©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Aug 19, 2024; 14(8): 1244-1253
Published online Aug 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1244
Published online Aug 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1244
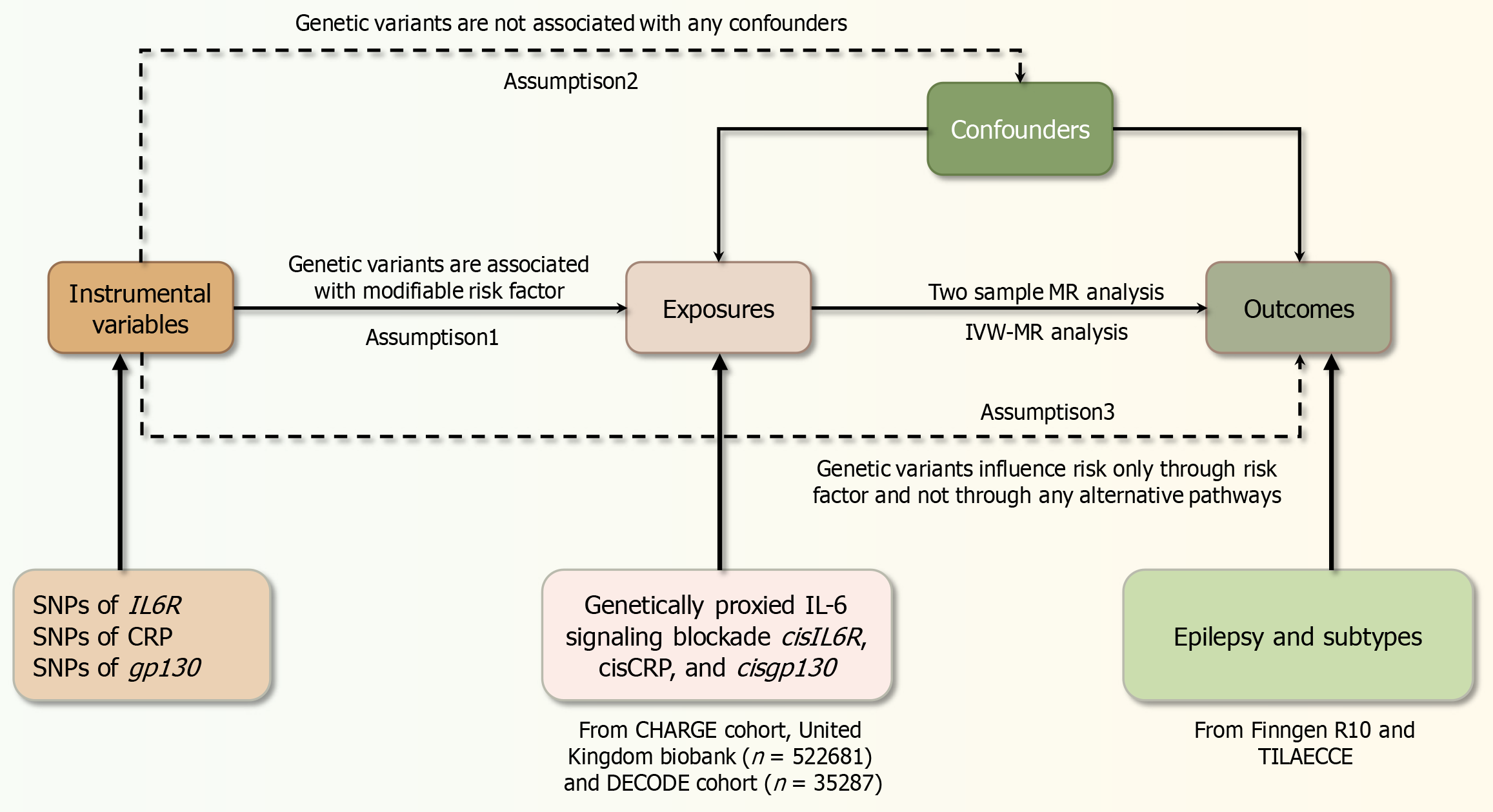
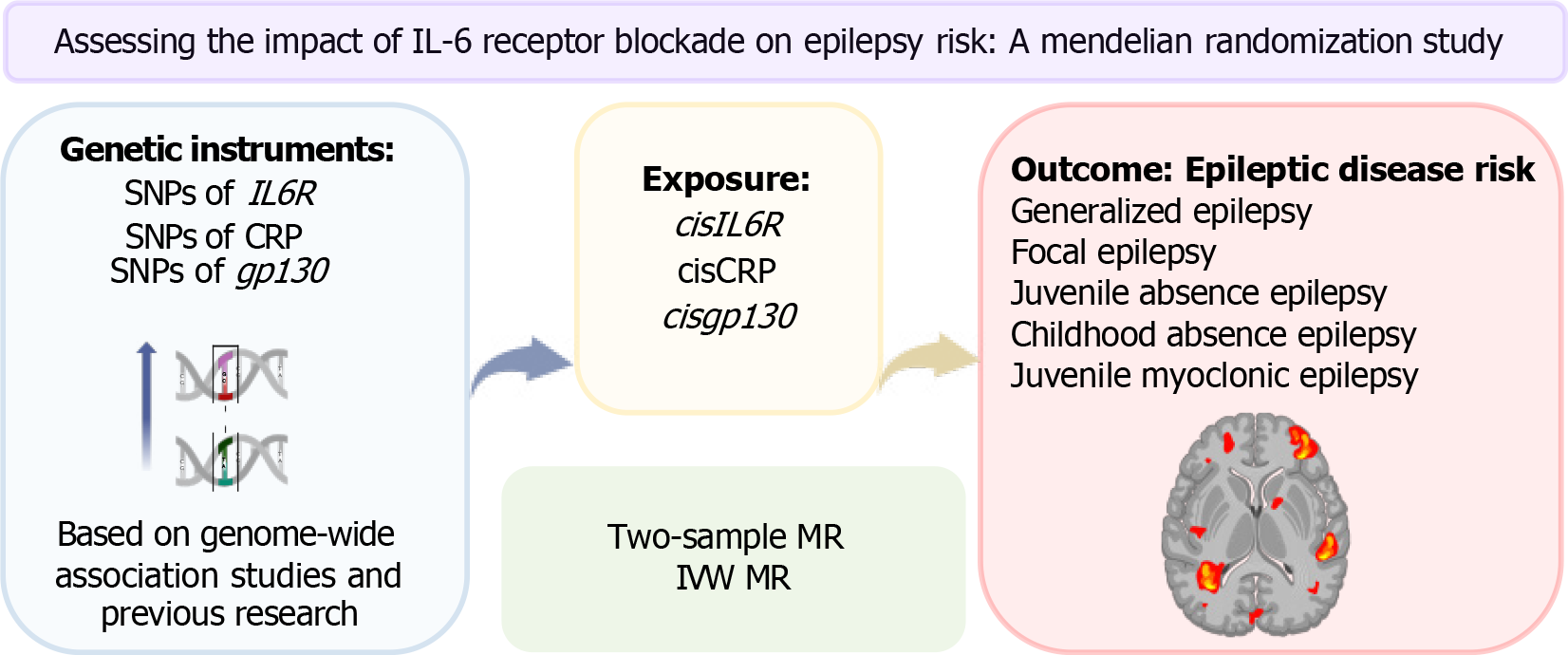
Figure 1 Summary of the study design employed in our mendelian randomization investigation.
IL: Interleukin; MR: Mendelian randomization; IVW: Inverse variance weighting; SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; IL6R: IL-6 receptor; CRP: C-reactive protein; cis: Cis-acting; gp130: Glycoprotein 130.
