©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2025; 15(3): 100103
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.100103
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.100103
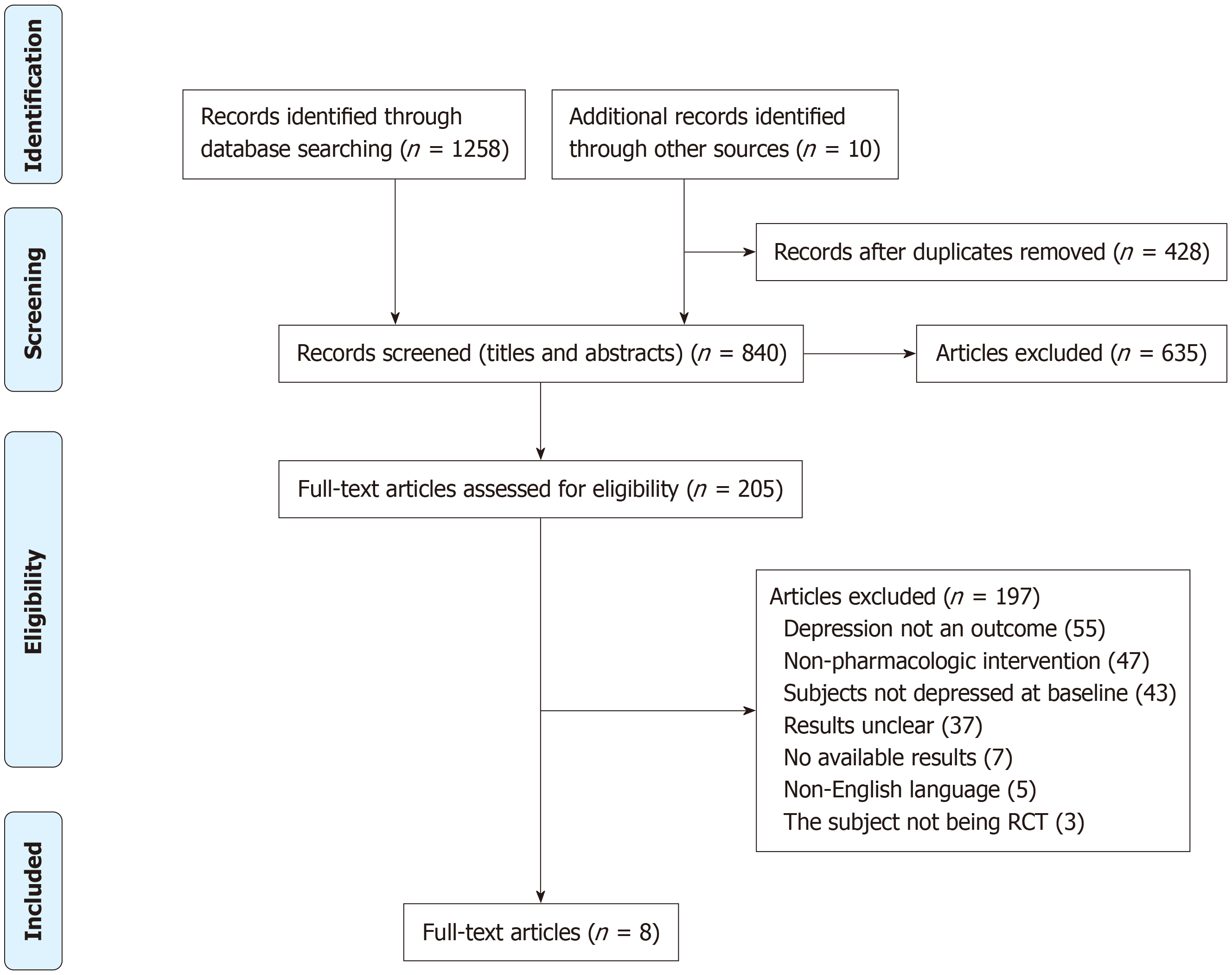
Figure 1 Studies included and excluded from the meta-analysis according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
RCT: Randomized clinical trial.
