©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Transplant. Aug 18, 2022; 12(8): 268-280
Published online Aug 18, 2022. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v12.i8.268
Published online Aug 18, 2022. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v12.i8.268
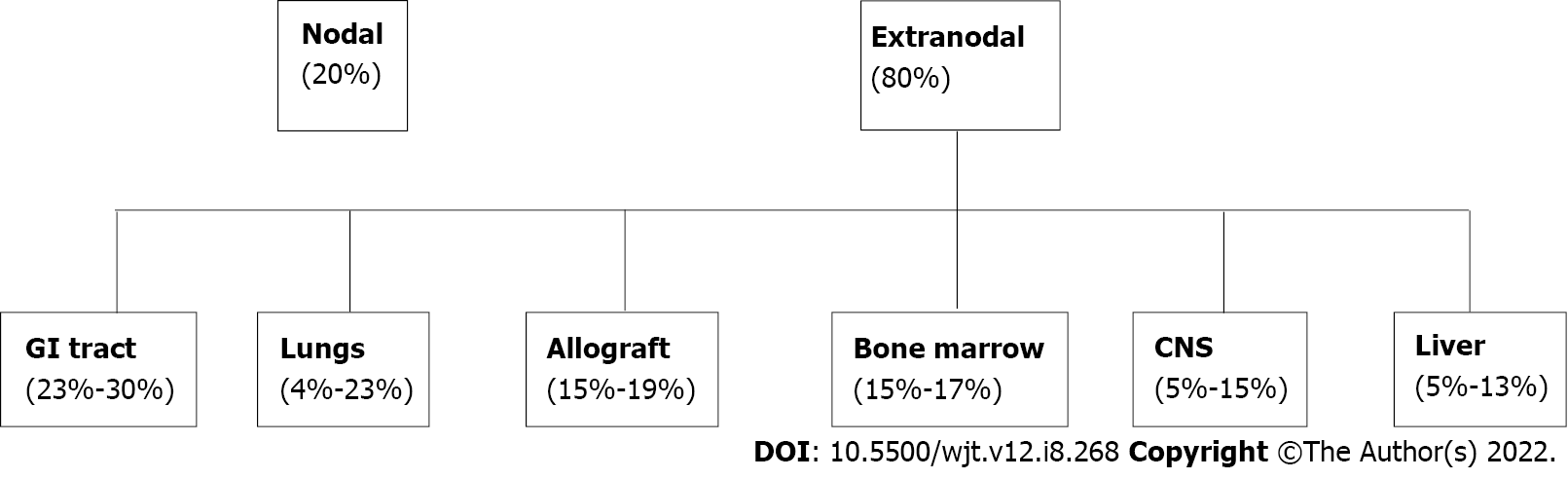
Figure 1 Distribution of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder by organ involvement.
GI: Gastrointestinal.
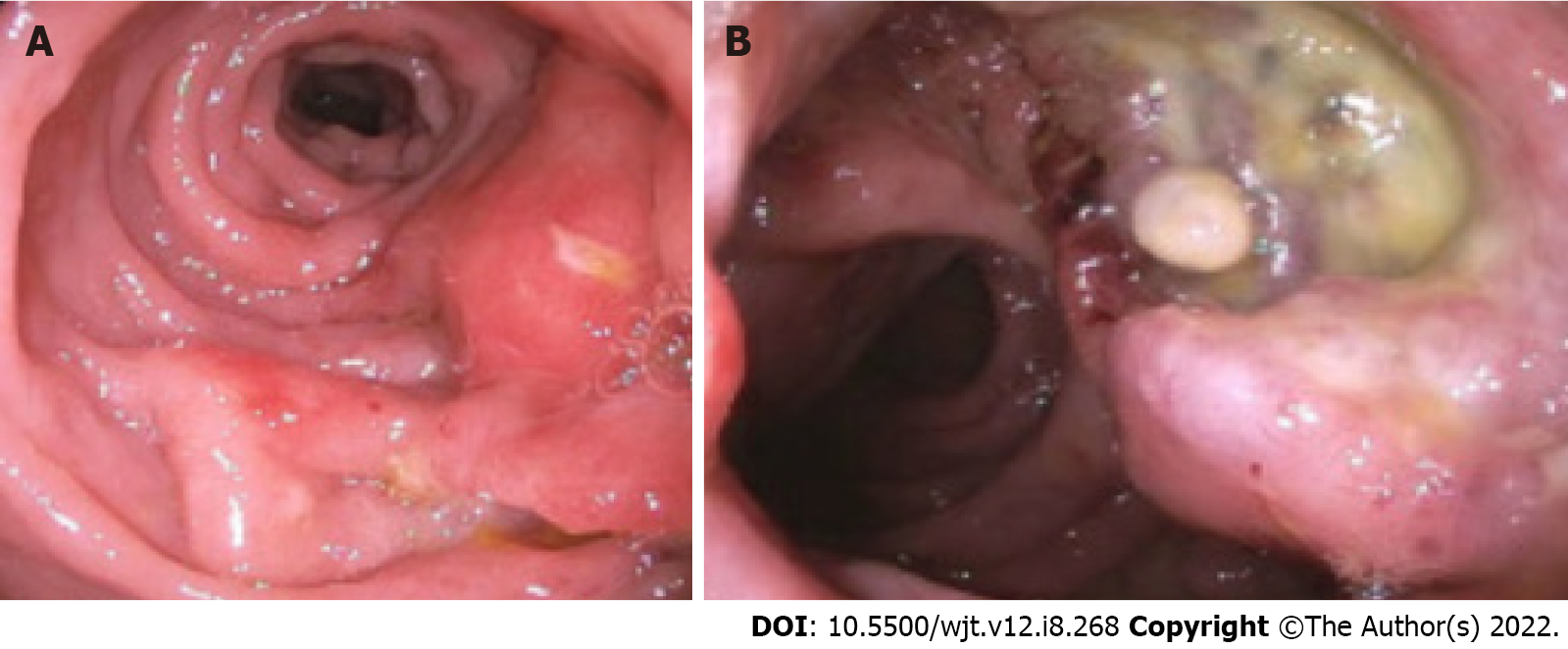