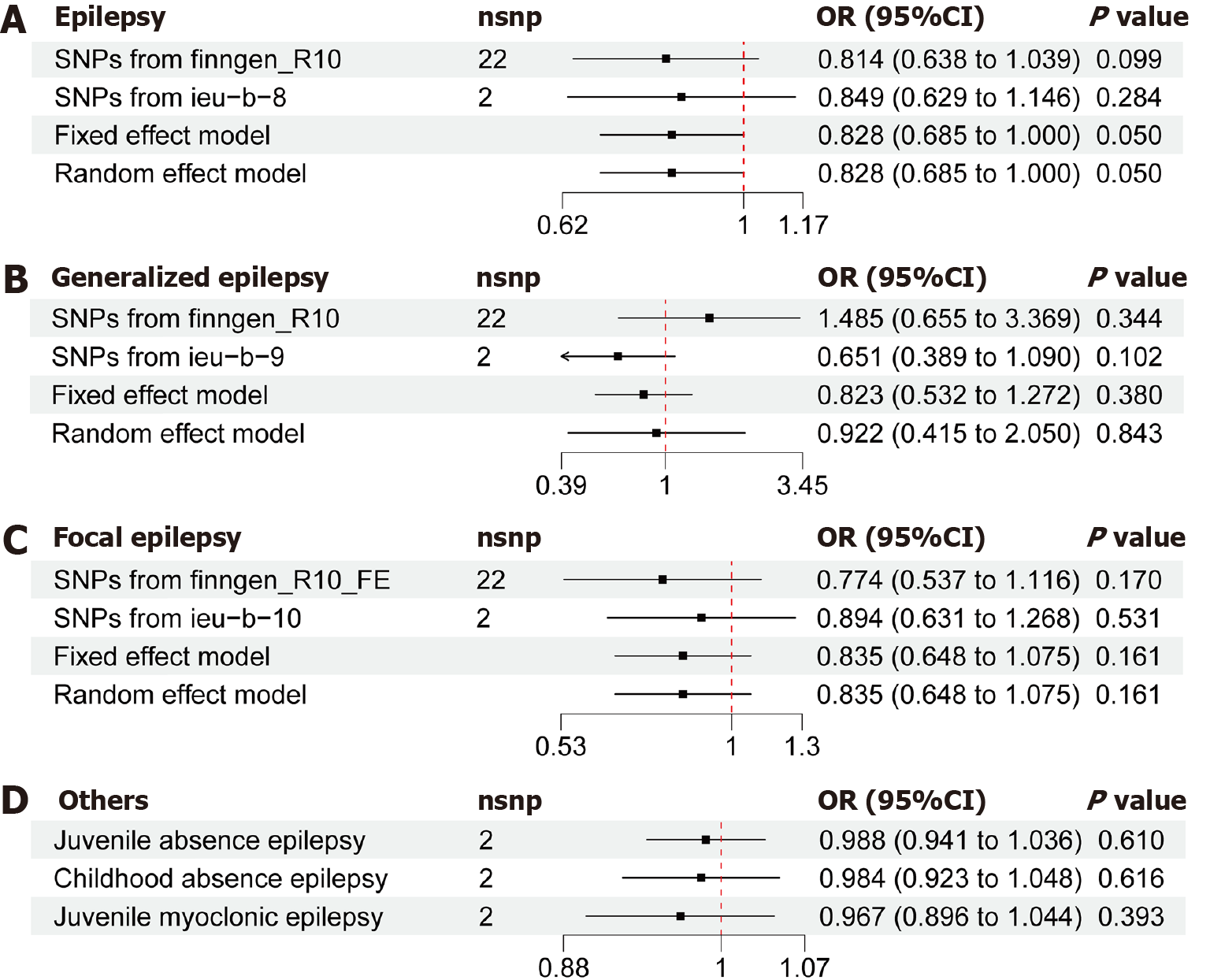
Figure 2 Correlation between genetically mediated inhibition of interleukin 6 signaling and the risk of epilepsy.
A: Forest plot displaying mendelian randomization (MR) effect estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the genetic proxied blockade effect of interleukin (IL)-6 receptor (IL6R) on epilepsy; B: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the genetic proxied blockade effect of IL6R on generalized epilepsy; C: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the genetic proxied blockade effect of IL6R on focal epilepsy; D: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the genetic proxied blockade effect of IL6R on juvenile absence epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy, and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence intervals.
