©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Aug 19, 2024; 14(8): 1254-1266
Published online Aug 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1254
Published online Aug 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1254
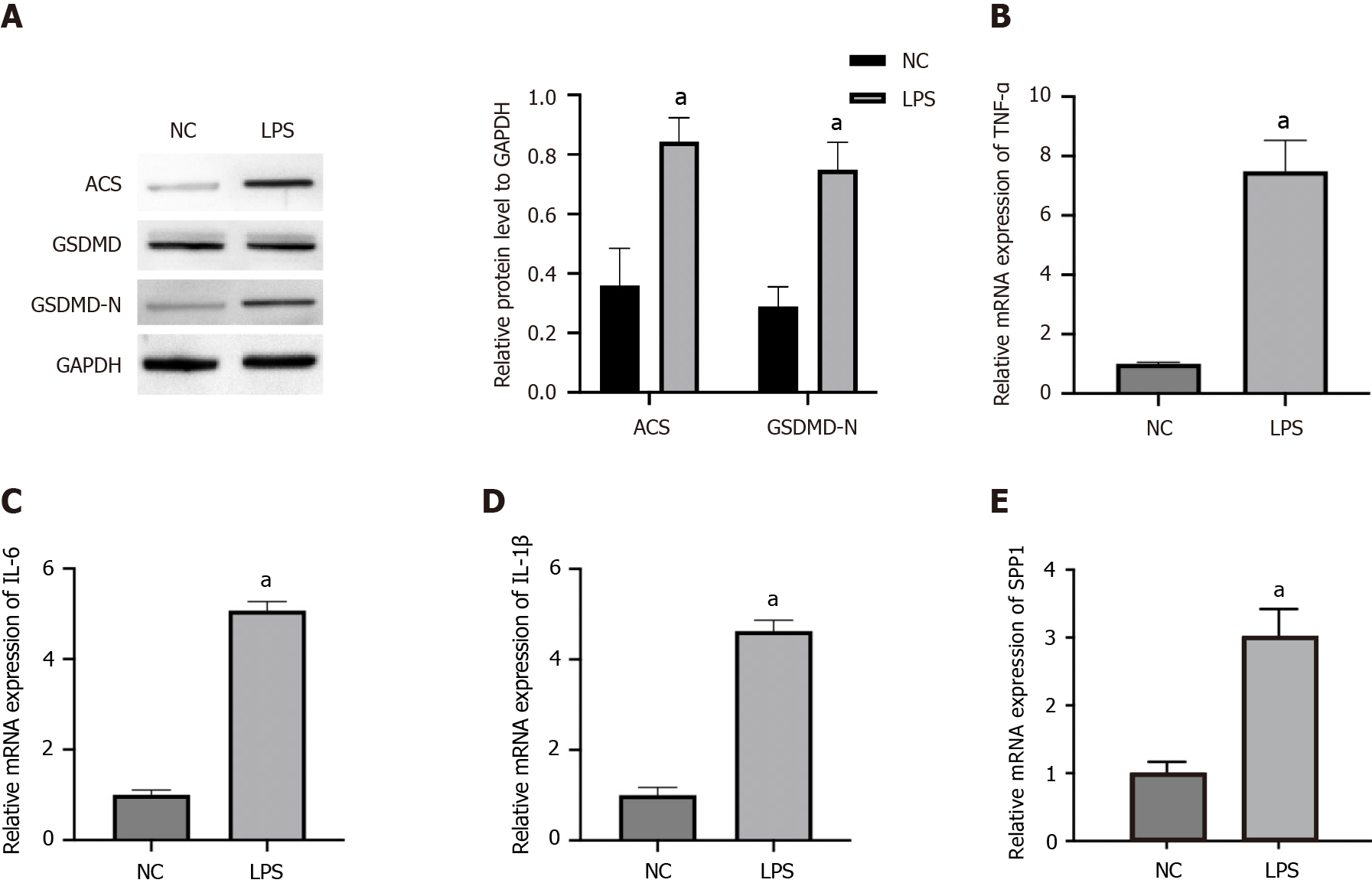
Figure 1 SPP1 and pyroptosis are activated in lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia.