Figure 2 Endoscopic appearance of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder.
A: Nodular and ulcerated mucosa noted in the sigmoid colon; B: Ulcerated rectal mass.
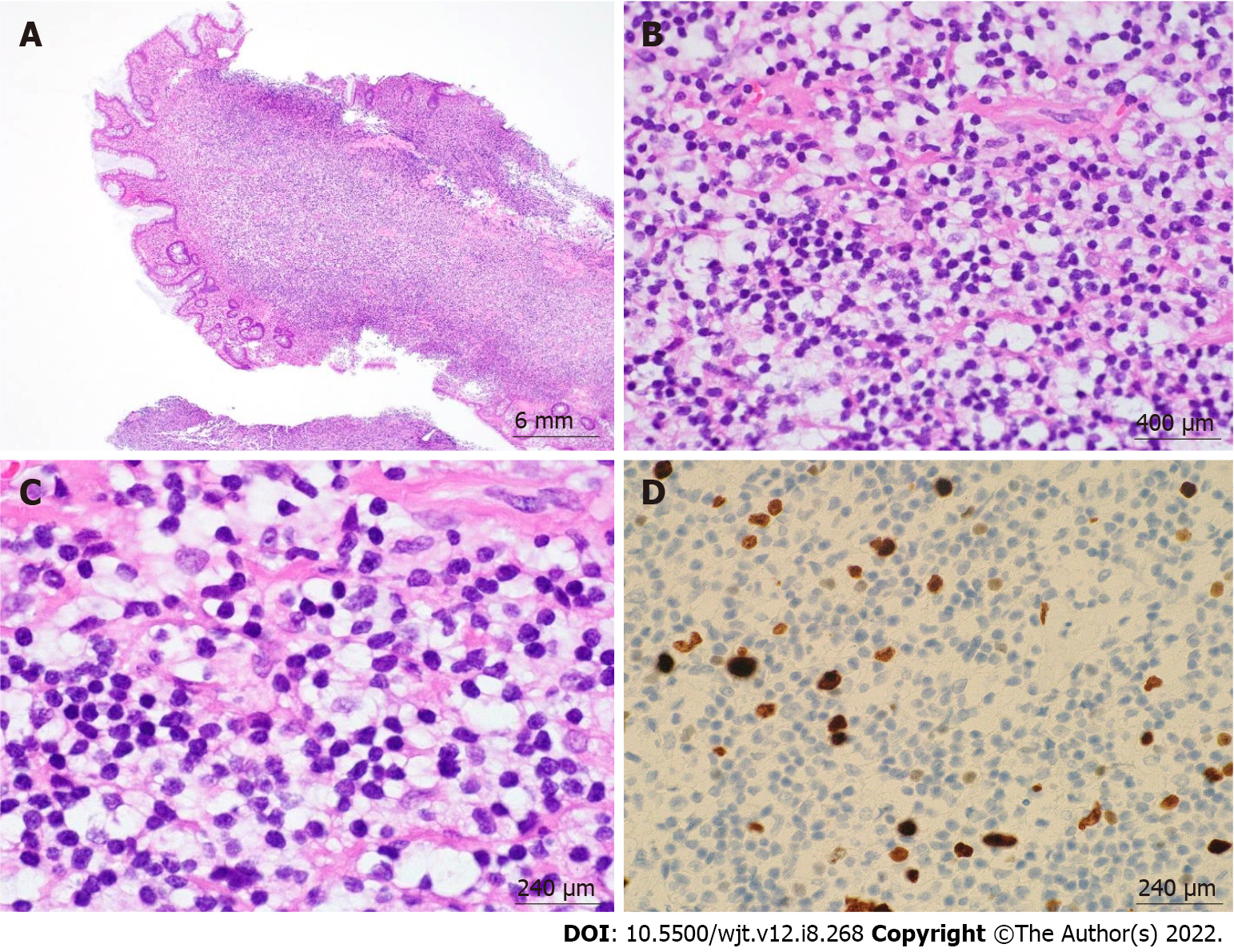
Figure 3 Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, monomorphic type (extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) arising in a sigmoid colon polyp.
