©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Feb 19, 2024; 14(2): 276-286
Published online Feb 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i2.276
Published online Feb 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i2.276
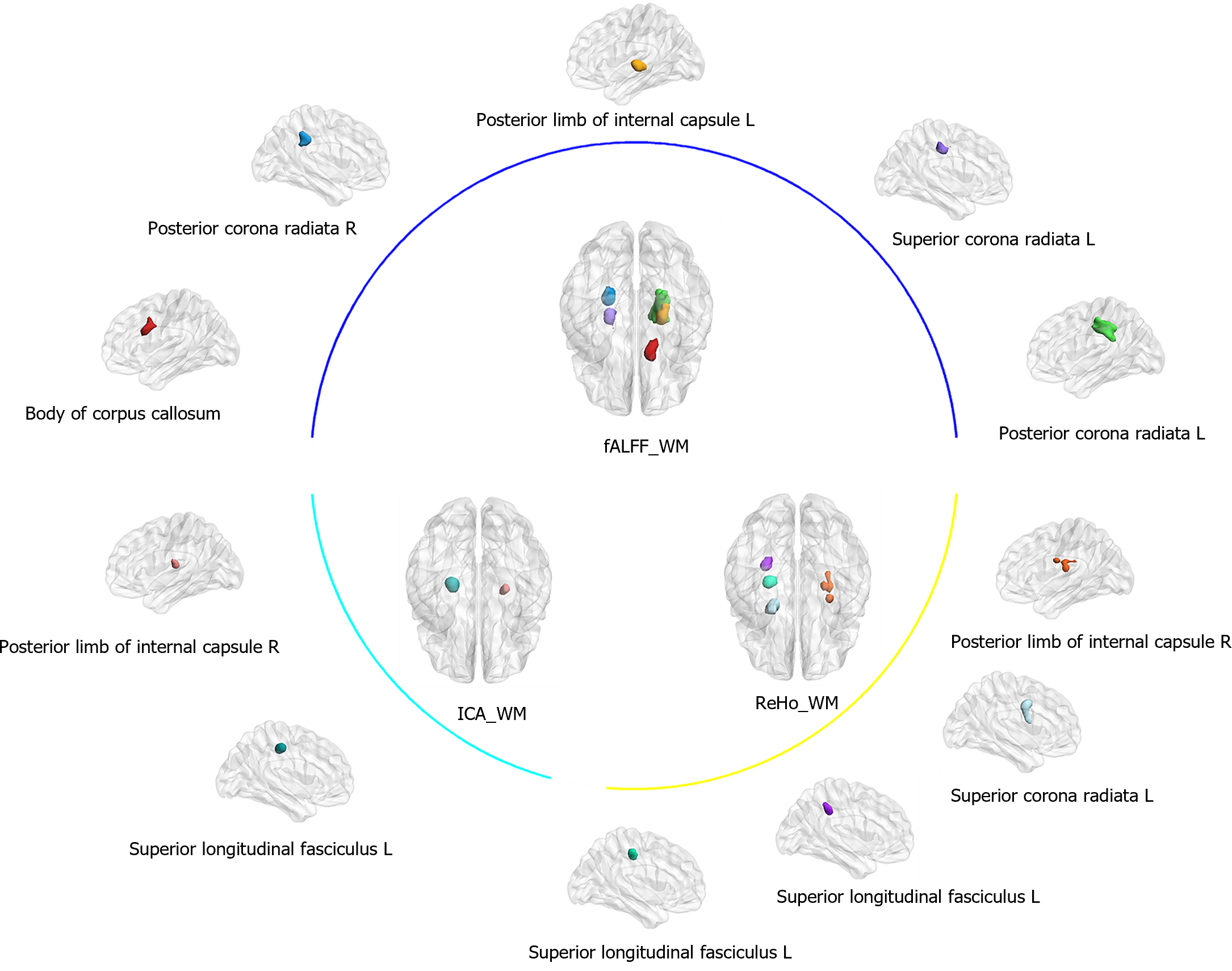
Figure 1 White matter regions with significant differences in fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuations, regional homogeneity and independent component analysis in adolescents with major depression disorders compared to healthy controls.
