©The Author(s) 2026.
World J Psychiatry. Jan 19, 2026; 16(1): 111471
Published online Jan 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i1.111471
Published online Jan 19, 2026. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v16.i1.111471
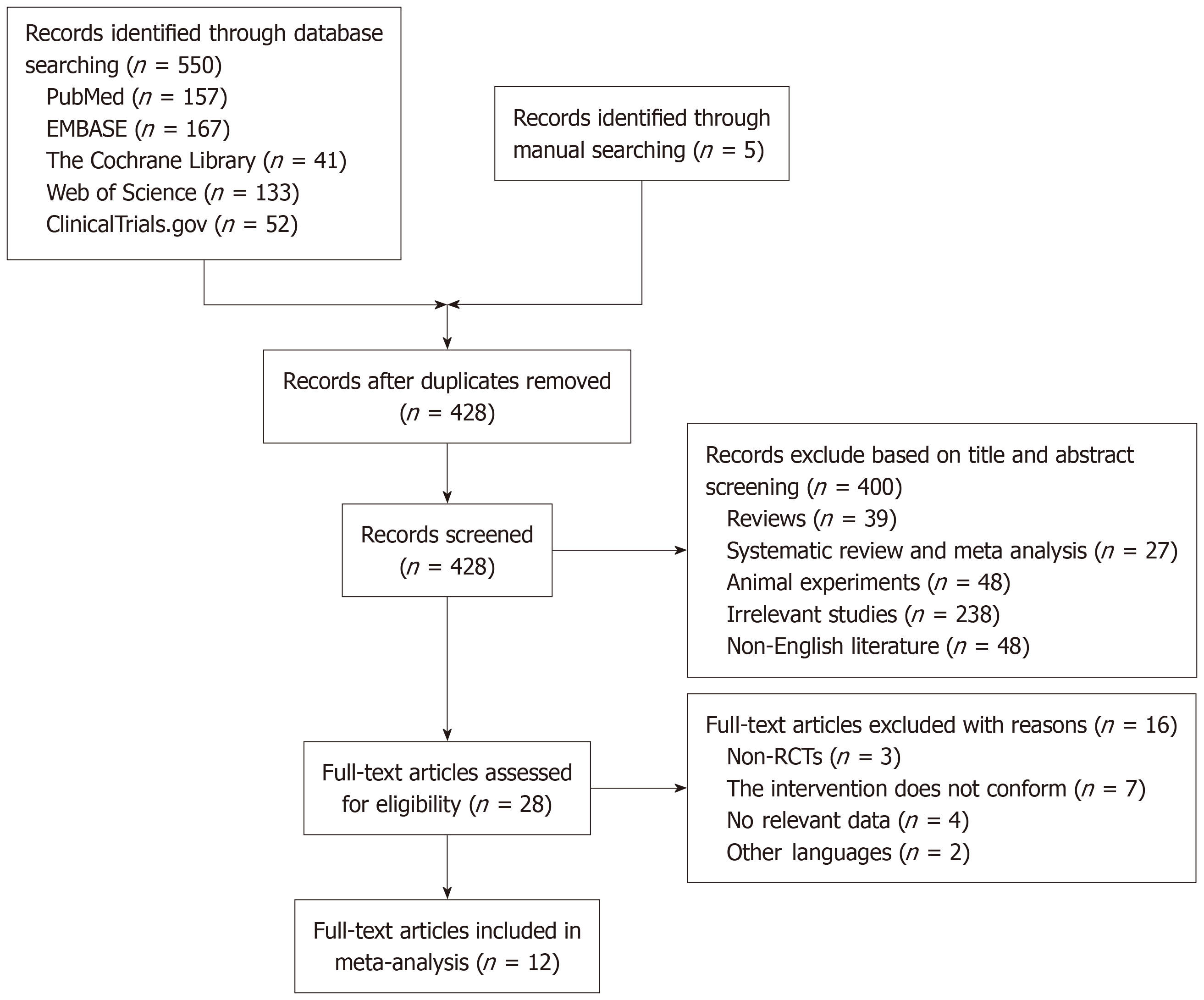
Figure 1 Literature screening process.