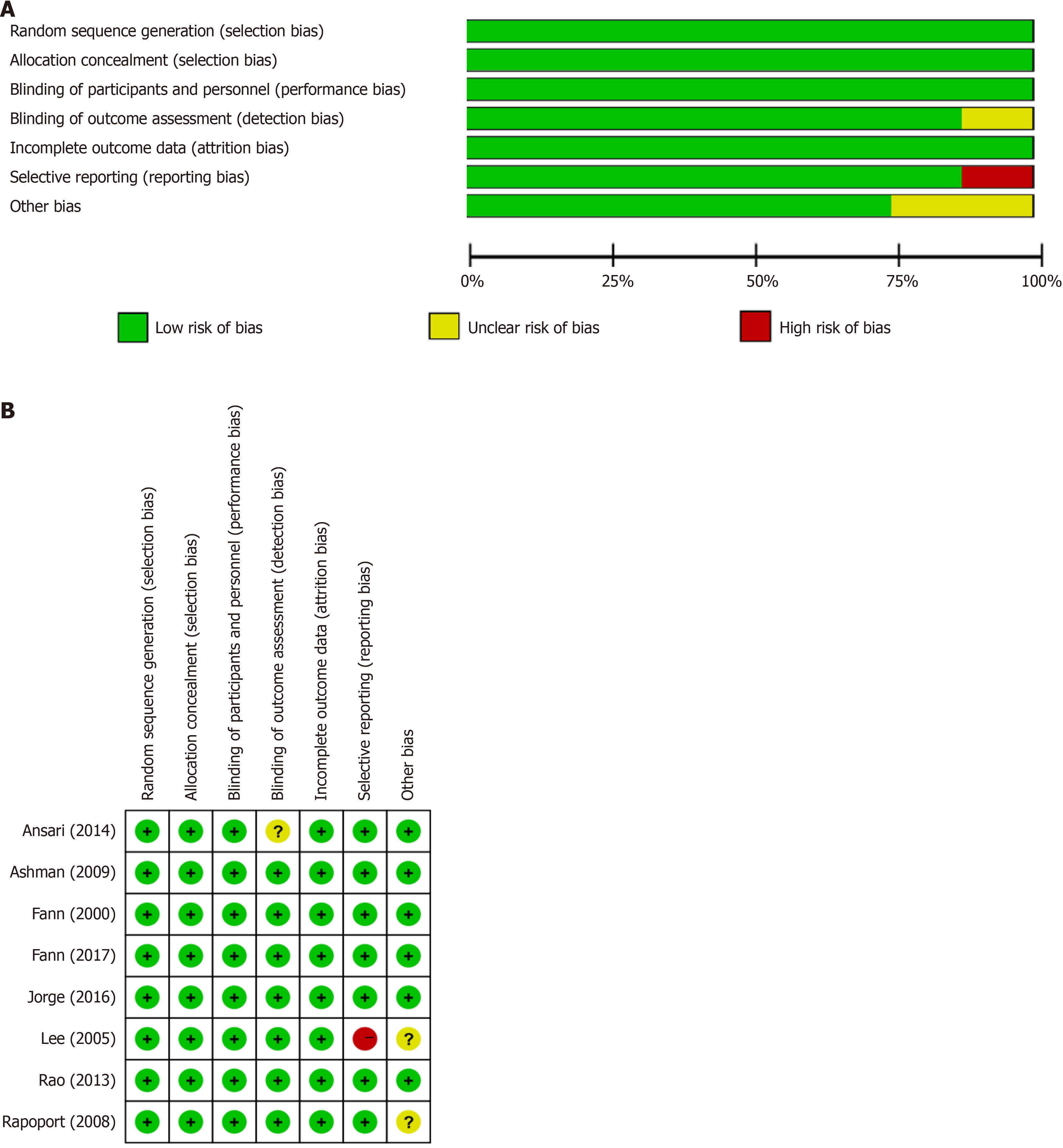
Figure 2 Risk of bias in included studies.
