©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Jul 19, 2025; 15(7): 104812
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.104812
Published online Jul 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.104812
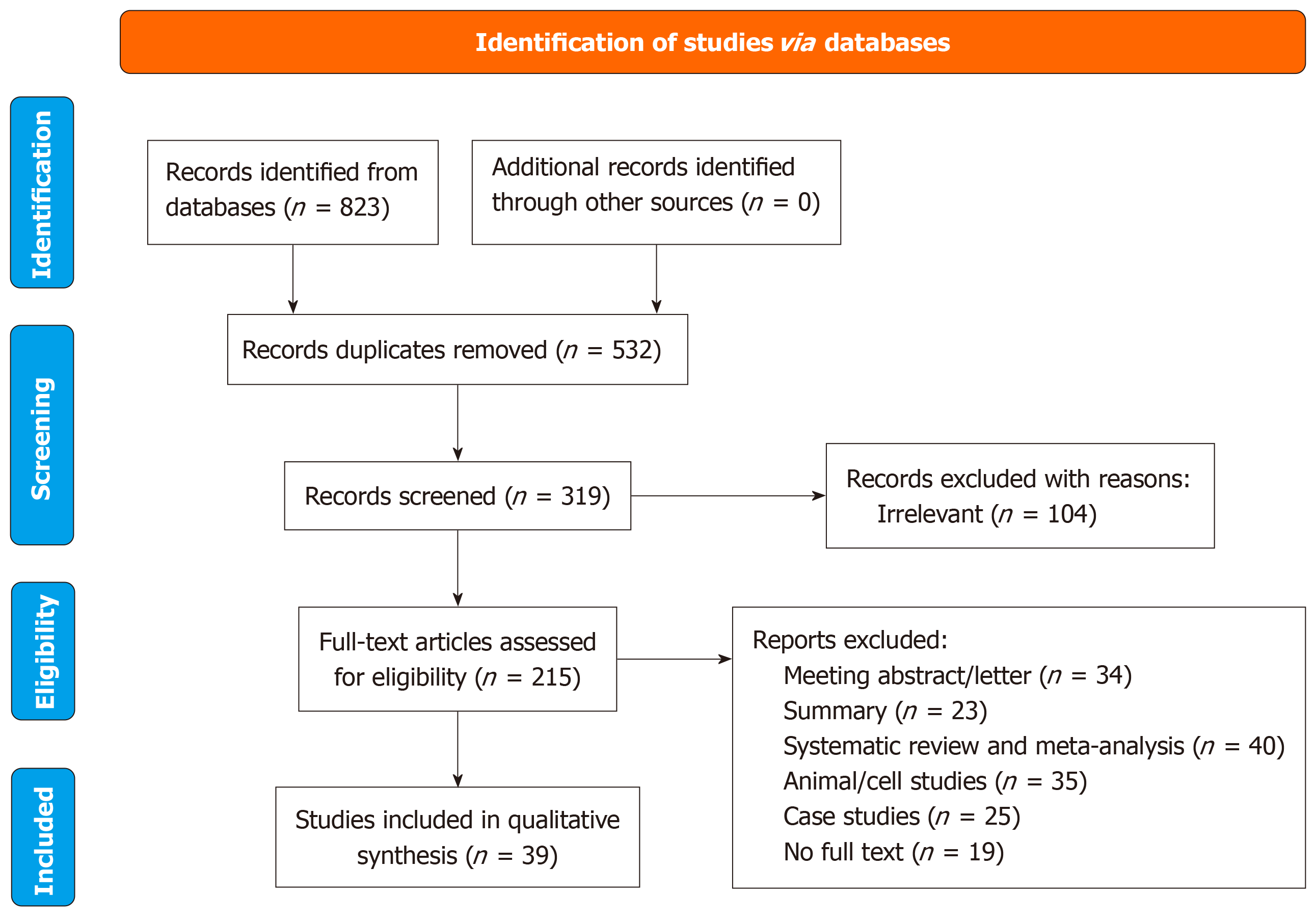
Figure 1 Literature retrieval process.
