©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2026; 16(2): 113124
Published online Feb 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i2.113124
Published online Feb 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i2.113124
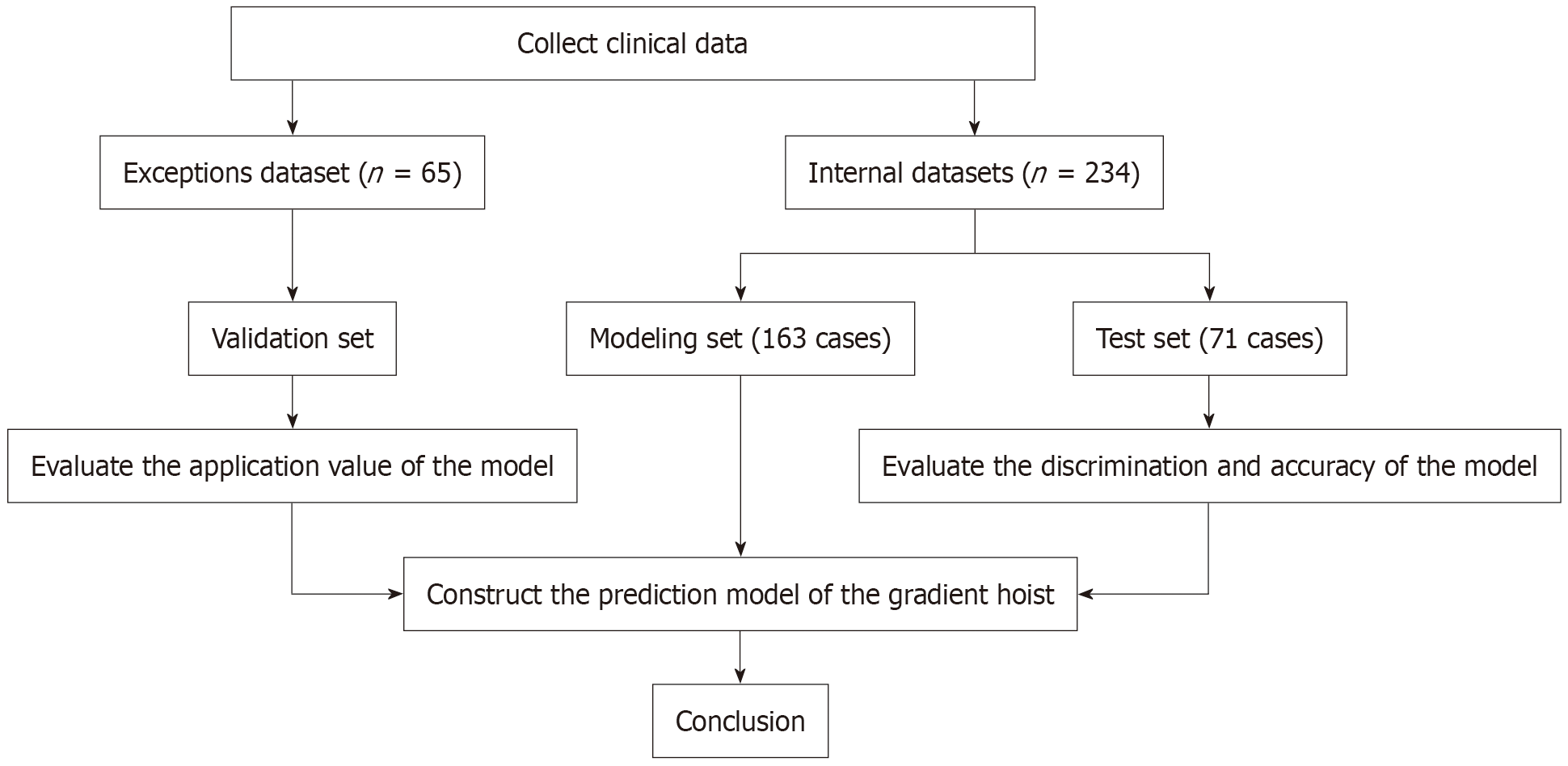
Figure 1 Research flowchart.