A-E: The microglia were treated with lipopolysaccharide. The expression of ACS, GSDMD, and GSDMD-N was measured by western blot (A). The levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (B-D). The expression of SPP1 was analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (E). aP < 0.001. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; NC: Negative control.
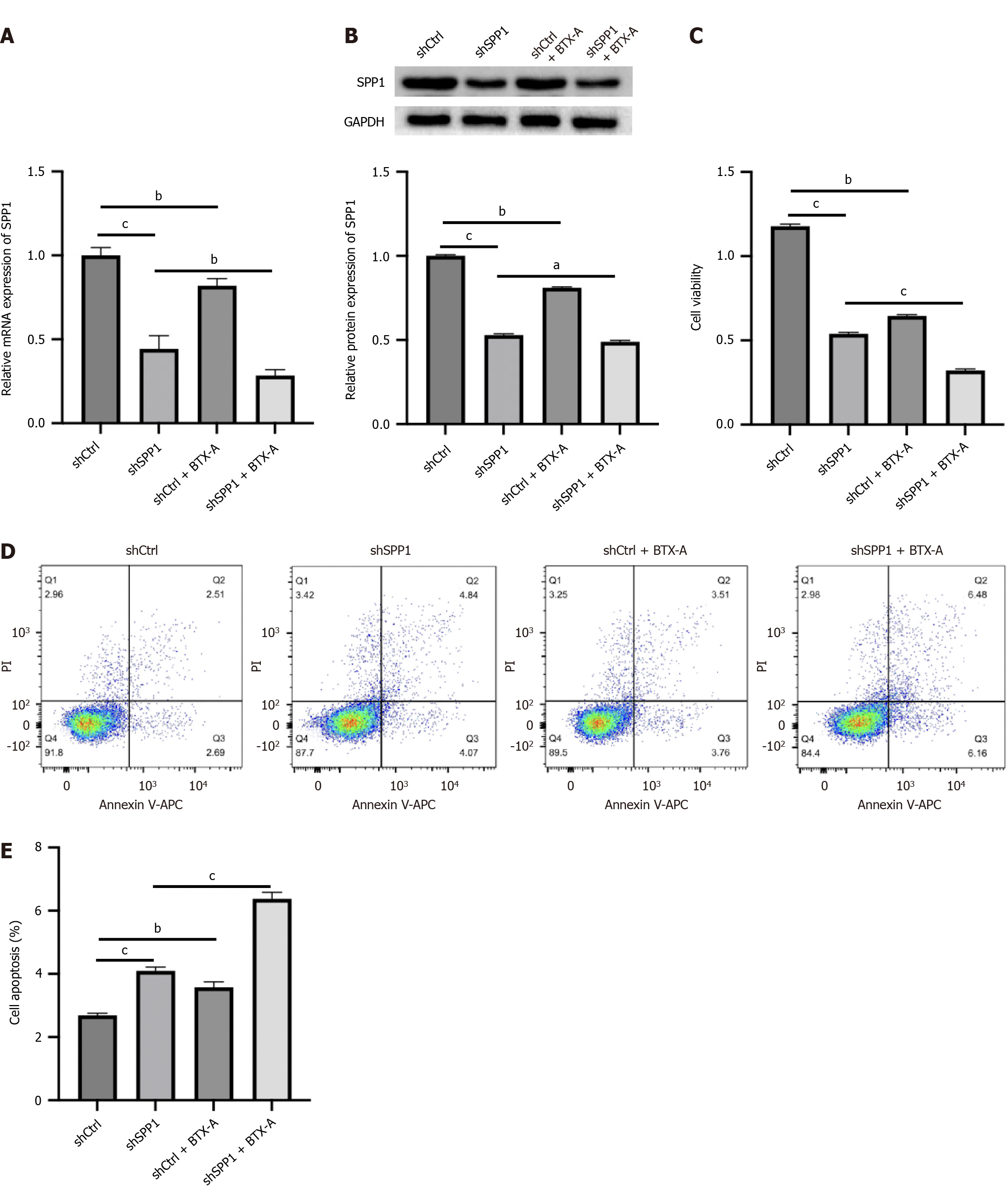
Figure 2 SPP1 targeted by botulinum toxin type A promotes proliferation and represses apoptosis of lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia.