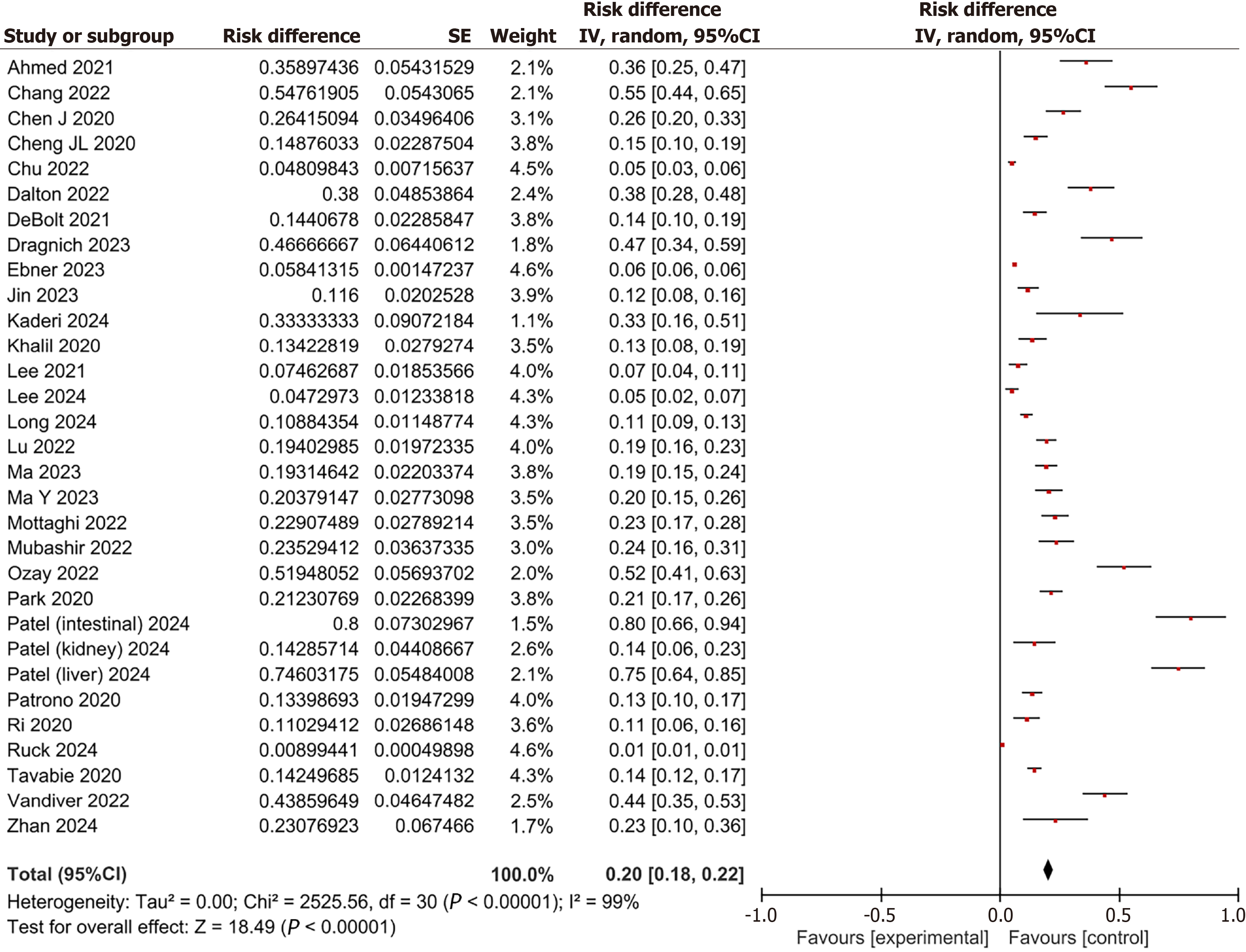
Figure 2 Meta-analysis of the incidence of postoperative delirium in organ transplant patients from 2020 to 2024.
CI: Confidence interval.