A: 4 ×/6 mm; B: 60 ×/400 μm; C: 100 ×/240 μm; D: 100 ×/240 μm. Hematoxylin & eosin stain showed a dense lymphoid infiltrate in the lamina propria composed of monotonous small-sized lymphoid cells with mature chromatin and abundant clear cytoplasm. Ki-67 showed low proliferation index.
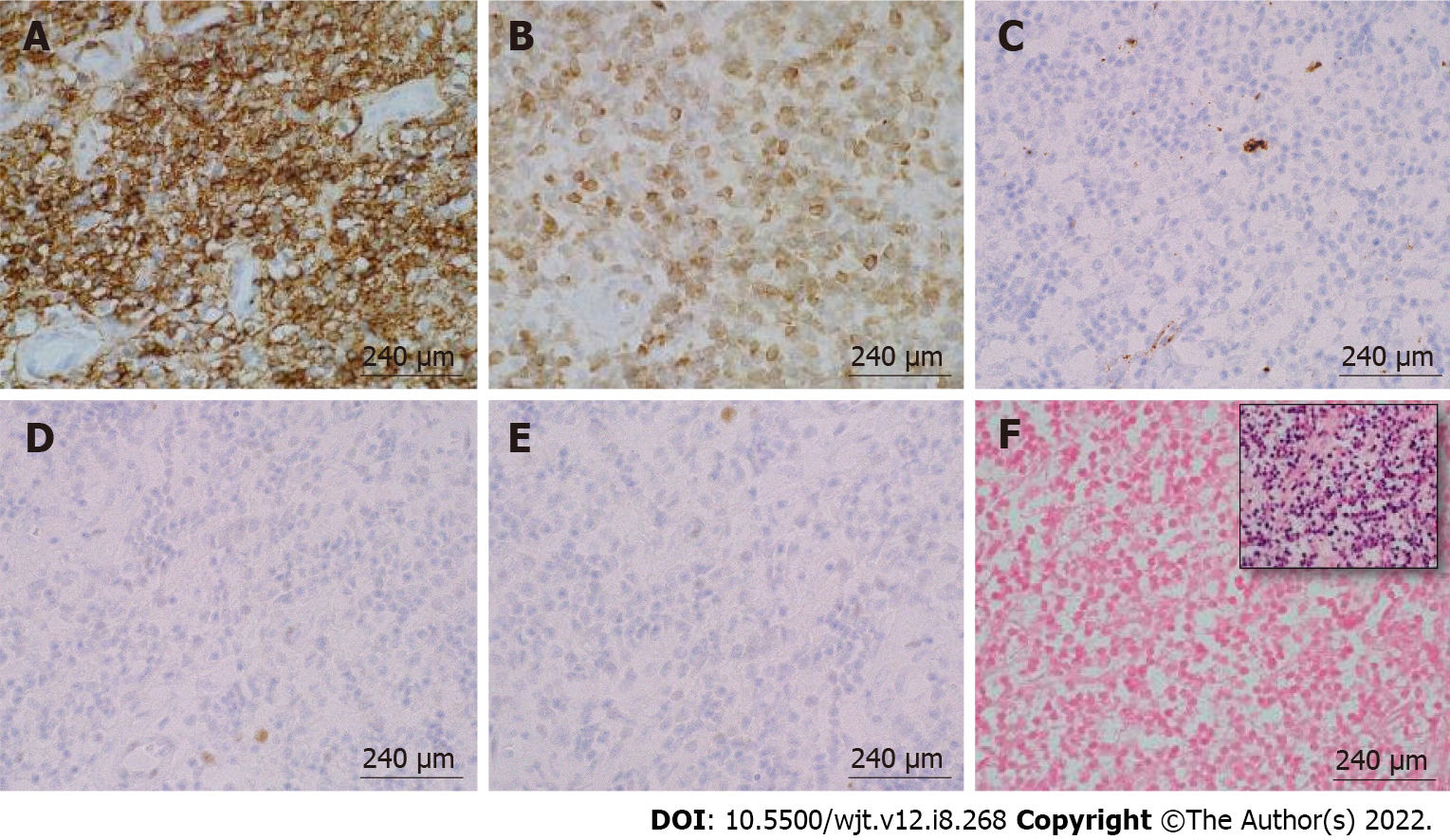
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical and in-situ hybridization staining of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, monomorphic type (extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue) arising in a sigmoid colon polyp.