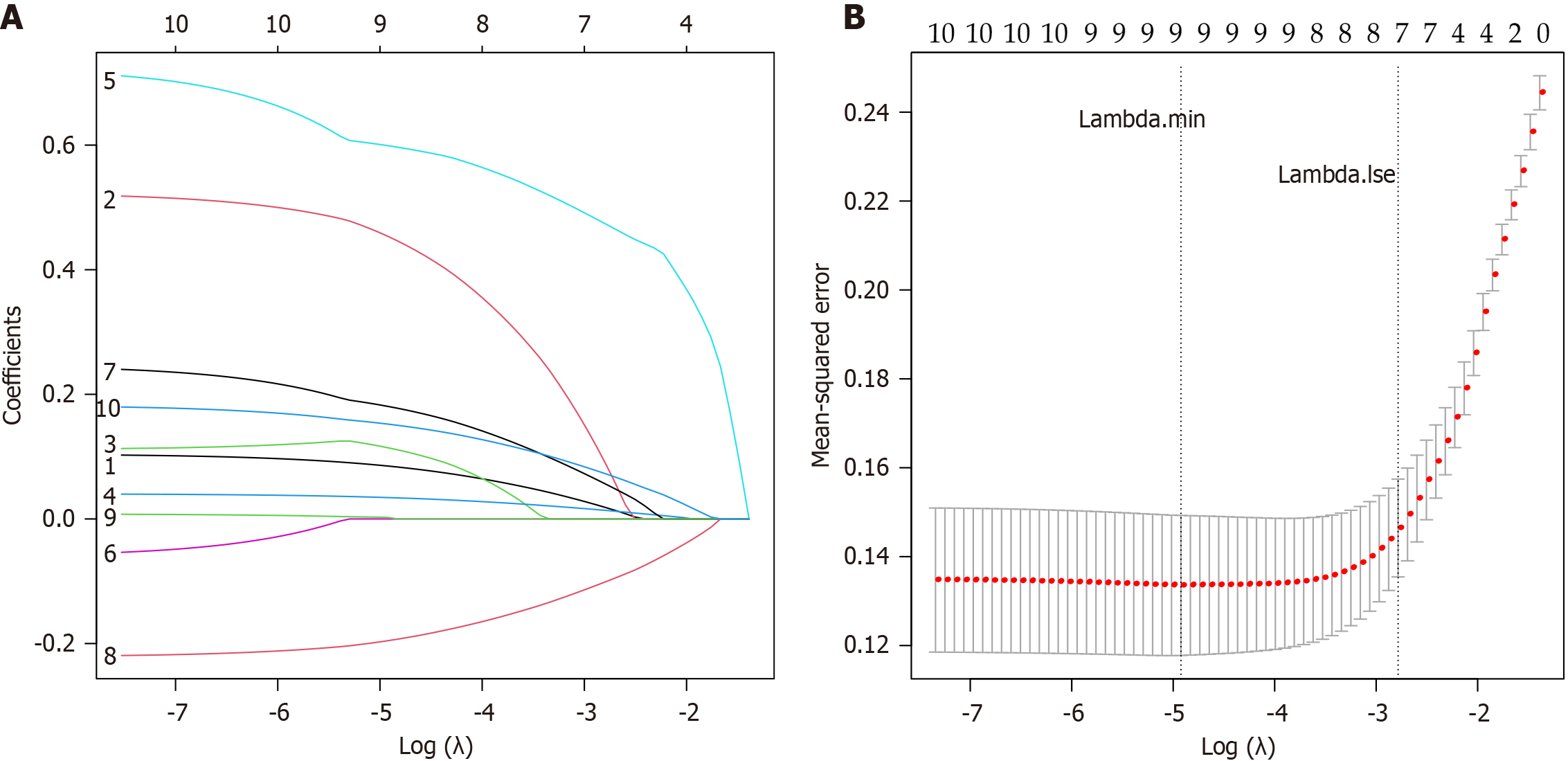
Figure 2 Least absolute contraction and selection operator regression screening of independent variables.
A: Coefficient path diagram; B: Cross-validation curve.