A-E: Lipopolysaccharide-treated microglia were treated with control short hairpin RNA (shRNA) or SPP1 shRNA, or co-treated with botulinum toxin type A. The expression of SPP1 was analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (A). The expression of SPP1 was measured by western blot (B). Cell viability was detected by cell counting kit-8 assay (C). Cell apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry (D and E). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. BTX-A: Botulinum toxin type A.
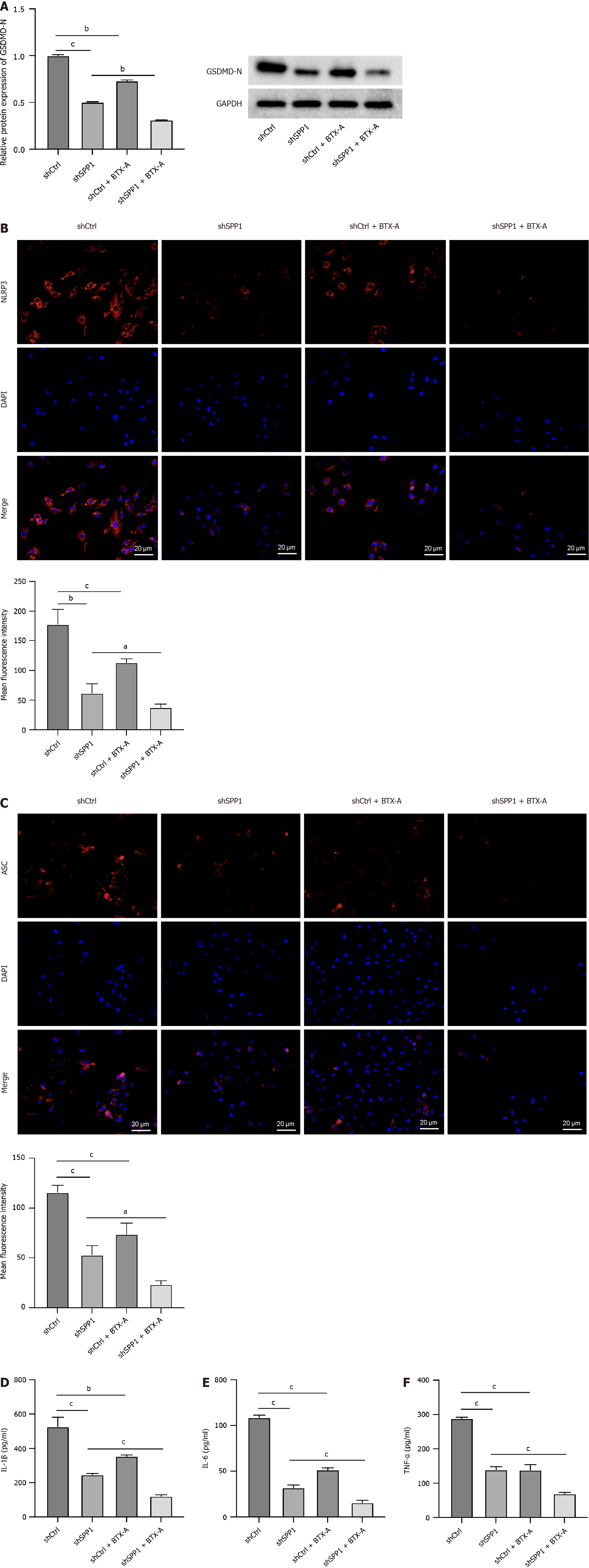
Figure 3 SPP1 targeted by botulinum toxin type A contributes to pyroptosis of lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia.