A: CD20, 100 ×/240 μm; B: B-cell lymphoma (BCL)-2, 100 ×/240 μm; C: CD10, 100 ×/240 μm; D: BCL-6, 100 ×/240 μm; E: CD5, 100 ×/240 μm; F: EBER-ISH (inset: Positive control), 100 ×/240 μm. The monotonous small-size lymphocytes stained positive for CD20 and B-cell lymphoma-2 and were negative for the rest of the stains.
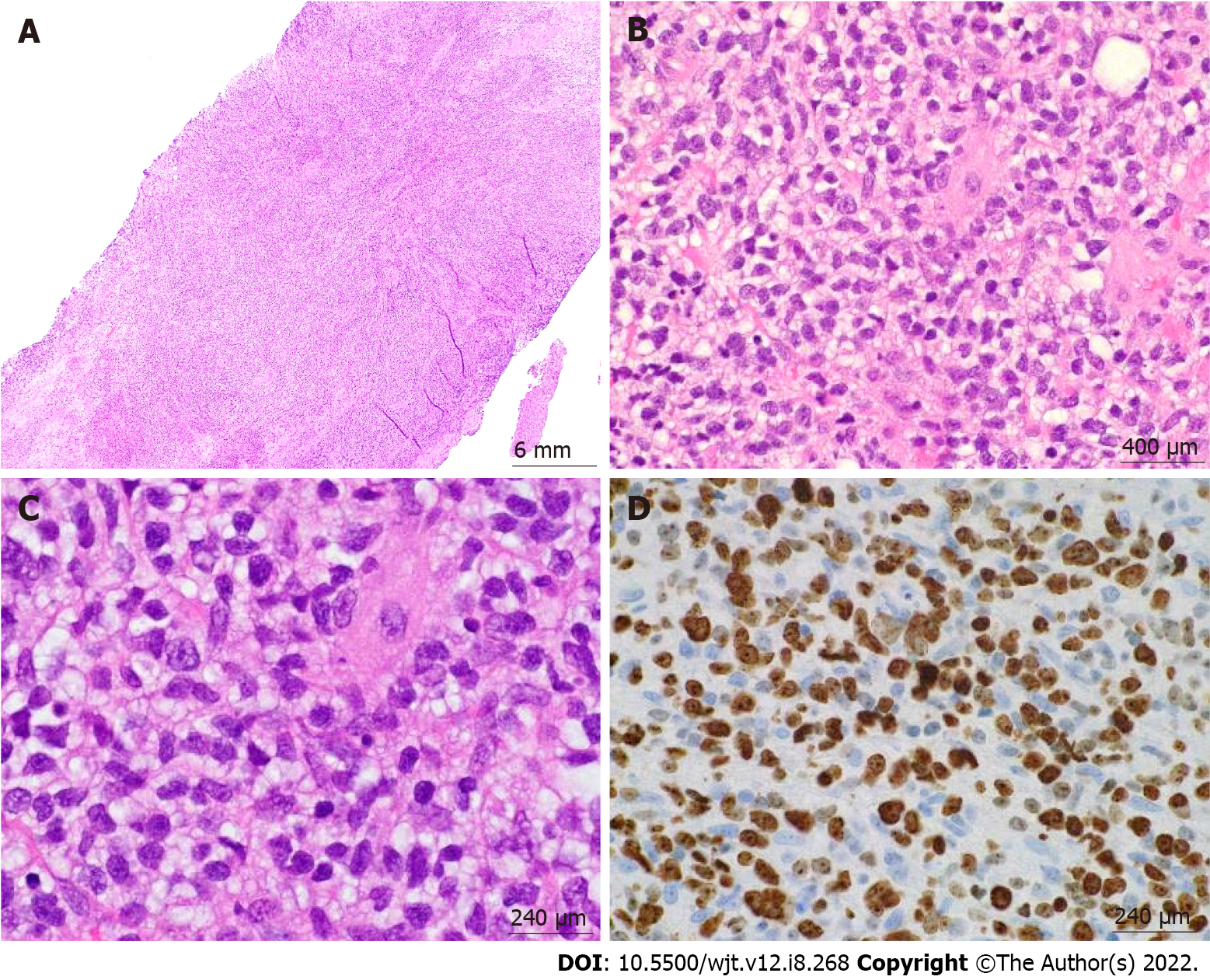
Figure 5 Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, monomorphic type (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, non-germinal center type) arising from an ulcerated anal mass.
A: 4 ×/6 mm; B: 60 ×/400 μm; C: 100 ×/240 μm; D: 100 ×/240 μm. Hematoxylin & eosin stain showed a diffuse lymphoid infiltrate composed of large pleomorphic cells with clear to eosinophilic cytoplasm, irregular nuclear contours, and prominent nucleoli in a background of fibroadipose tissue. Ki-67 showed high proliferation index.