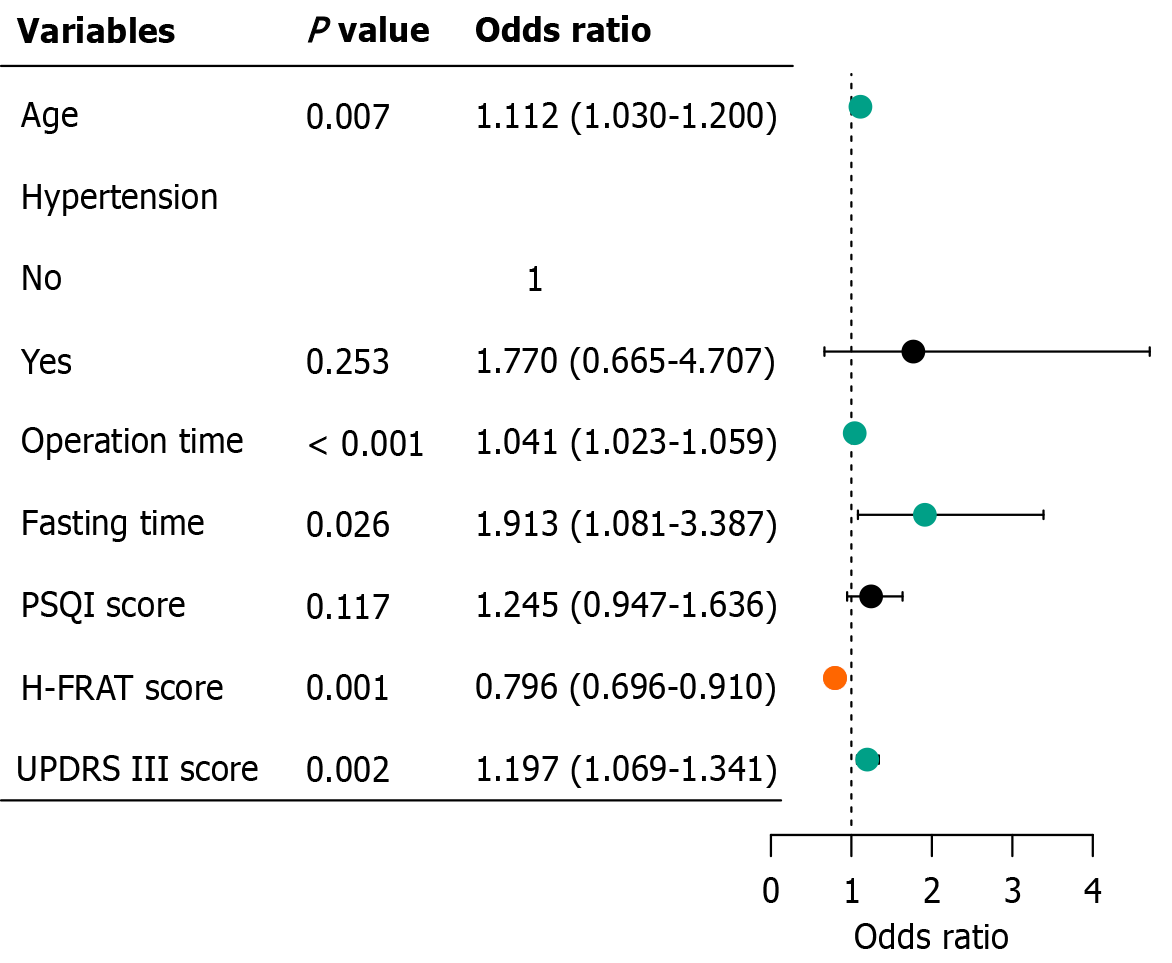
Figure 3 Forest plot of the results of multivariate analysis.
PSQI: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; H-FRAT: Family Relationship Health Assessment Scale; UPDRS III: Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Part III.