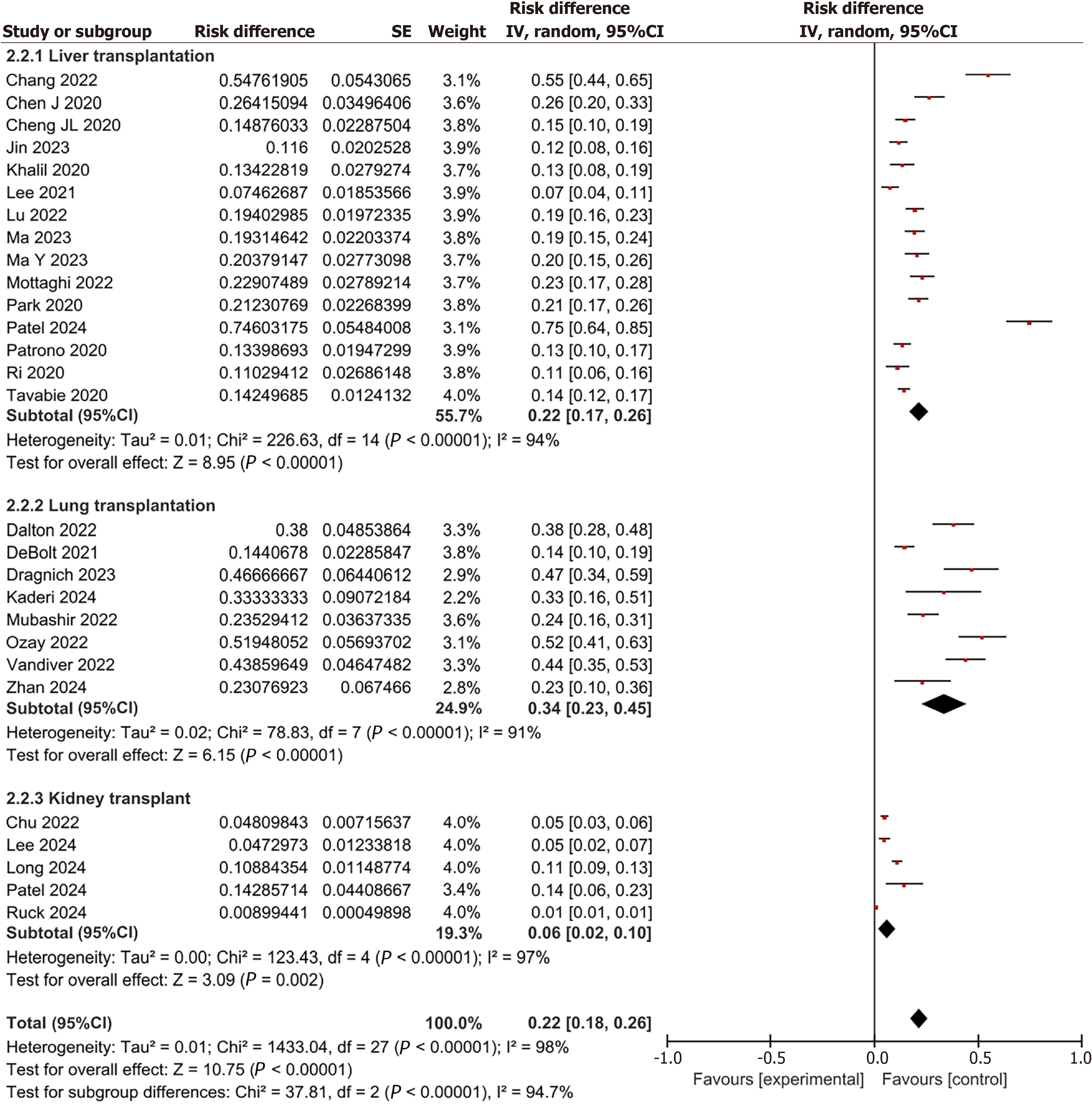
Figure 3 Subgroup analysis of the incidence of postoperative delirium in patients undergoing liver, lung, and kidney transplantations.
CI: Confidence interval.