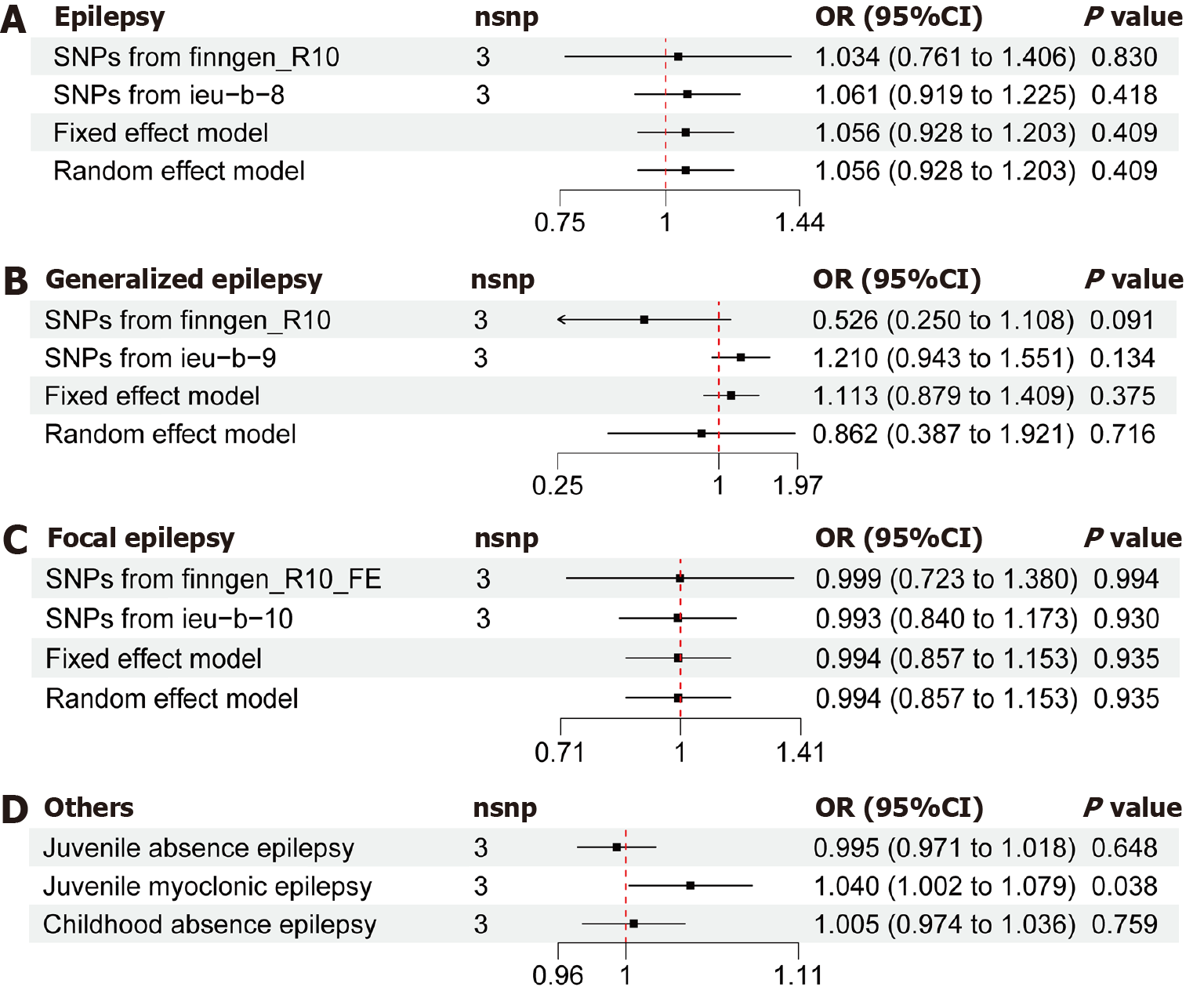
Figure 3 Correlation between genetically mediated C-reactive protein levels and the risk of epilepsy.
A: Forest plot illustrating mendelian randomization (MR) effect estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the genetically mediated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels' impact on epilepsy; B: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the genetically mediated CRP levels' impact on generalized epilepsy; C: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the genetically mediated CRP levels' impact on focal epilepsy; D: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the genetically mediated CRP levels' impact on juvenile absence epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy, and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence intervals.