RCT: Randomized controlled trial.
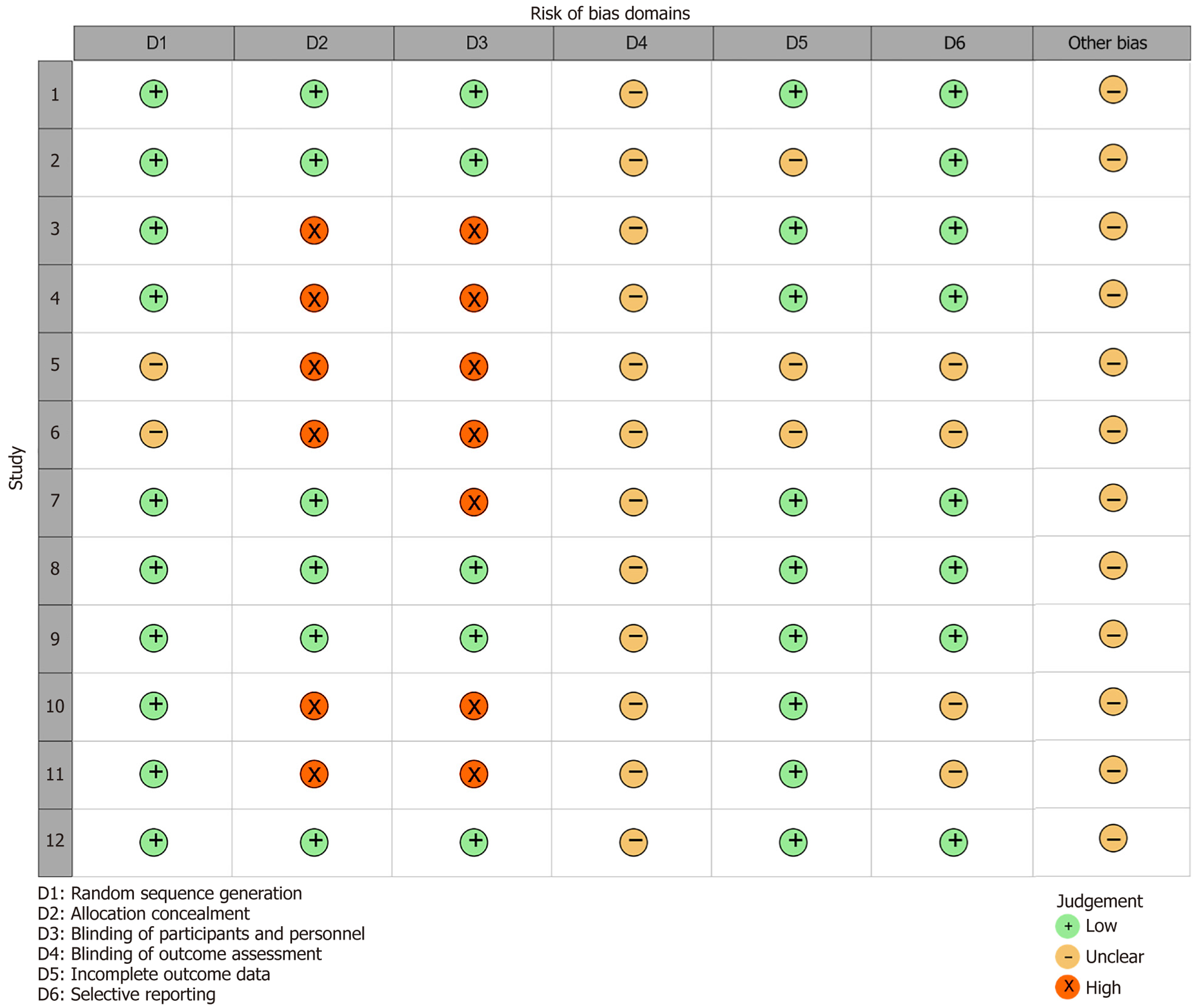
Figure 2 Results of risk of bias assessment for 12 included studies.