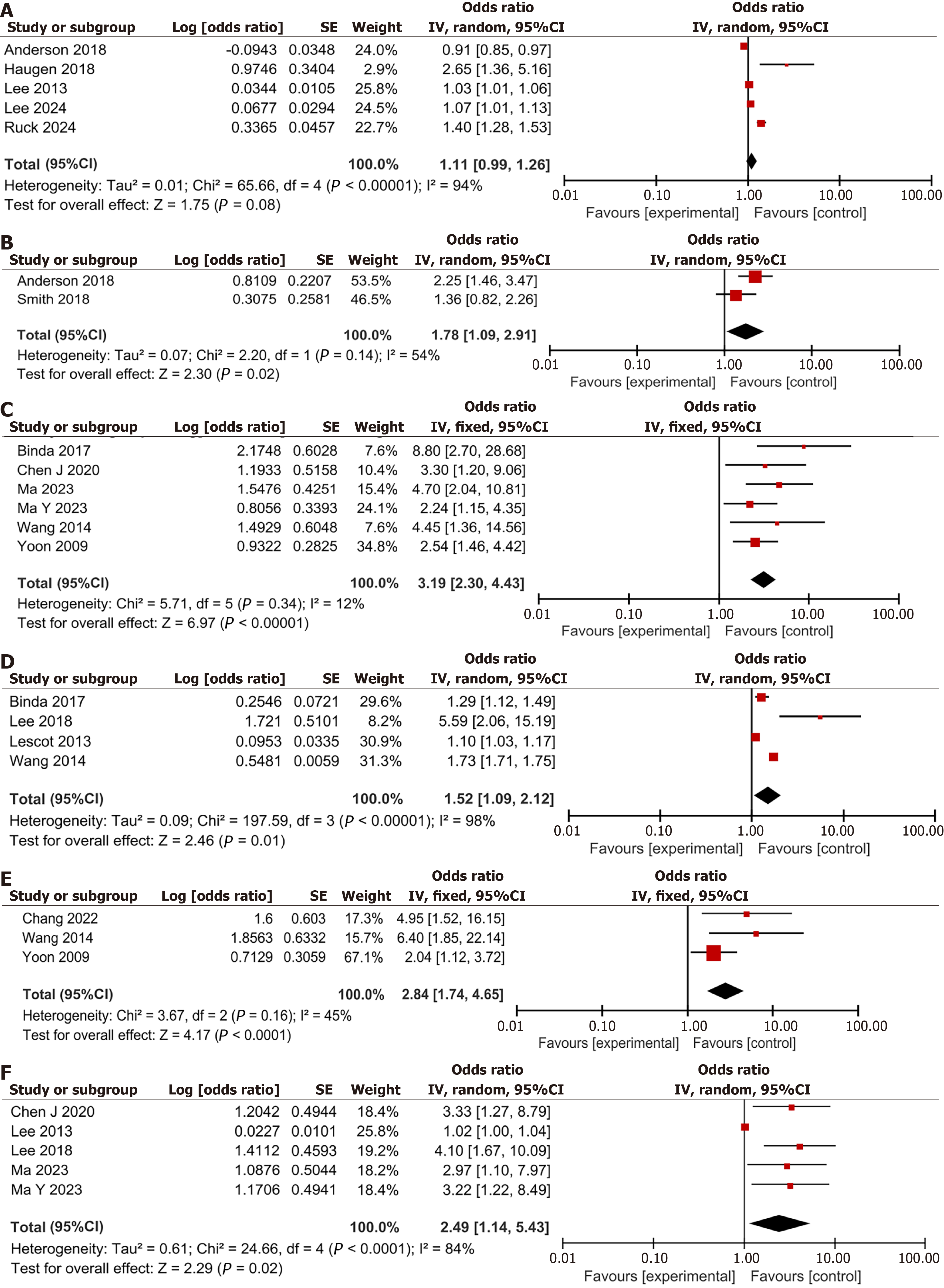
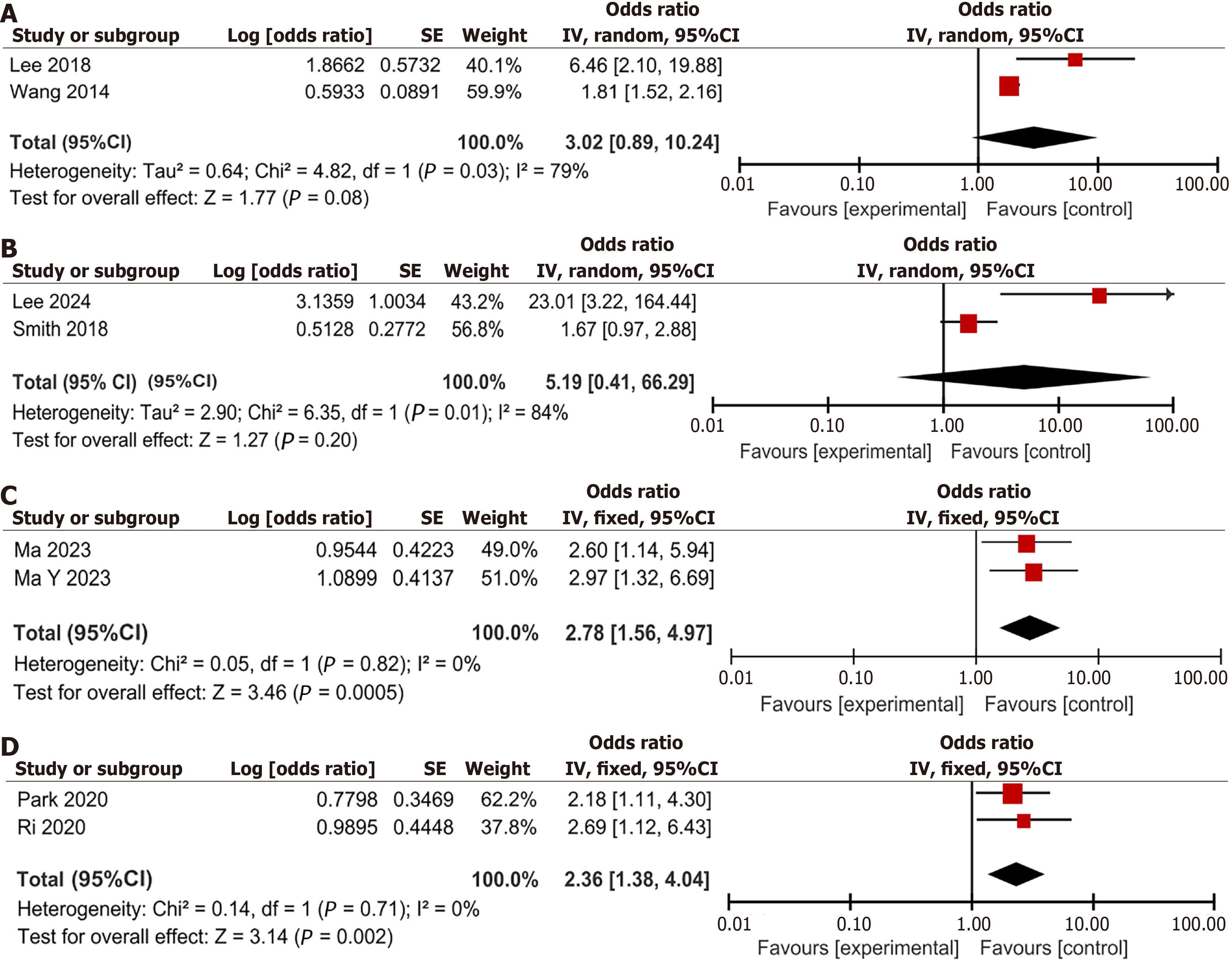
Figure 4 Forest plot of patient-related factors.
A: Age; B: Primary graft dysfunction; C: History of hepatic encephalopathy; D: Acute Physiologic and Health Evaluation II score; E: Alcohol abuse history; F: Model for end stage liver disease score. CI: Confidence interval.