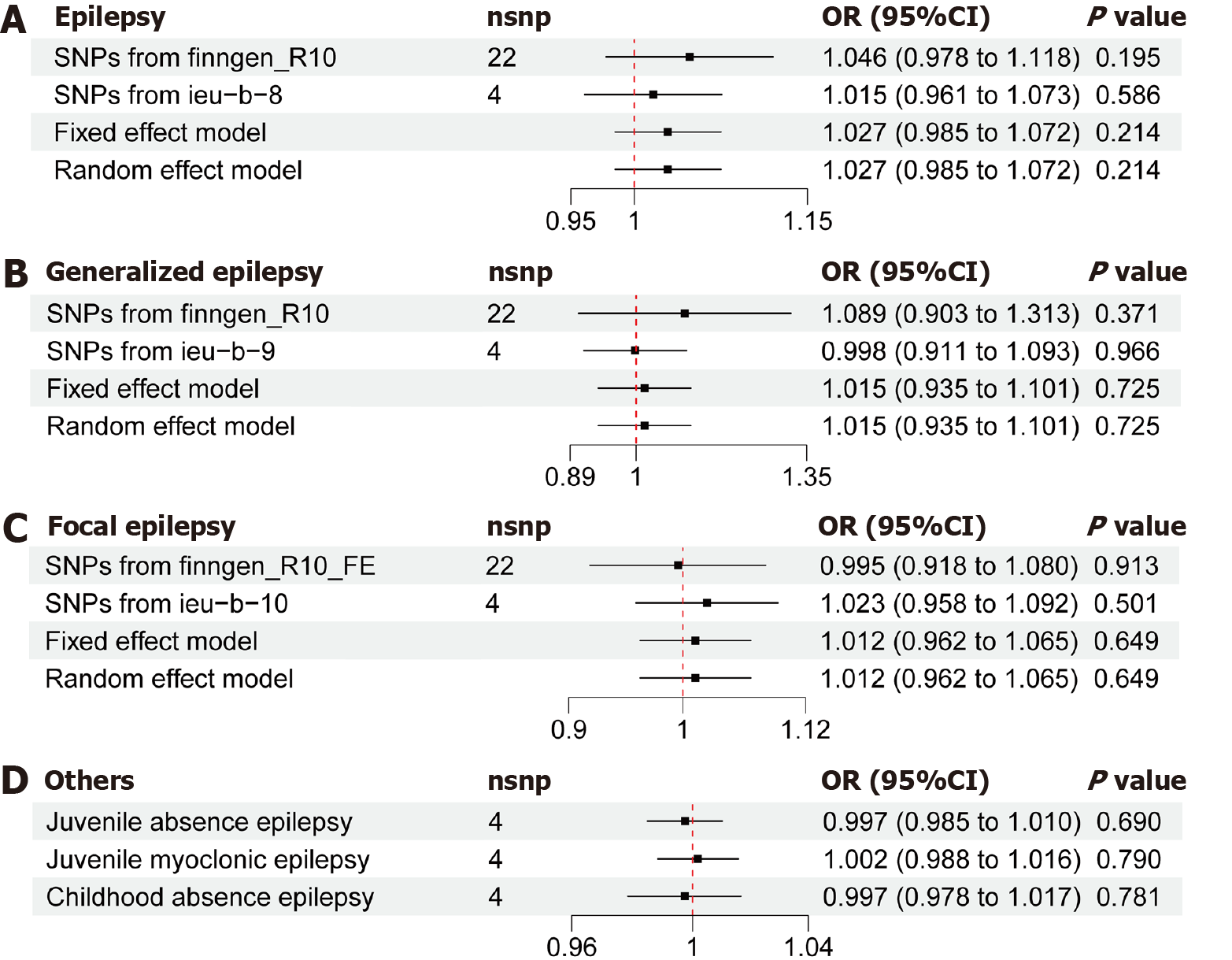
Figure 4 Correlation between genetically mediated glycoprotein 130 levels and the risk of epilepsy.
A: Forest plot illustrating mendelian randomization (MR) effect estimates and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for the impact of genetically mediated plasma protein levels of glycoprotein (gp) 130 on epilepsy; B: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the impact of genetically mediated plasma protein levels of gp130 on generalized epilepsy; C: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the impact of genetically mediated plasma protein levels of gp130 on focal epilepsy; D: Forest plot displaying MR effect estimates and 95%CI for the impact of genetically mediated plasma protein levels of gp130 on juvenile absence epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy, and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; OR: Odds ratio; CI: Confidence intervals.
Figure 5 Graphic summary of this study.
IL: Interleukin; SNP: Single nucleotide polymorphism; CRP: C-reactive protein; MR: Mendelian randomization; IVW: Inverse variance weighting; gp130: Glycoprotein 130; cis: Cis-acting; IL6R: IL-6 receptor.
- Citation: Yu YM, Jin GH, Zhong C, Qian H, Wang L, Zhan F. Exploring the role of interleukin-6 receptor blockade in epilepsy and associated neuropsychiatric conditions through a mendelian randomization study. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(8): 1244-1253
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i8/1244.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i8.1244