A: Risk of bias summary: Each bias risk item of all included studies was judged by review authors; B: Risk of bias graph: The review authors quantified each bias risk item of included studies as a percentage. The risk of bias assessment for each included study in accordance with “Cochrane RoB 2”. Low risk (+), unclear (?), and high risk (-).
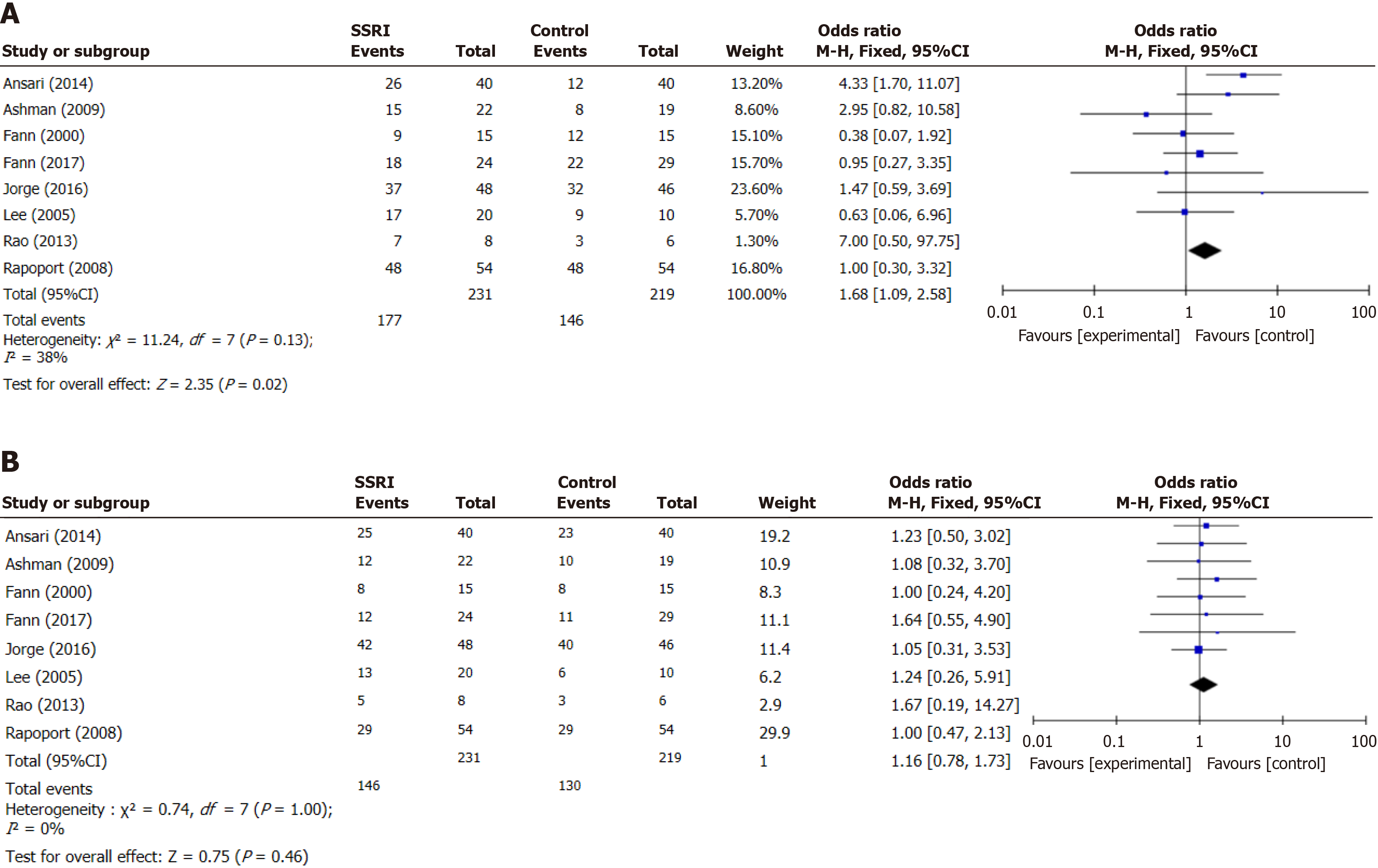
Figure 3 Forest plot of major depressive disorder after selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor treatment of traumatic brain injury.