The column of numbers on the left side of the figure corresponds to the literature ID in Table 2.
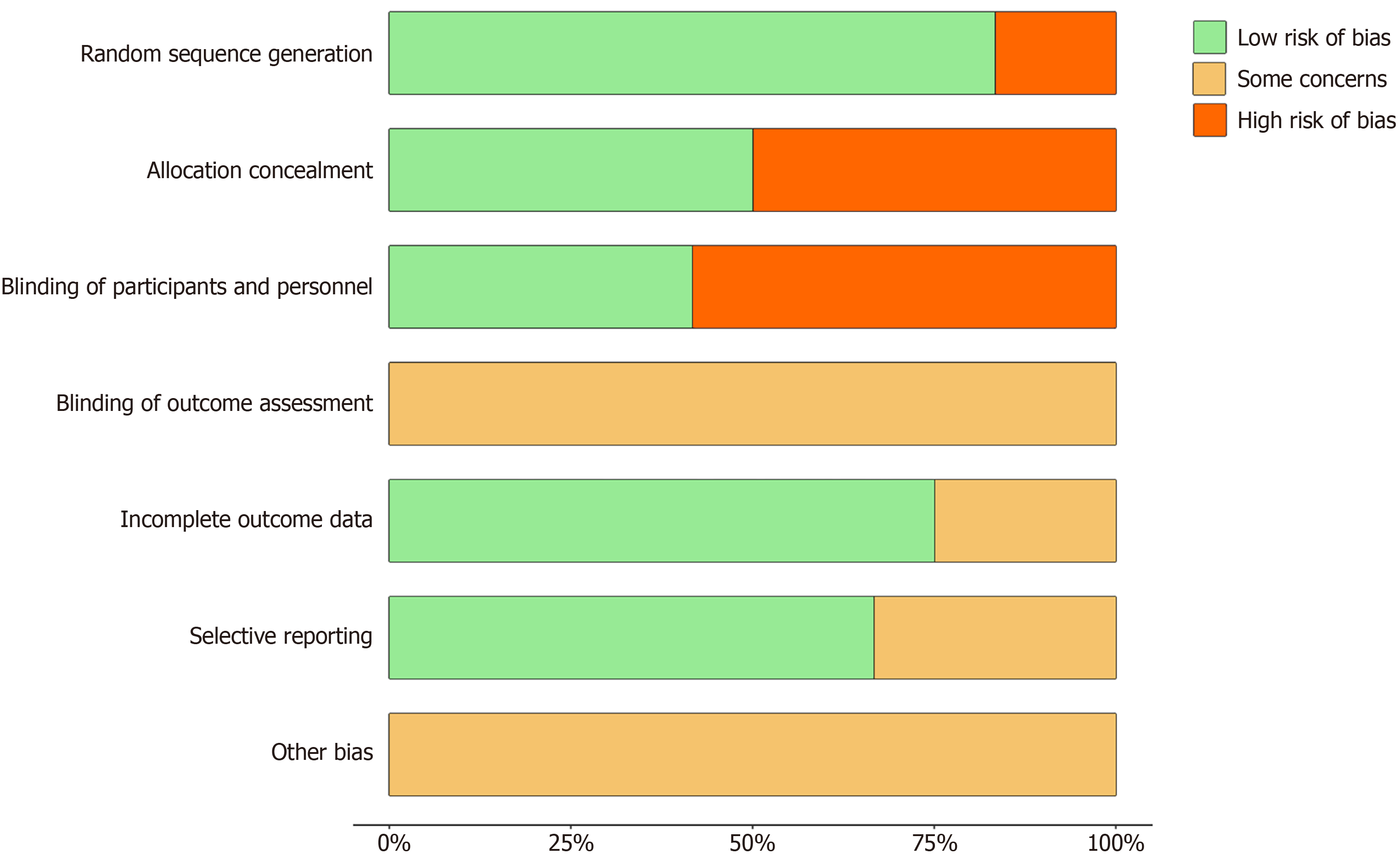
Figure 3 Results of overall risk of bias assessment for 12 included studies.