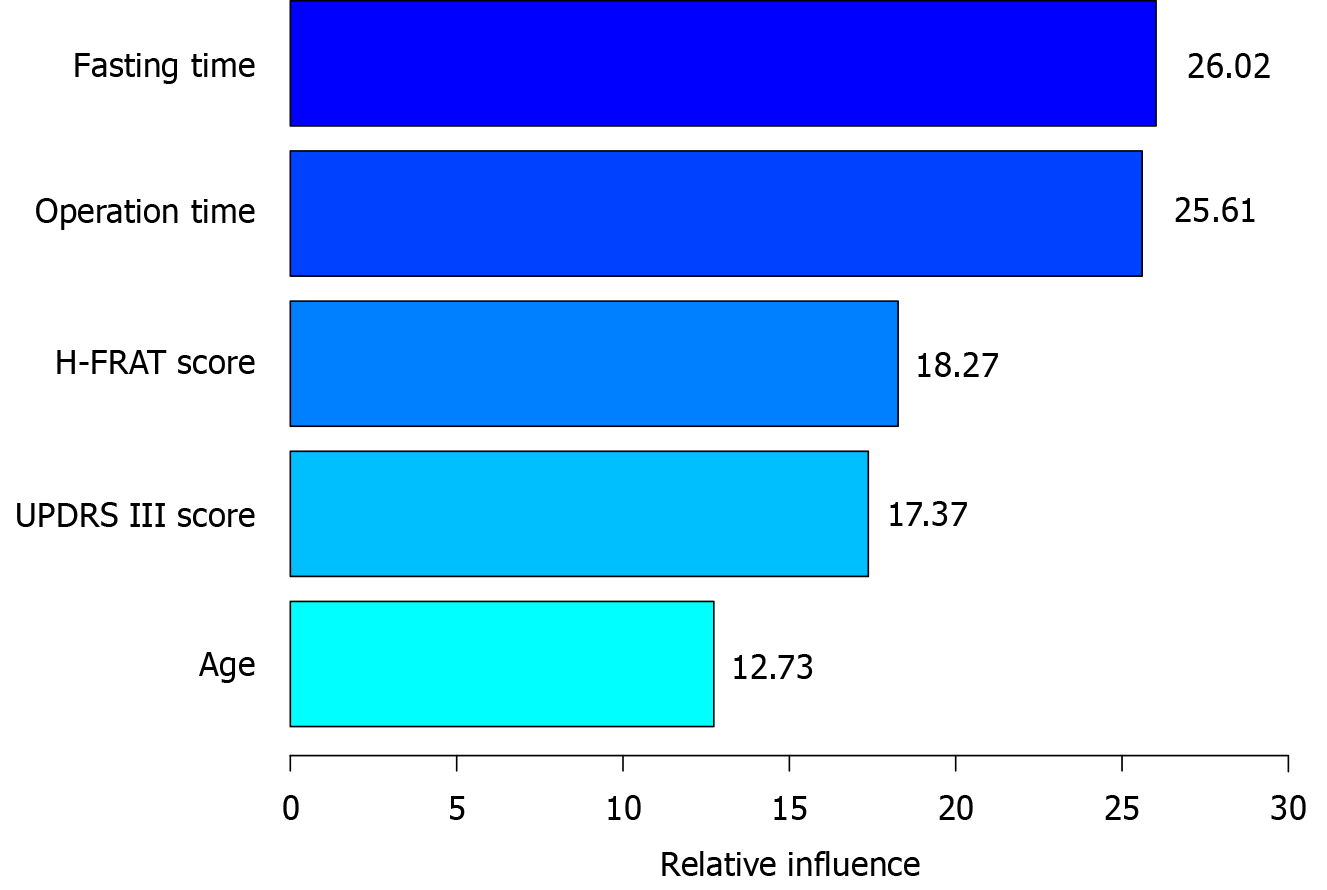
Figure 4 The scores of important variables.
H-FRAT: Family Relationship Health Assessment Scale; UPDRS III: Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Part III.