A: Forest plot of the reduction in depression scores of major depressive disorder (MDD) after selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI); B: Forest plot of the incidence of adverse reactions in SSRI-treated MDD after TBI. Diamond: Pooled estimate; squares: Individual study effects; horizontal lines: Confidence intervals; MDD: Major depressive disorder; SSRI: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor.
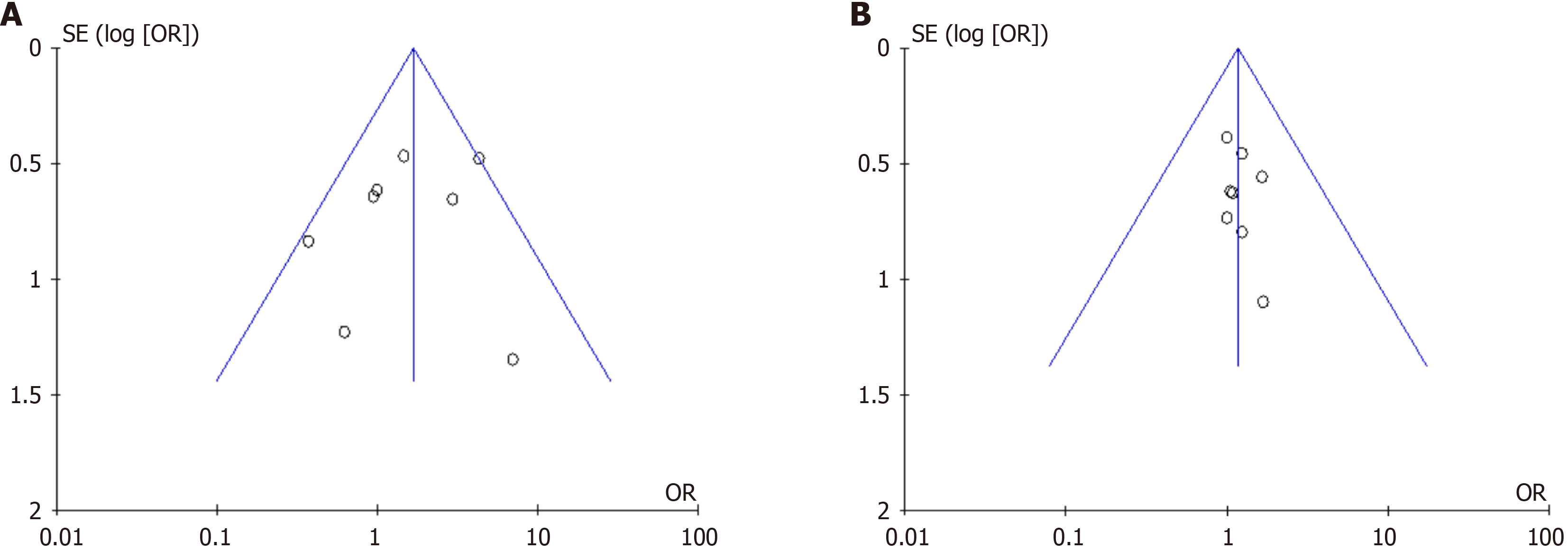
Figure 4 The funnel plot of this study.
A: The reduction in depression scores of major depressive disorder; B: Adverse reactions. OR: Odds ratio.
- Citation: Gao RX, Zhang XN, Zhu P. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in the treatment of major depressive disorder after brain trauma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(3): 100103
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i3/100103.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.100103