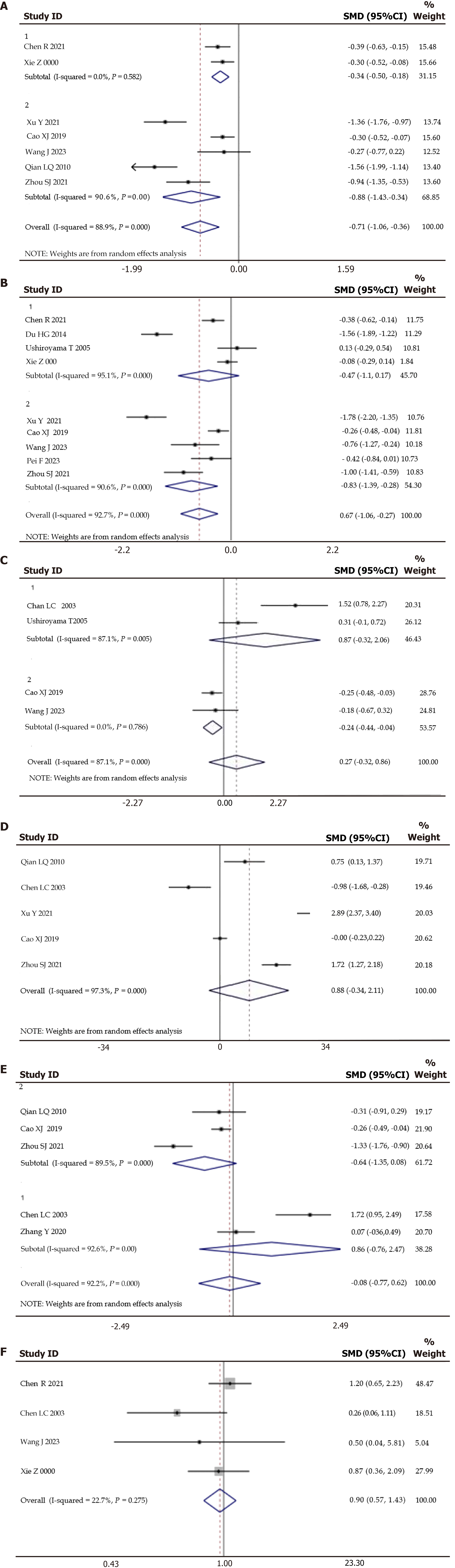
Figure 4 Forest plot of meta-analysis.
A: Anxiety symptom scores; B: Depression symptom scores; C: Greene scores; D: Estradiol level; E: Follicle-stimulating hormone level; F: Adverse reactions. 1: Treatment group using liver-soothing formulas alone; 2: Treatment group combining liver-soothing formulas with other treatments/interventions. SMD: Standardized mean difference; 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; OR: Odds ratio.