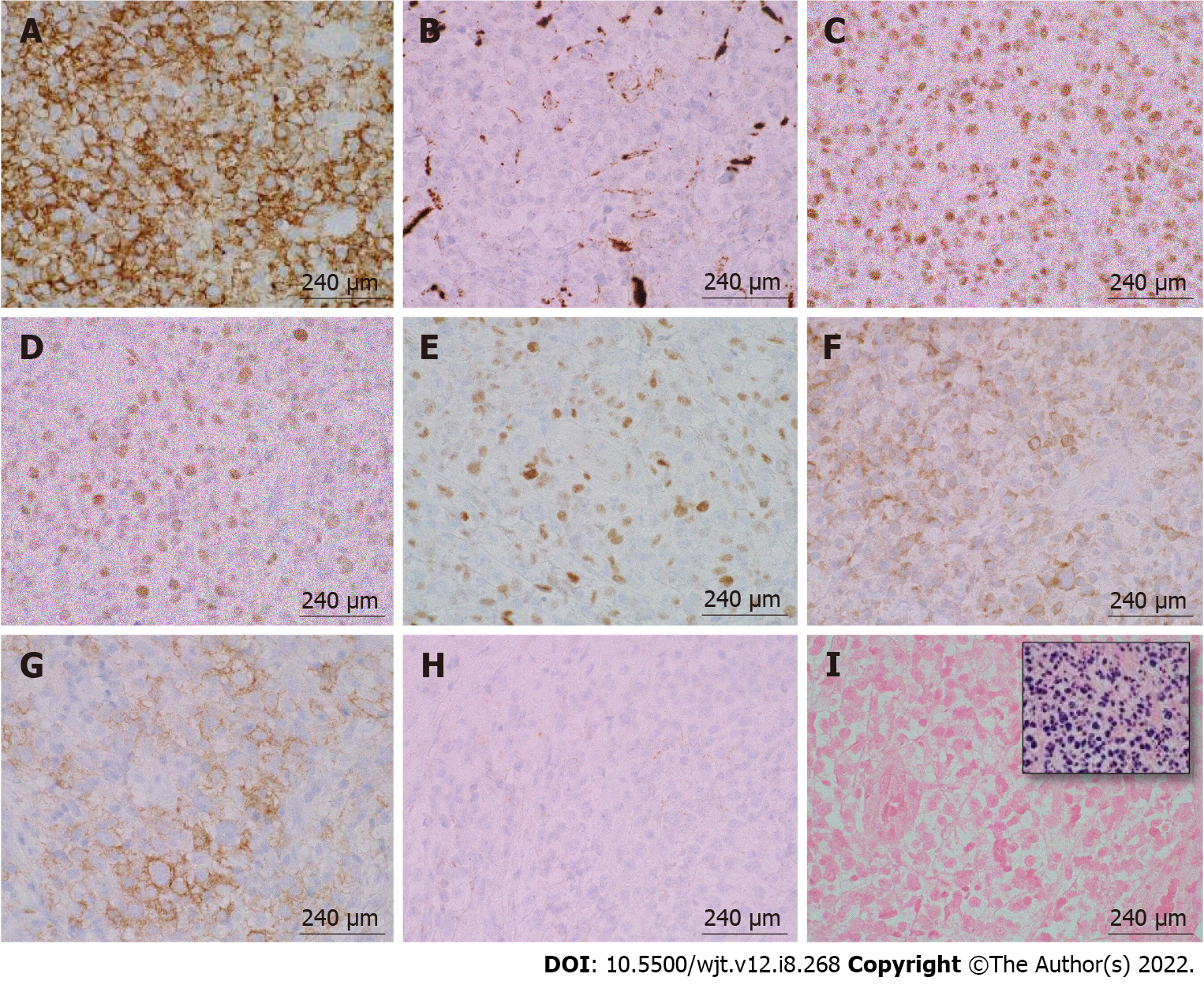
Figure 6 Immunohistochemical and in-situ hybridization staining of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder, monomorphic type (diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, non-germinal center type) arising from an ulcerated anal mass.
A: CD20, 100 ×/240 μm; B: CD10, 100 ×/240 μm; C: B-cell lymphoma (BCL)-6, 100 ×/240 μm; D: MUM-1, 100 ×/240 μm; E: c-MYC, 100 ×/240 μm; F: BCL-2, 100 ×/240 μm; G: CD30, 100 ×/240 μm; H: CD21, 100 ×/240 μm; I: EBER-ISH (inset: Positive control), 100 ×/240 μm. The large pleomorphic lymphocytes stained positive for CD20, B-cell lymphoma (BCL)-6, MUM-1, and BCL-2. These cells had a borderline staining for c-MYC (30%-40%), but FISH studies were negative for c-MYC rearrangements. CD30 was positive only in a subset of cells. EBER-ISH was negative.CD21 was negative and showed loss of follicular dendritic meshwork.