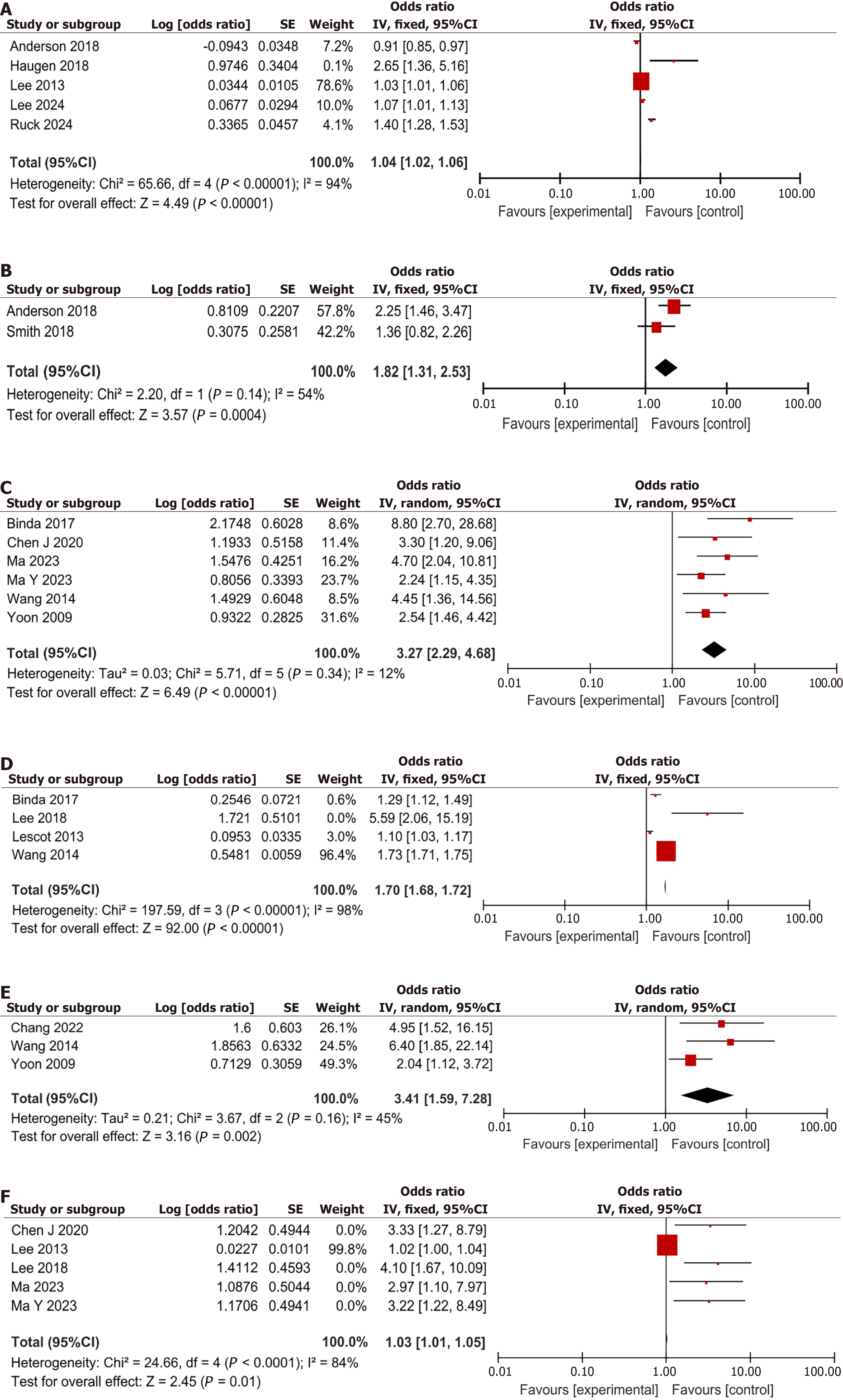
Figure 5 Forest plot of operative related factors.
A: Endotracheal intubation (day); B: Psychotropic medications use; C: Preoperative infections; D: With diuretics. CI: Confidence interval.