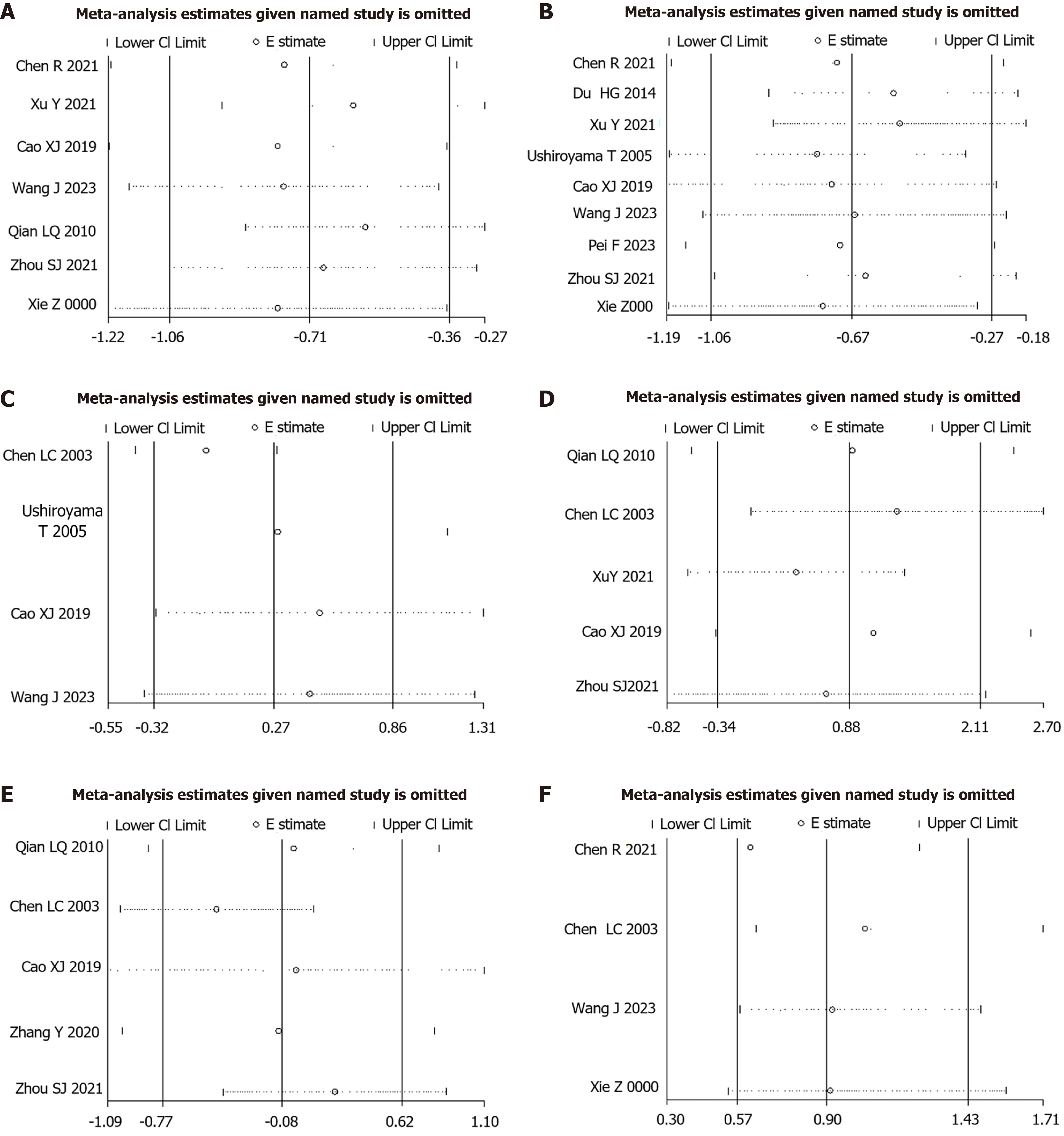
Figure 5 Sensitivity analysis.
A: Anxiety symptom scores; B: Depression symptom scores; C: Greene scores; D: Estradiol level; E: Follicle-stimulating hormone level; F: Adverse reactions. CI: Confidence interval.