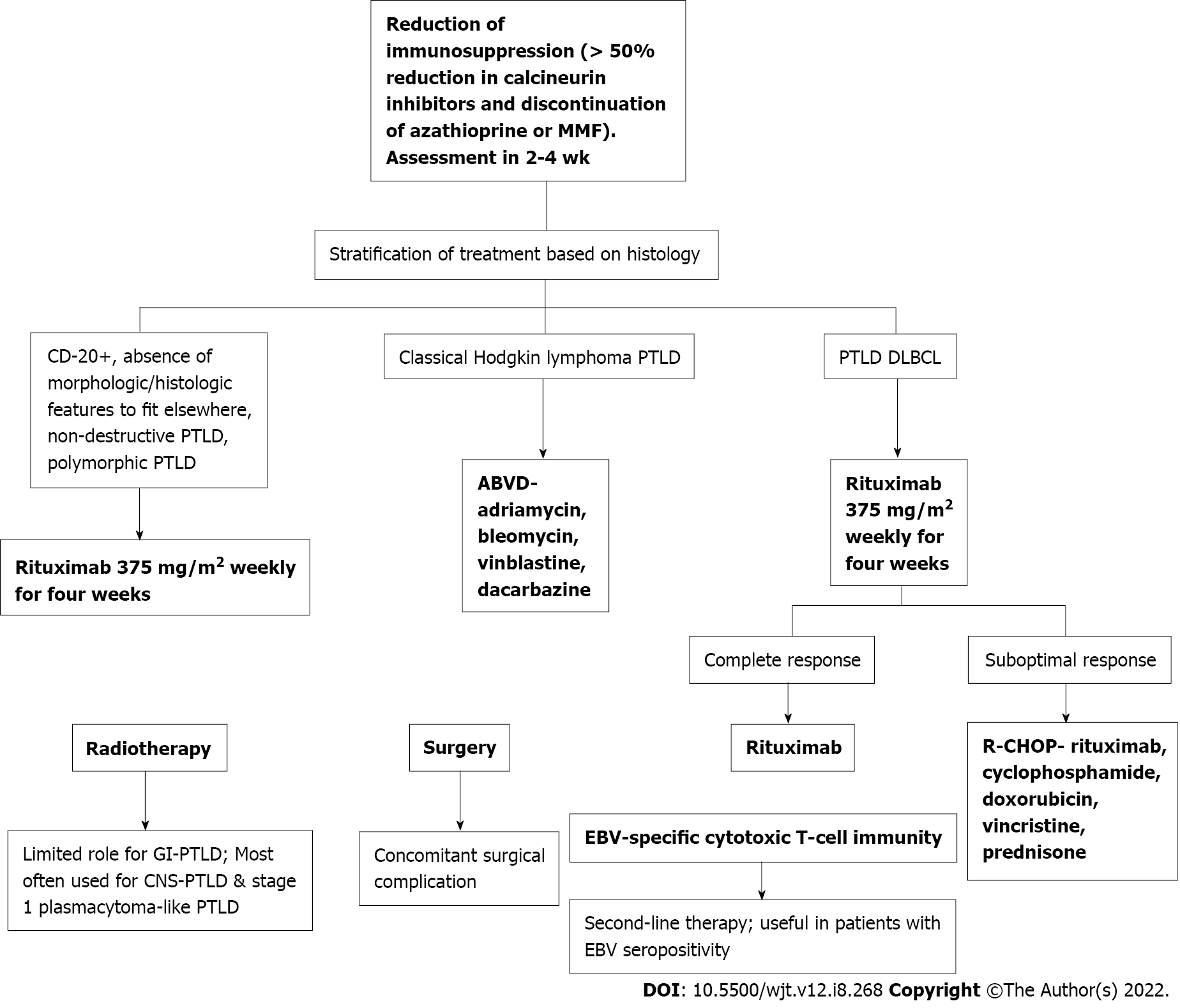
Figure 7 Workflow of the treatment for post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder.
PTLD: Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; GI: Gastrointestinal; MMF: Mycophenolate mofetil; ABVD: Doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine; DLBCL: Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas.
- Citation: Reiche W, Tauseef A, Sabri A, Mirza M, Cantu D, Silberstein P, Chandan S. Gastrointestinal manifestations, risk factors, and management in patients with post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder: A systematic review. World J Transplant 2022; 12(8): 268-280
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v12/i8/268.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v12.i8.268