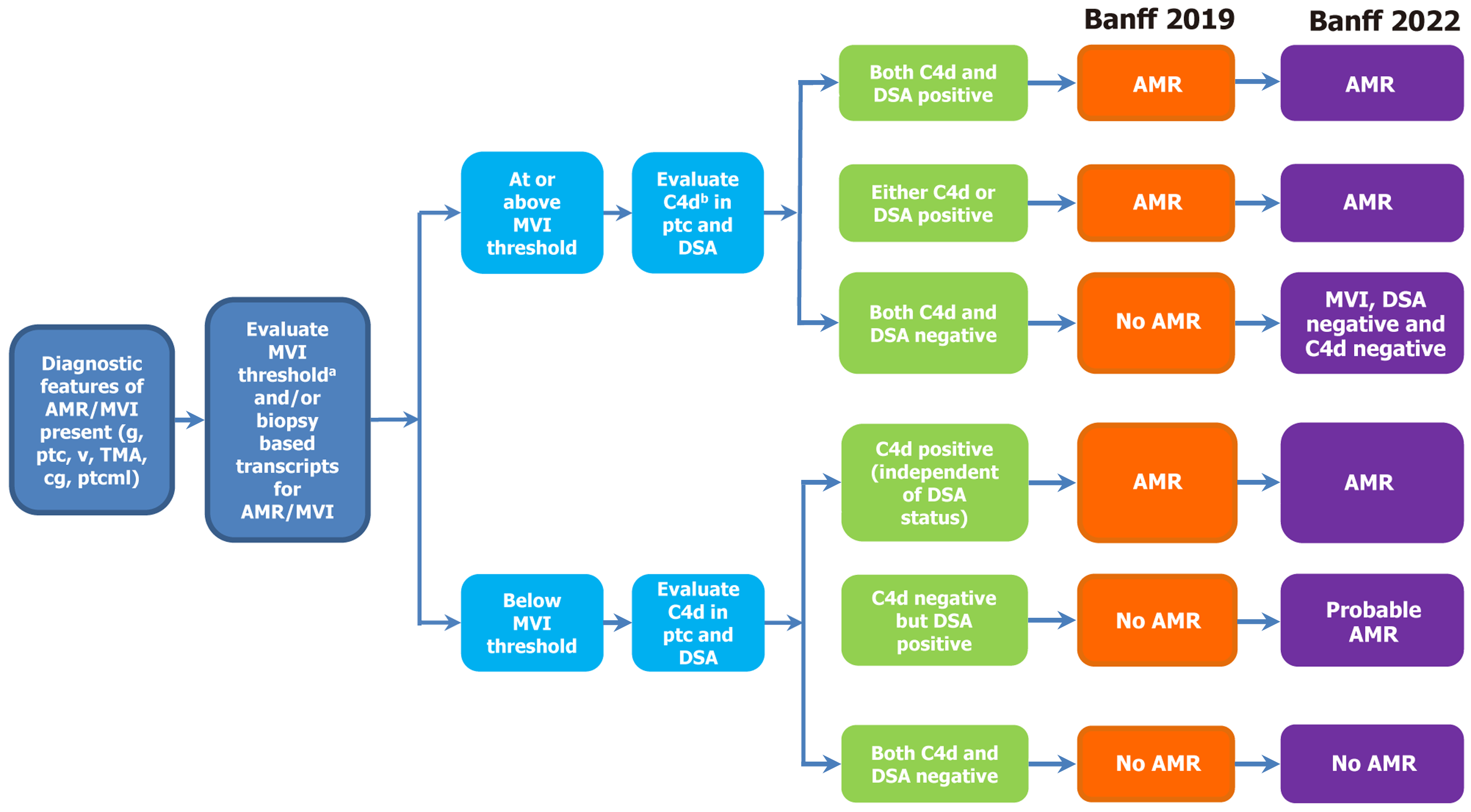
Figure 3 An update and comparison of the Banff 2019 and Banff 2022 on antibody-mediated rejection and microvascular inflammation.
AMR: Antibody mediated rejection; MVI: Microvascular inflammation; g: Glomerulitis; ptc: Peritubular capillaritis; v: Arteritis; TMA: Thrombotic microangiopathy; cg: Chronic glomerulopathy; ptcml: Peritubular capillary basement membrane multilayering; DSA: Donors-specific antibodies.
- Citation: Elahi T, Ahmed S, Mubarak M. Update on diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation. World J Transplant 2026; 16(1): 111524
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v16/i1/111524.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v16.i1.111524