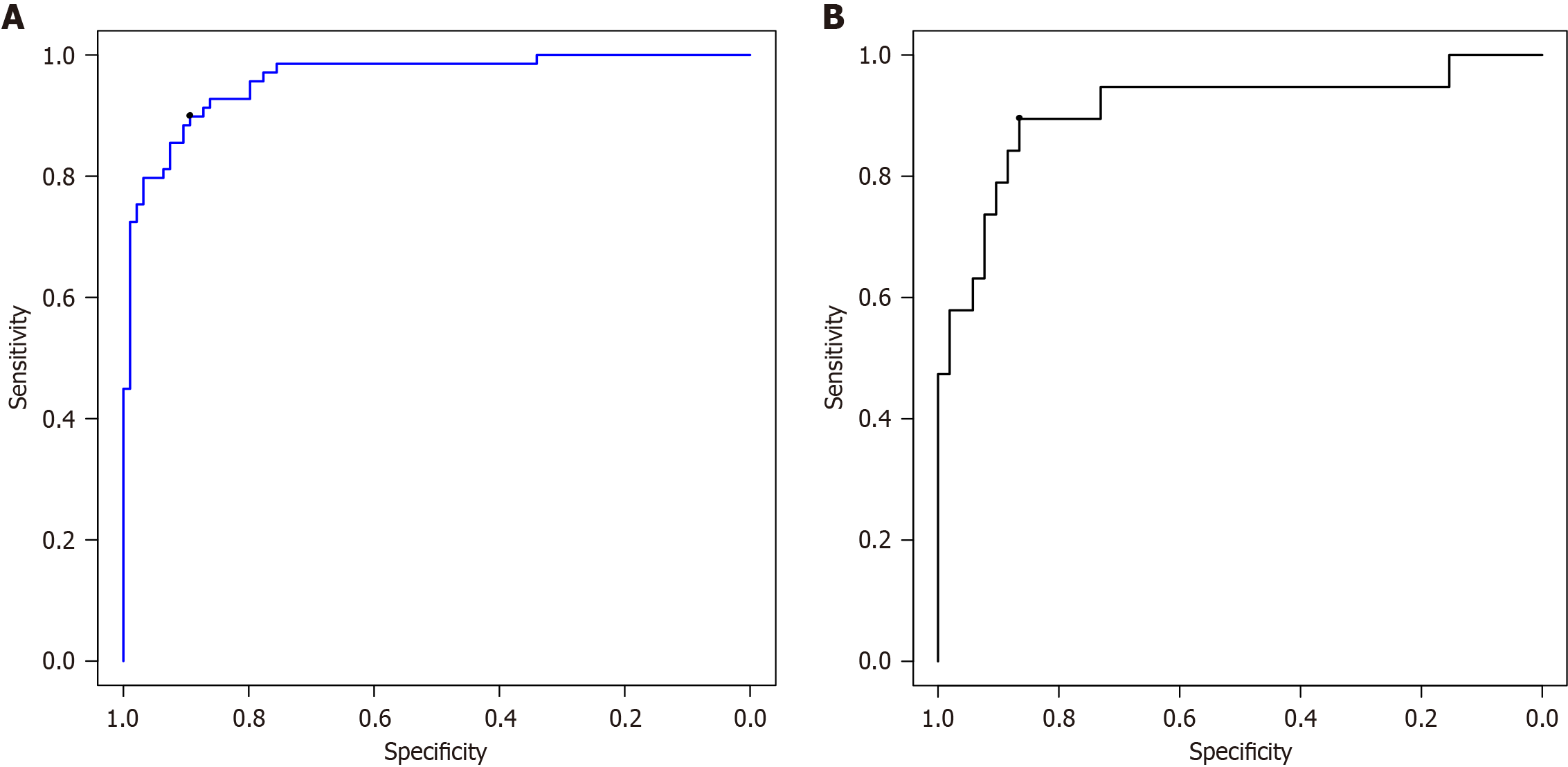
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic curve.
A: Modeling set; B: Test set.