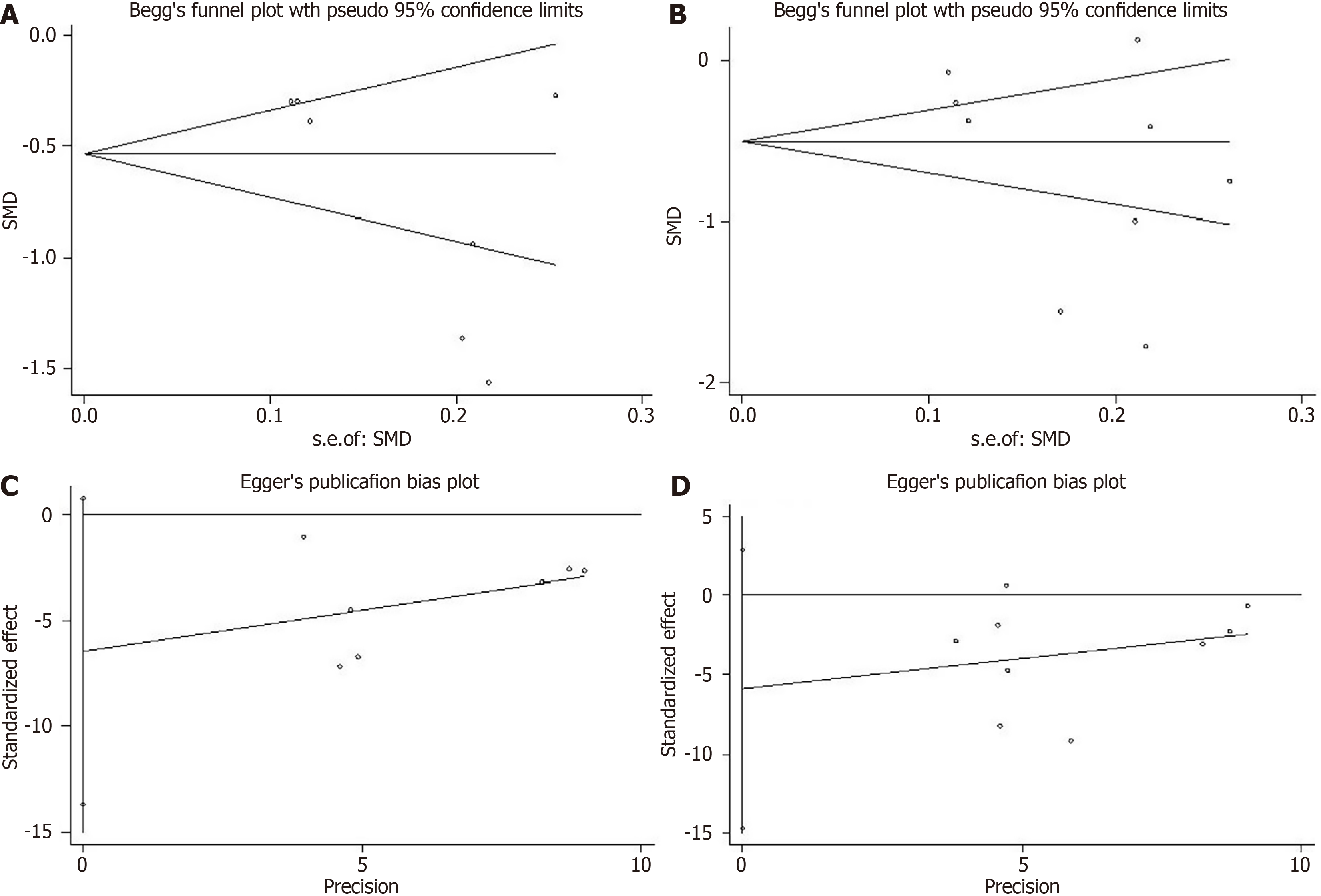
Figure 6 Begg's rank correlation test and Egger's linear regression test.
A: Begg's rank correlation test for publication bias of anxiety scores; B: Begg's rank correlation test for publication bias of depression scores; C: Eegg's rank correlation test for publication bias of anxiety scores; D: Eegg's rank correlation test for publication bias of depression scores. SMD: Standardized mean difference.
- Citation: Wang R, Wu MX, Wang XF, Chen ZT. Meta-analysis on the efficacy of liver-soothing formulas for perimenopausal anxiety and depression. World J Psychiatry 2026; 16(1): 111471
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v16/i1/111471.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v16.i1.111471