©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jul 19, 2025; 15(7): 105992
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.105992
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.105992
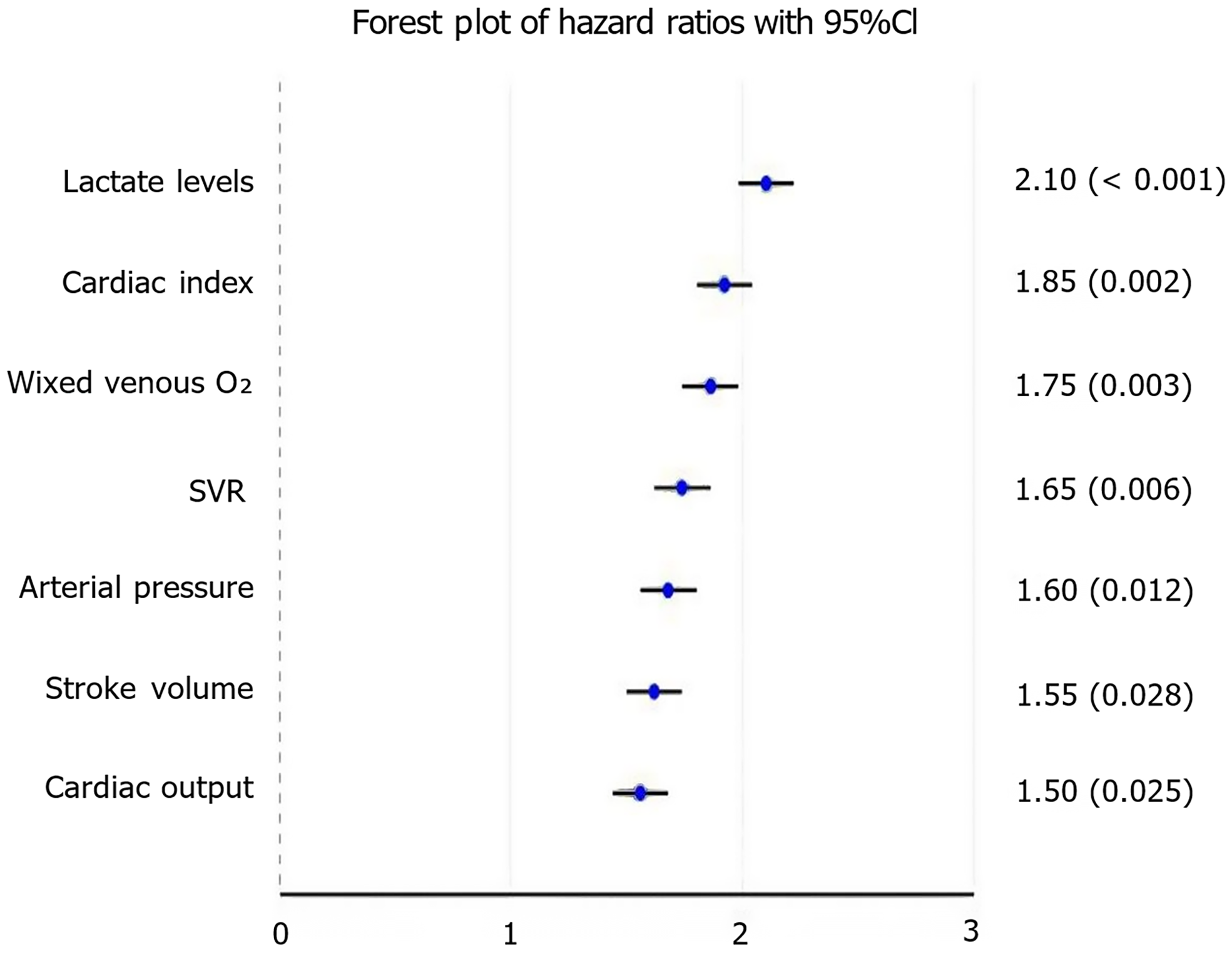
Figure 1 Multivariate analysis.
Lower cardiac index [hazard ratio (HR): 1.85; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.25-2.75; P = 0.002] and mean arterial pressure (HR: 1.60; 95%CI: 1.10-2.30; P = 0.012) were associated with increased delirium risk. Reduced cardiac output (HR: 1.50; 95%CI: 1.05-2.15; P = 0.025) was linked to higher anxiety severity. Elevated lactate levels (HR: 2.10; 95%CI: 1.40-3.15; P < 0.001) were correlated with overall neuropsychiatric symptom severity. Higher systemic vascular resistance (HR: 1.65; 95%CI: 1.15-2.35; P = 0.006) was associated with cognitive impairment. Higher pulmonary artery wedge pressure (HR: 1.45; 95%CI: 1.00-2.10; P = 0.048) was linked to poorer sleep quality. Lower mixed venous oxygen saturation (HR: 1.75; 95%CI: 1.20-2.55; P = 0.003) was associated with more severe overall symptoms. CI: Confidence interval; SVR: Systemic vascular resistance.
- Citation: Li HN, Wang JL, Chen W. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in the context of hemodynamic disruption during septic shock. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(7): 105992
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i7/105992.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.105992