A-F: Lipopolysa
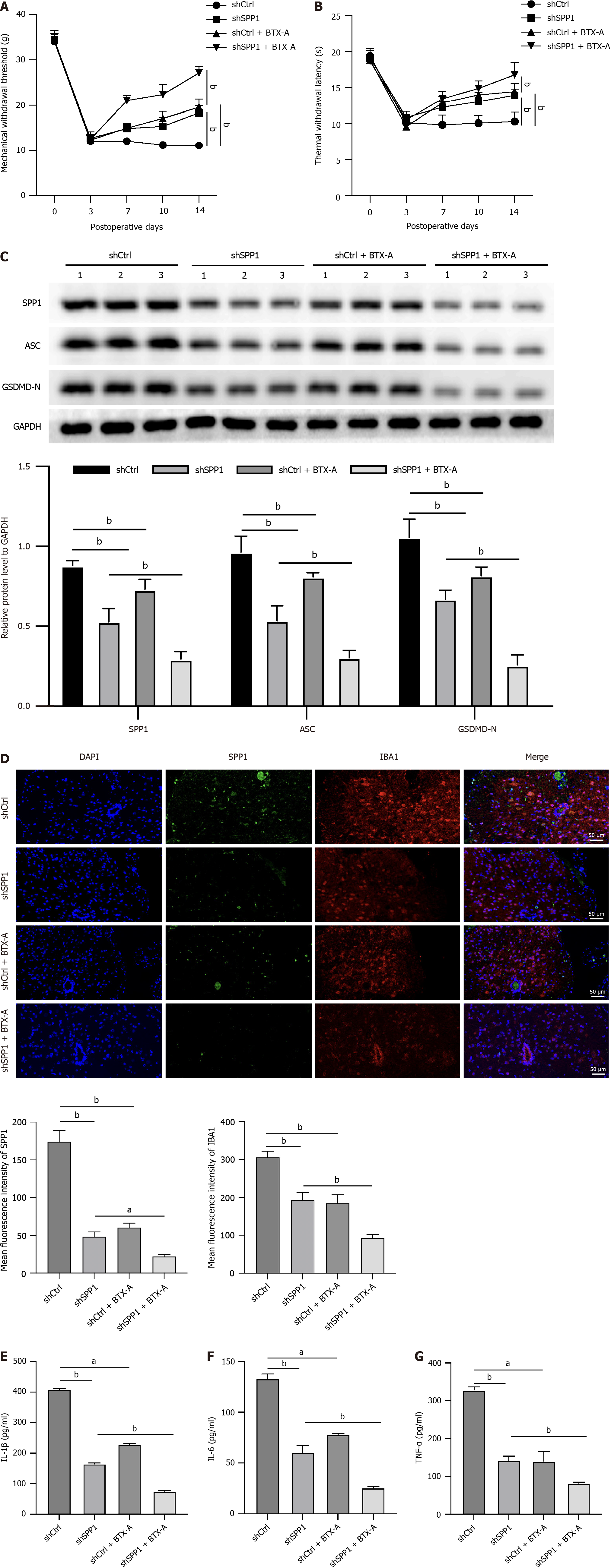
Figure 4 SPP1 targeted by botulinum toxin type A enhances microglia pyroptosis during neuropathic pain induced by spared nerve injury in rat.
A-G: The spared nerve injury model was established in SD rats and the rats were treated with control short hairpin RNA (shRNA) or SPP1 shRNA, or co-treated with botulinum toxin type A. The mechanical withdrawal threshold and thermal withdrawal latency were analyzed in the rats (A and B). The expression of SPP1, ACS, and GSDMD-N was measured by western blot in spinal cord of the rats (C). The levels of IBA1 and SPP1 were detected by immunofluorescence in spinal cord of the rats (D). The levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-1β were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (E-G). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001. TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin; BTX-A: Botulinum toxin type A.
- Citation: Chen LP, Gui XD, Tian WD, Kan HM, Huang JZ, Ji FH. Botulinum toxin type A-targeted SPP1 contributes to neuropathic pain by the activation of microglia pyroptosis. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(8): 1254-1266
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i8/1254.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1254