©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Psychiatr. Mar 22, 2016; 6(1): 102-117
Published online Mar 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.102
Published online Mar 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.102
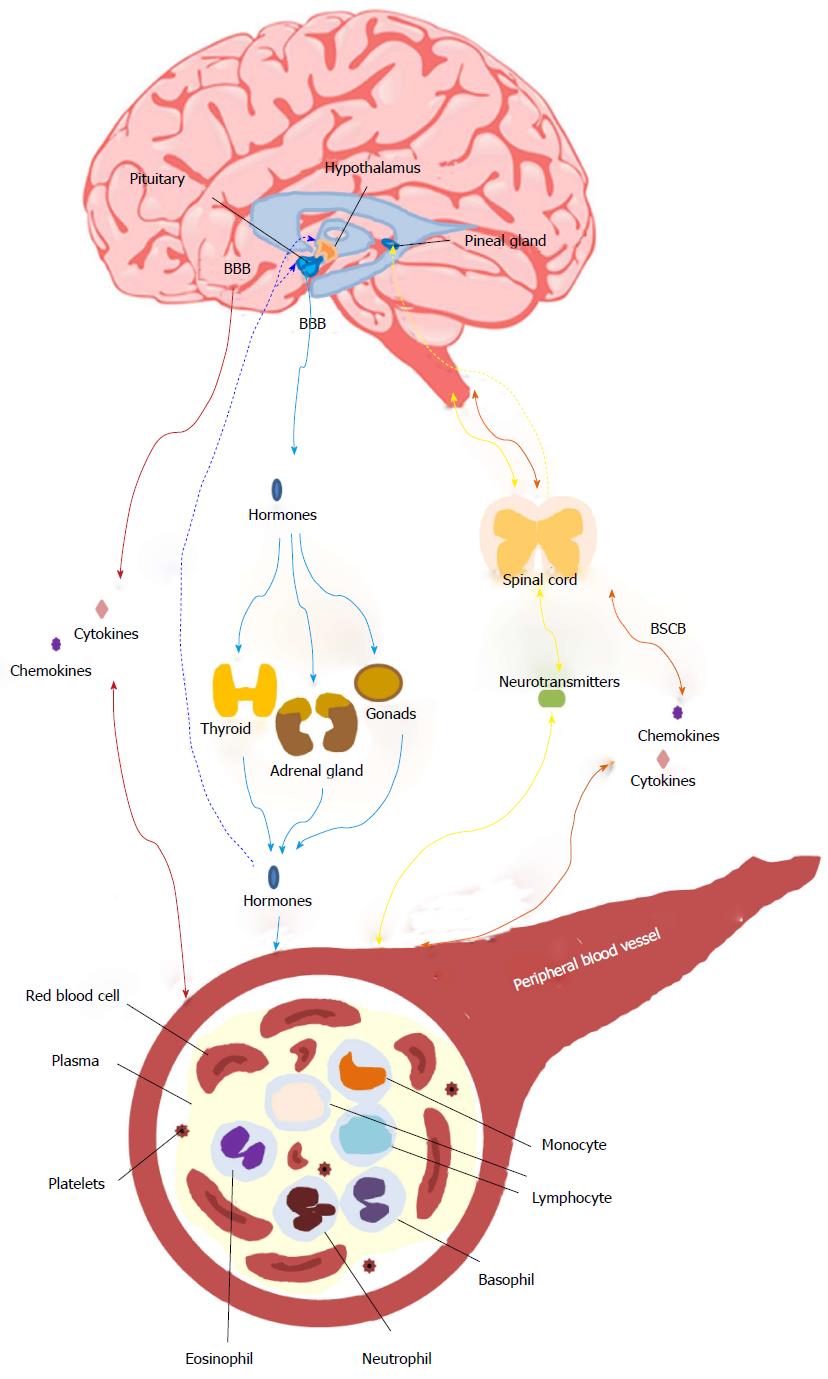
Figure 1 A schematic representation of central nervous system-peripheral blood tissue interactions.
CNS stress may influence gene expression, DNA methylation, and cell metabolism in the peripheral blood via cytokines, neurotransmitters, or hormones with different transportation methods. Cytokines or chemokines can transport across the BBB (red lines) or BSCB (orange line) either from CNS to peripheral blood tissue or vice versa. The hormones are exerted by CNS and transported across the BBB via blood system to the target tissue (blue lines) and in turn regulate CNS through negative feedback (blue dashed lines). Another connection is the stimulated (yellow line) or negative feedback inhibition (yellow dashed line) via spinal cord via the parasympathetic or sympathetic nervous system. It is noted that there are several blood cell types with their own features in the peripheral blood vessel. The figure is an extension of Figure 1 in Marques-Deak et al[23]. BSCB: Blood-spinal cord barrier; CNS: Central nervous system; BBB: Blood-brain barrier.