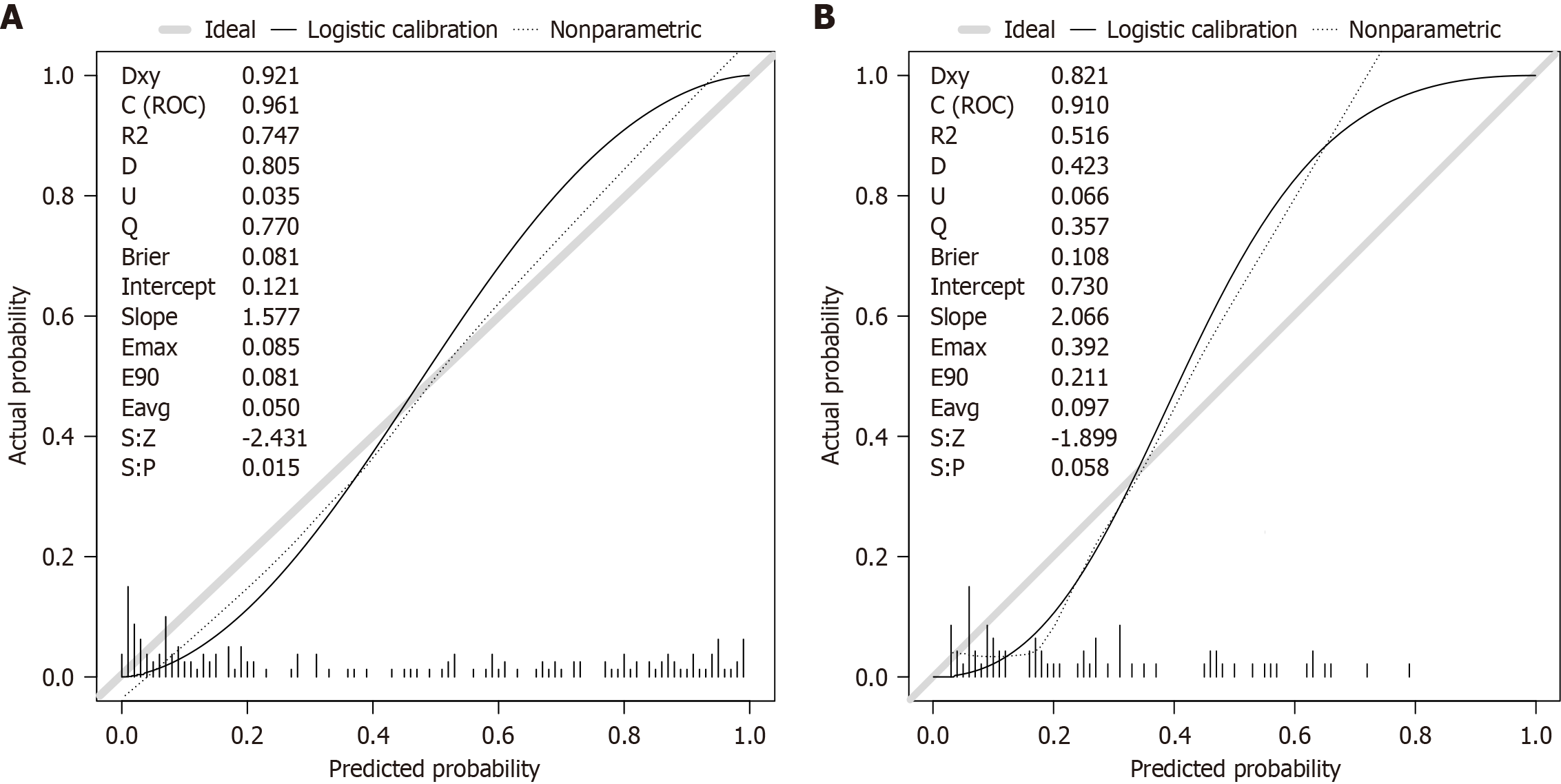
Figure 6 Calibration curve.
A: Modeling set; B: Test set. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; Dxy: Somers’ Dxy rank correlation; D: Discrimination index; U: Unreliability index; Q: Quality index; Eavg: Average error; S:z: Z value of the z test; S:p: P value of the z test.