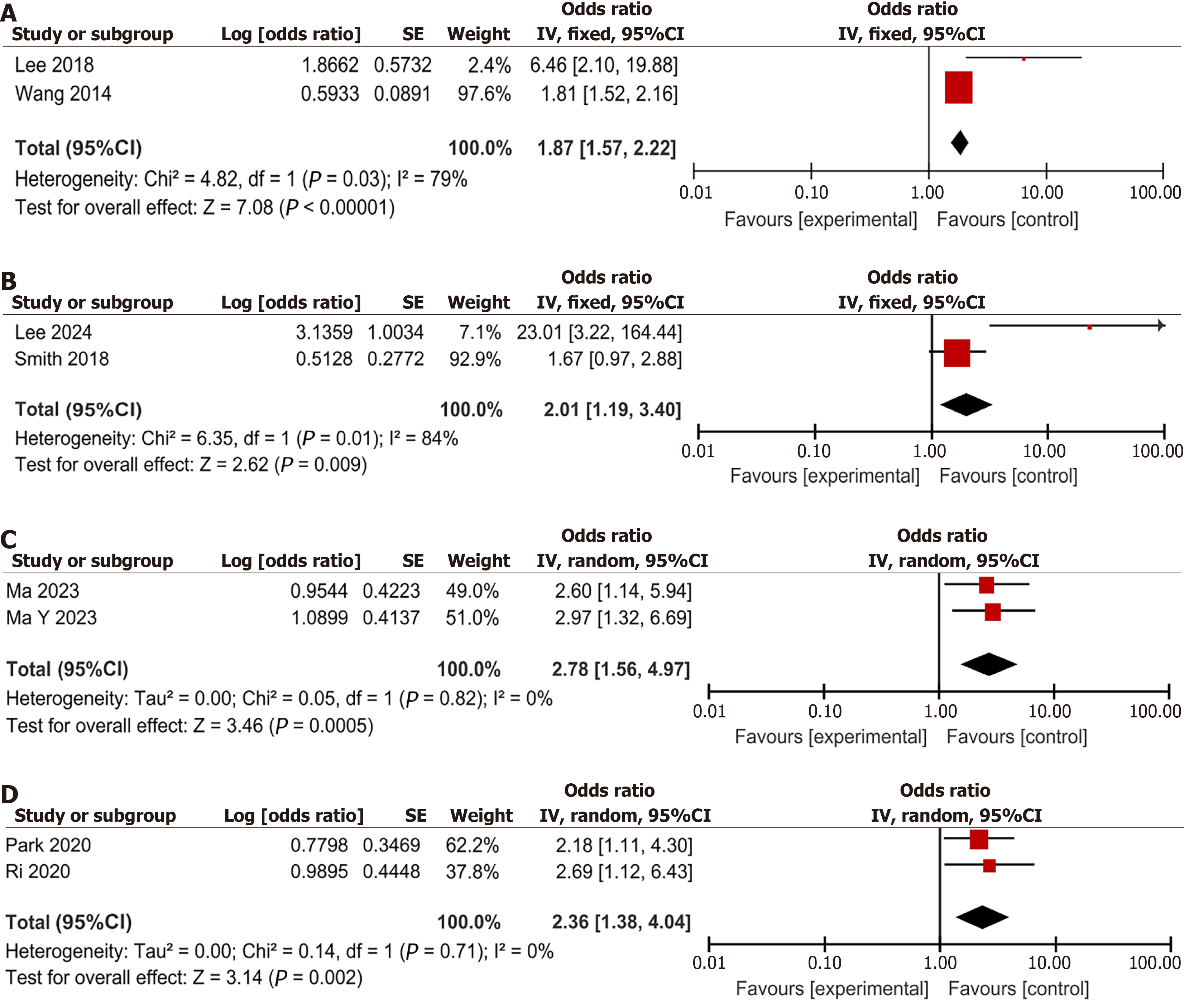
Figure 6 Sensitivity analysis of patient-related factors.
A: Age; B: Primary graft dysfunction; C: History of hepatic encephalopathy; D: Acute Physiologic and Health Evaluation II score; E: Alcohol abuse history; F: Model for end stage liver disease score. CI: Confidence interval.
Figure 7 Sensitivity analysis of operative related factors.
A: Endotracheal intubation (day); B: Psychotropic medications use; C: Preoperative infections; D: With diuretics. CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Hou SS, Liu J, Qiao PF, Yang DG, Huang LF, Liu F, Liu Y, Jia TT, Wang HL. Meta-analysis of the incidence and risk factors of postoperative delirium in organ transplant patients. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(7): 104812
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i7/104812.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i7.104812