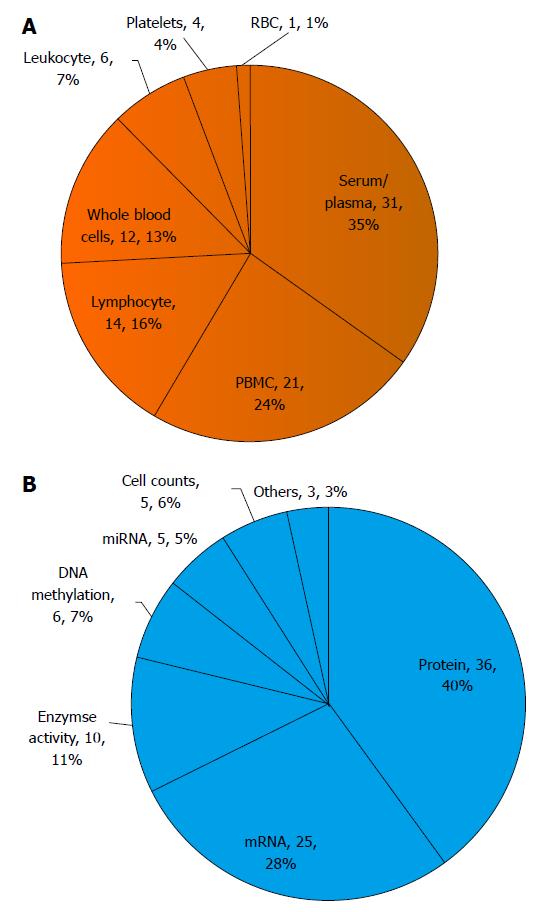
Figure 2 A summation of studies into peripheral biomarkers for schizophrenia.
Studies are classified based on A: Blood cell types (e.g., serum/plasma, PBMC, lymphocytes, whole blood cells, leukocyte, plateles or red blood cells); B: Research focus (e.g., proteins, mRNA, enzyme activity assays, DNA methylation, or miRNA). The numbers indicate the number of studies in the categories, and its overall percentage. PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; RBC: Red blood cell.
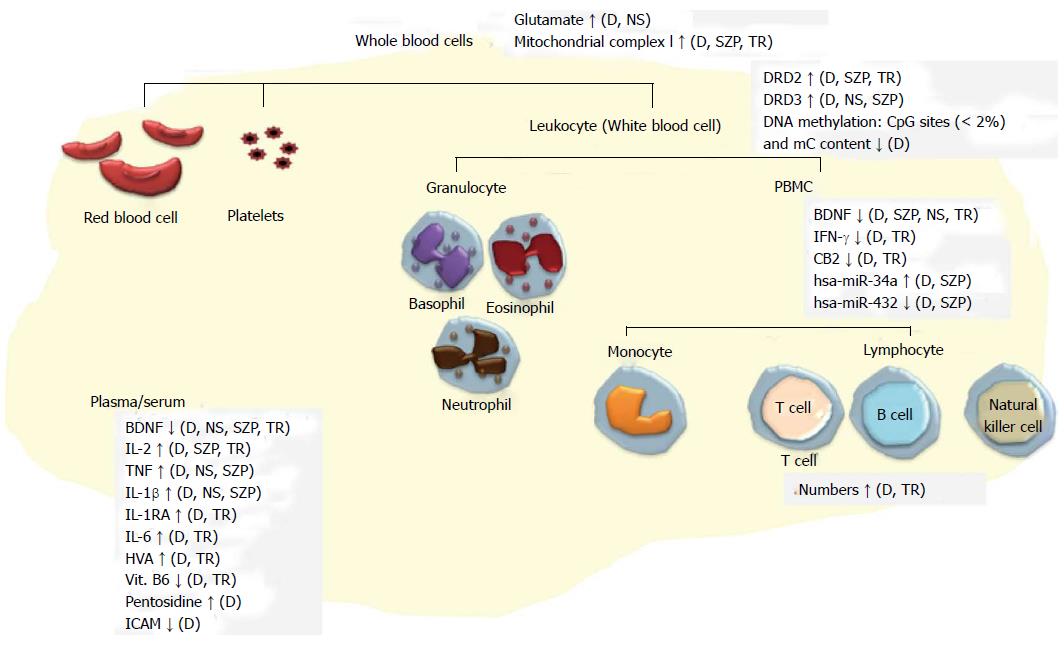
Figure 3 Representation of potential peripheral biomarkers for schizophrenia.
Only markers consistently reported in two or more individual peripheral studies are listed in the figure. The markers were classified as either diagnostic (D), antipsychotic TR or both. SZP indicates those markers have been reported to correlate with phenotypes (i.e., clinical symptom or cognitive function) in people with schizophrenia. Some markers were NS for schizophrenia. PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cell; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; HVA: Homovanillic acid; Vit. B6: Vitamin B6 (pyridoxamine); ICAM: Intercellular adhesion molecule; DRD2: Dopamine receptors D2; IFN: Interferon; CB2: Cannabinoid receptor; TR: Treatment response; NS: Not specific.
- Citation: Lai CY, Scarr E, Udawela M, Everall I, Chen WJ, Dean B. Biomarkers in schizophrenia: A focus on blood based diagnostics and theranostics. World J Psychiatr 2016; 6(1): 102-117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v6/i1/102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.102