Maps a threshold at P < 0.001, FWE voxel correction. fALFF: Fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuations; WM: White matter; ReHo: Regional homogeneity; ICA: Independent component analysis; L: Left; R: Right; MDD: Major depression disorders.
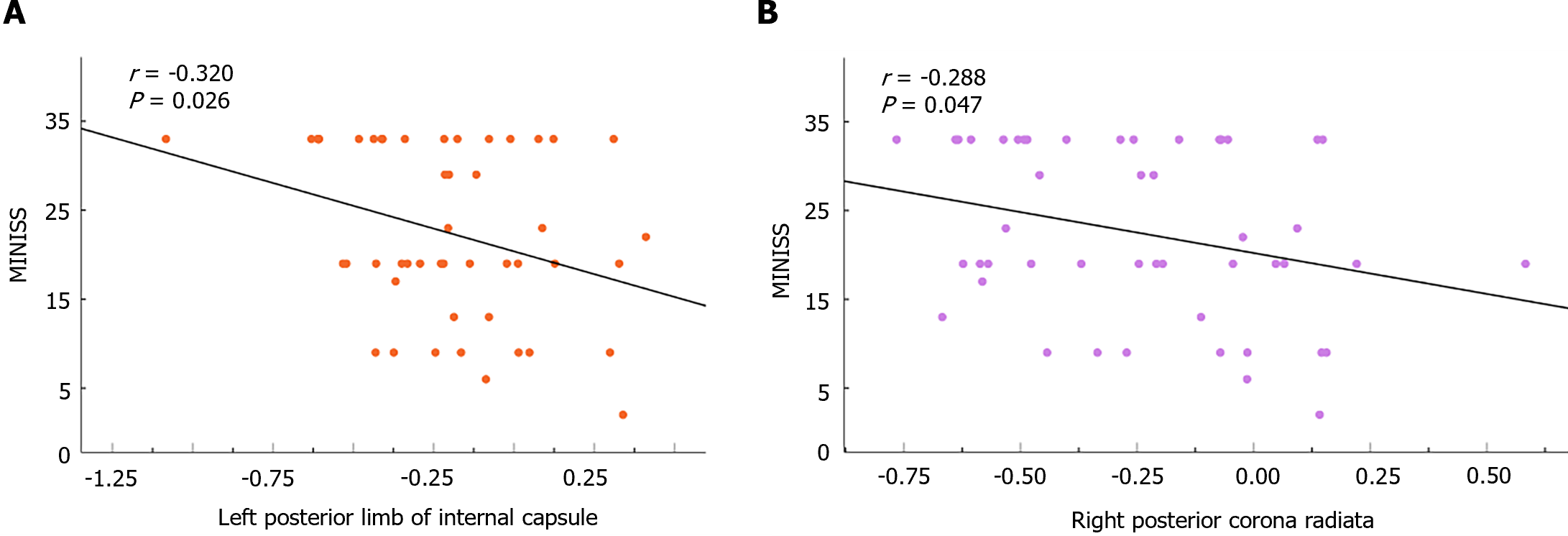
Figure 2 Correlations between clinical psychiatric symptoms and white matter regions with significant differences in the major depression disorders and healthy controls groups.
A: It is a significant brain region left posterior limb of internal capsule in fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuations (fALFF) of white matter (WM); B: It is a significant brain region right posterior corona radiata in fALFF of WM. MINISS: The mini international neuropsychiatric interview suicidality subscale.
- Citation: Huang XL, Gao J, Wang YM, Zhu F, Qin J, Yao QN, Zhang XB, Sun HY. Neuropathological characteristics of abnormal white matter functional signaling in adolescents with major depression. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(2): 276-286
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i2/276.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i2.276