©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Nov 19, 2025; 15(11): 107604
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.107604
Published online Nov 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.107604
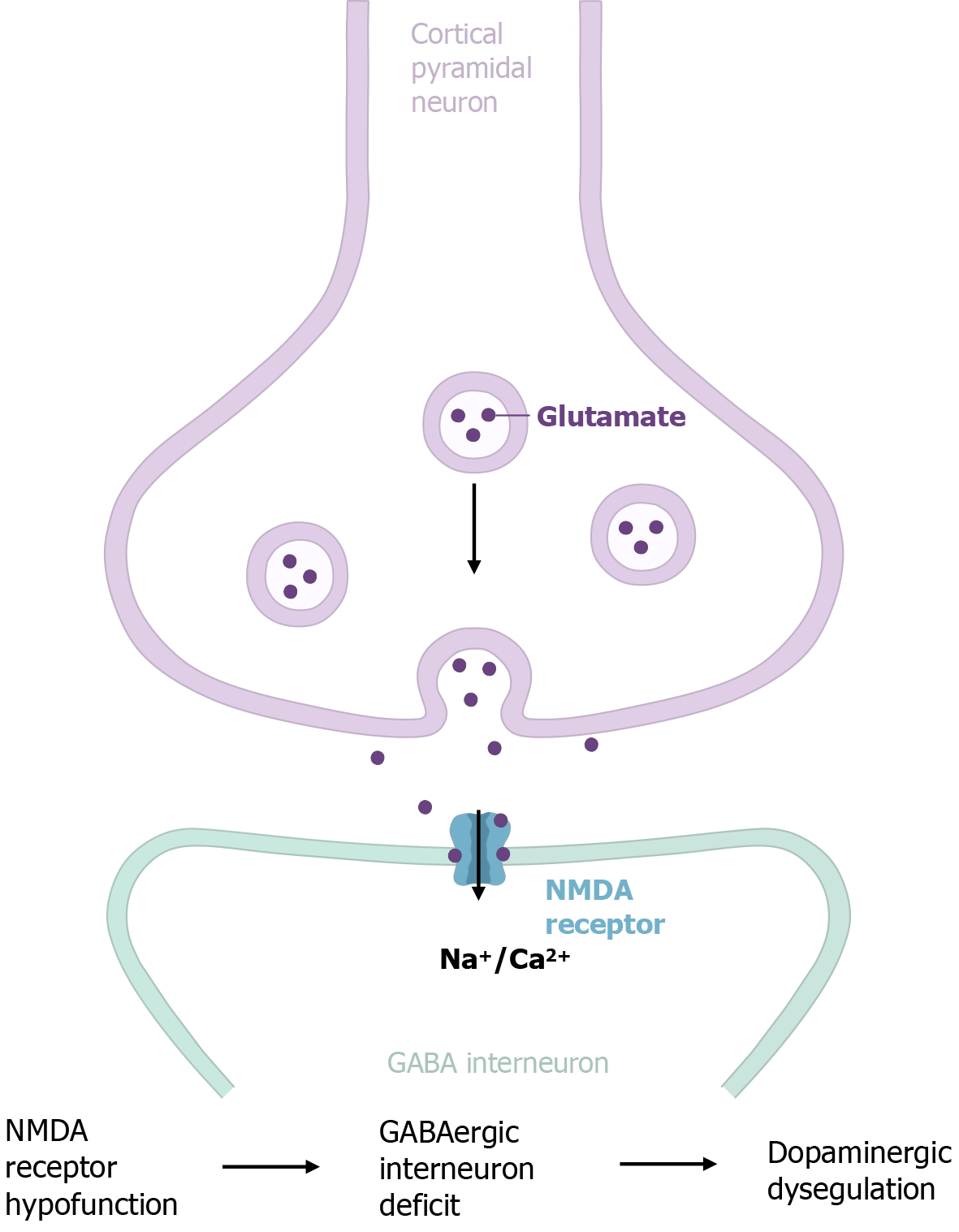
Figure 1 N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor hypofunction-induced GABAergic disruption and dopaminergic dysregulation in schizophrenia.
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor hypofunction on GABAergic interneurons disrupts the excitatory-inhibitory balance in cortical circuits, leading to excessive glutamatergic activity. This imbalance impairs neural synchrony and information processing, contributing to positive and cognitive symptoms. Furthermore, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor dysfunction induces deficits in GABAergic interneurons, resulting in aberrant local circuit dynamics and long-range disconnections, including dysregulation of the dopamine system. NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate; GABA: Gamma aminobutyric acid.
- Citation: Cheng BF, Liang Y, Wu Q. Unraveling the mysteries of schizophrenia: Insights into prefrontal cortex dysfunction and therapeutic implications. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(11): 107604
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i11/107604.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i11.107604