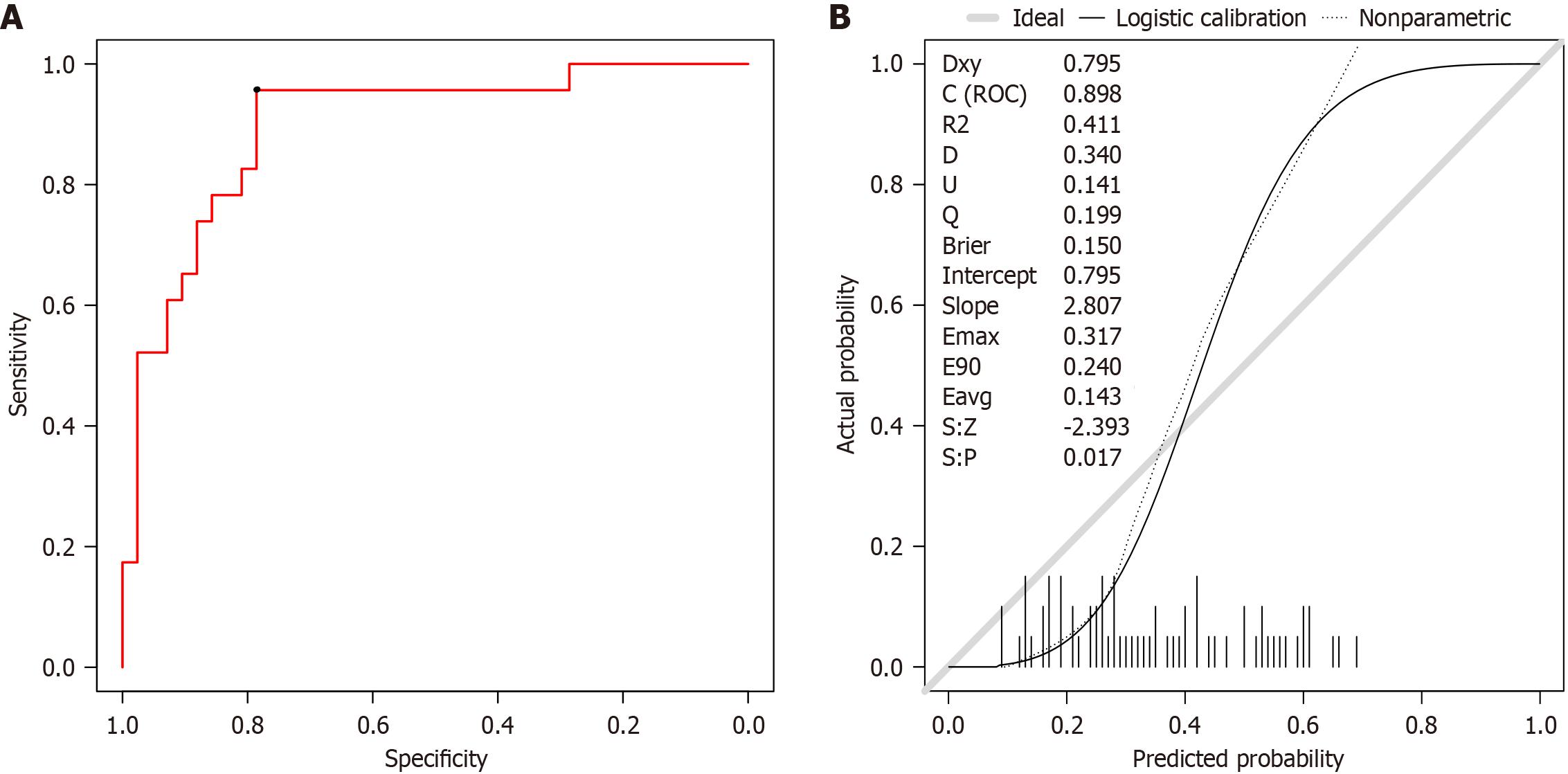
Figure 7 Application effect of the gradient boosting machine prediction model.
A: Receiver operating characteristic; B: Calibration curve. ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; Dxy: Somers’ Dxy rank correlation; D: Discrimination index; U: Unreliability index; Q: Quality index; Eavg: Average error; S:z: Z value of the z test; S:p: P value of the z test.
