Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2022; 12(3): 470-482
Published online Mar 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i3.470
Published online Mar 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i3.470
Figure 1 Hamilton anxiety rating and the Hamilton depression rating scores according to age of onset.
A: The median (interquartile range) of Hamilton anxiety rating (HAM-A scale scores in early-onset and late-onset groups were 5 (5.5) and 8.5 (7.5), respectively. The HAM-A scale score was significantly higher in the late-onset group than early-onset group (P < 0.001); B: The Hamilton depression rating (HAM-D) score levels in early-onset and late-onset groups were 7 (8) and 10.5 (7.75), respectively. The HAM-D scale score was significantly higher in the late-onset group than early-onset group (P = 0.018). P value was calculated using Mann-Whitney U test.
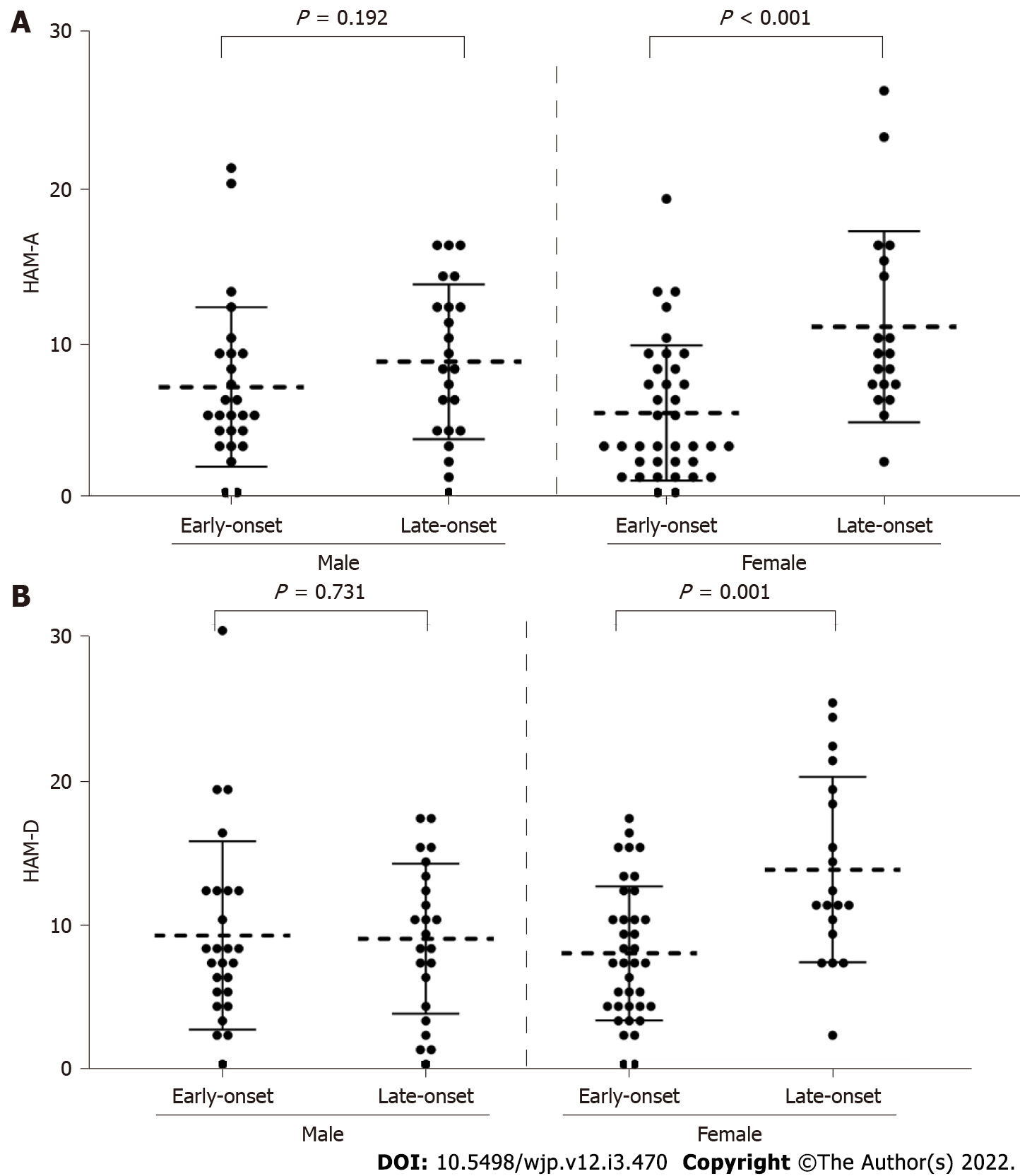
Figure 2 Hamilton anxiety rating and the Hamilton depression rating scores according to age of onset and sex.
A: The median (interquartile range) of Hamilton anxiety rating (HAM-A scale levels in late-onset groups were 3 (6), and 9 (8), respectively, and HAM-A scale scores were significantly higher in late-onset group than early-onset group in women (P < 0.001); B: The Hamilton depression rating (HAM-D) score levels in early-onset and late-onset groups were 7 (7) and 11 (10), respectively, and HAM-D scale score was significantly higher in late-onset group than early-onset group in women (P = 0.001). There were no significant differences in men for both HAM-A and HAM-D scale scores. P value was calculated using Mann-Whitney U test.
- Citation: Yu L, Qiu L, Ran H, Ma Q, Lu YR, Liu WB. Studying the relationship between clinical features and mental health among late-onset myasthenia gravis patients. World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(3): 470-482
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i3/470.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i3.470