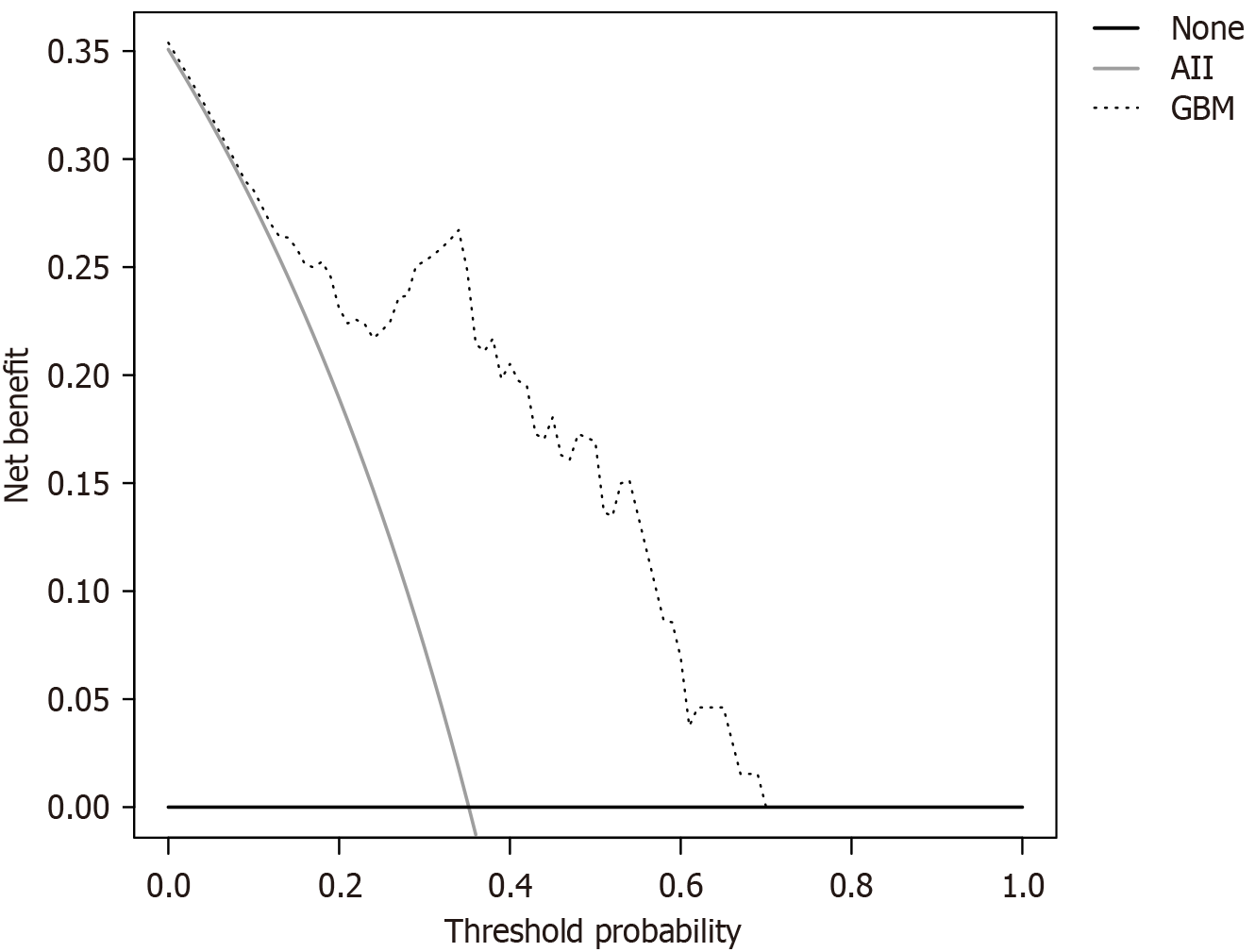
Figure 8 Decision curve.
GBM: Gradient boosting machine.
- Citation: Liao S, Tang JW, Li Y. Gradient boosting machine model predicts psychiatric complications after deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. World J Psychiatry 2026; 16(2): 113124
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v16/i2/113124.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v16.i2.113124